* 오라클 테이블 정보 및 데이터 쿼리 내보내기
- 해당 테이블 우클릭 후 익스포트
- 아래 화면 나오면 1번의 빨간박스 속 체크 해제
- 2번 저장될 경로 및 파일 이름 설정
- 다음 완료

* 결과

- 위 내용의 .sql 파일이
- 해당 경로에 board.sql 파일 생성된 것 확인가능 (아래)

'??' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Thymeleaf (text) / 자바스크립트에서 Thymeleaf 사용하기 (0) | 2024.05.08 |
|---|
* 오라클 테이블 정보 및 데이터 쿼리 내보내기
- 해당 테이블 우클릭 후 익스포트
- 아래 화면 나오면 1번의 빨간박스 속 체크 해제
- 2번 저장될 경로 및 파일 이름 설정
- 다음 완료

* 결과

- 위 내용의 .sql 파일이
- 해당 경로에 board.sql 파일 생성된 것 확인가능 (아래)

| Thymeleaf (text) / 자바스크립트에서 Thymeleaf 사용하기 (0) | 2024.05.08 |
|---|
에러 메세지
Removing obsolete files from server... Could not clean server of obsolete files: null java.lang.NullPointerException
▶ workspace에 있는 .metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core 안에
tmp0, tmp1 .. 과 같은 폴더 삭제 후 STS 다시 실행해 보기..
* thymeleaf는 기본적으로 html 태그 속성의 기능을 정의해서 동작한다.
예를 들어보자.
<span>Apple<span>→ 은 Apple가 출력된다.
▶ 같은 코드에 아래와 같이 th:text="${data}" 을 추가해주면
<span th:text="${data}">Apple<span>→ Apple 대신 ${data}의 값으로 치환되어 출력된다. (cf- ${data}의 값이 mango 면 mango가 출력될것이다.)
▶ 여기서 만약 나는 태그에 정의해서 출력하는 방법말고, <span></span> 태그 내용에 직접출력하고 싶다? → 그럴땐
<span>[[${data}]]<span>이런식으로 작성해 주면 된다. (cf - 타임리프는 html이 깨지는 것을 방지하기 위해 escape를 기본적으로 지원한다.)
▶ escape 를 제외하고 출력을 원한다면 → 2가지 방법 예시
<span th:utext="${data}"></span>· html 태그 속성의 기능을 정의
<span>[(${data})]<span>· 태그 내용에 직접출력
◈ 여기서 escape 란? (참)
https://www.zerocho.com/category/HTML&DOM/post/587f50b1308ed50018a00d51#google_vignette
(HTML&DOM) HTML 엔티티(entity) - 이스케이프(escape), 이스케이핑(escaping)
안녕하세요. 이번 시간에는 HTML 엔티티에 대해서 알아보겠습니다! 혹시 HTML 소스를 보다가 나 < 또는 >를 보신 적이 있나요? 이 문자들은 HTML 파일이 깨져서 나타나는 문자가 아닙니다.
www.zerocho.com
https://giveme-happyending.tistory.com/33
[HTML] 이스케이프 문자
이스케이프 문자 이스케이프 문자: 특수한 의미를 가지는 문자를 일반적인 문자로 인식하도록 지시하는 역할 예시:
giveme-happyending.tistory.com
| 오라클 익스포트 - 테이블 정보 내보내기 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
|---|
** 예제 1218_9 - keypress() 메서드**

** 예제 1219 - hide() / show() 메서드 **

** 예제 1219_2 - slideUp() / slideDown() / slideToggle() 메서드 **

** 예제 1218_3 - 자바스크립트 / 제이쿼리 회원가입 **





** 예제 1219 - hide() / show() 메서드 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
// hide() / show() 메서드
$("ans").hide();
$("p.q1").click(function(){
$("ans.q1").show();
});
$("ans.q1").click(function(){
$(this).hide();
});
$("p.q2").click(function(){
$("ans.q2").show();
});
$("ans.q2").click(function(){
$(this).hide();
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>질문1 : 대한민국의 수도는 어디입니까?</h2>
<p class="q1">[정답 보기]</p>
<ans class="q1">대한민국의 수도는 <strong>서울</strong>입니다.</ans>
<br /><br />
<h2>질문2 : 대한민국의 국보1호는 무엇입니까?</h2>
<p class="q2">[정답 보기]</p>
<ans class="q2">대한민국의 국보1호는 <strong>숭례문</strong>입니다.</ans>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1219_2 - slideUp() / slideDown() / slideToggle() 메서드 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#panel").click(function(){
$("#panel").slideUp("fast"); //"fast"분에 값 정의 가능
});
$("#slide").click(function(){
$("#panel").slideDown(5000);
});
$("#flip").click(function(){
$("#panel").slideToggle("slow");
});
$("#stop").click(function(){
$("#panel").stop();
});
});
</script>
<style>
#slide, #panel, #flip {
padding:5px;
text-align:center;
background-color: #e5eecc;
border:solid 1px #c3c3c3;
}
#panel {
padding:70px;
display: none;
background-color: #ffff00;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="slide">[오늘의 공지사항]</div>
<div id="panel">[오늘은 jQuery 프로그램을 학습합니다.<br />
예제를 작성 후 실행해보세요.]</div>
<div id="flip">Toggle slide</div>
<p></p>
<button id="stop">Stop sliding</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_3 - 자바스크립트 / 제이쿼리 회원가입 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
/*
function checkz(){
alert("회원가입");
}*/
var getCheck = RegExp(/^[a-zA-Z0-9]{4,12}$/);
var getMail = RegExp(/^[A-Za-z0-9_\.\-]+@[A-Za-z0-9\-]+\.[A-Za-z0-9\-]+/); //이메일 정규표현식은 대부분 같다
var getName = RegExp(/^[가-힣]+$/);
var getFmt = RegExp(/^\d{6}[1234]\d{6}$/);
$(function(){
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
//alert("회원가입");
// 아이디 입력확인 (공백일 때 / 4자리이하 / 유효성)
if($.trim($("#tbID").val()) == "" ){ //val() 아이디 tbID인것의 값을 가져오기
alert("아이디를 입력하세요.");
$("#tbID").val("");
$("#tbID").focus();
return;
}
if($.trim($("#tbID").val()).length < 4){
//$("#tbID").val().trim().length;
alert("아이디는 4자 이상이어야 합니다.");
$("#tbID").focus();
return;
}
// 아이디 유효성 검사
if(!getCheck.test($("#tbID").val())){
alert("아이디는 영문 대.소문자 숫자로 4~12자리 입력해야합니다.");
$("#tbID").val("");
$("#tbID").focus();
return;
}
//비밀번호 입력확인
if($.trim($("#tbPwd").val()) == ""){
alert("비밀번호를 입력하세요.");
$("#tbPwd").val("");
$("#tbPwd").focus();
return;
}
if(!getCheck.test($("#tbPwd").val())){
alert("비밀번호는 영문 대소문, 숫자로 입력가능하며, 4~12자로 입력하셔야 합니다.");
$("#tbPwd").focus();
return;
}
// 아이디와 비밀번호가 동일한지 체크
if($("#tbID").val() == $("#cpass").val()){
alert("아이디와 비밀번호가 동일하게 사용할 수 없습니다.");
$("#tbPwd").val("");
$("#tbPwd").focus();
return;
}
//비밀번호 확인 체크
if($.trim($("#cpass").val()) == ""){
alert("비밀번호 확인을 입력하세요.");
$("#cpass").val("");
$("#cpass").focus();
return;
}
// 비밀번호와 비밀번호 확인 같은지 체크
if($("#tbPwd").val() != $("#cpass").val()){
alert("비밀번호와 비밀번호확인이 일치하지 않습니다. 다시 입력하세요.");
$("#tbPwd").val("");
$("#cpass").val("");
$("#cpass").focus();
return;
}
// 이메일 입력
if($.trim($("#mail").val()) == ""){
alert("이메일을 입력하세요.");
$("#mail").val("");
$("#mail").focus();
return;
}
// 이메일 유효성 체크
if(!getMail.test($("#mail").val())){
alert("이메일 형식에 맞게 입력하세요");
$("#mail").val("");
$("#mail").focus();
return;
}
// 이름 유효성 체크
if(!getName.test($("#name").val())){
alert("이름은 한글로만 입력 가능합니다.");
$("#name").val("");
$("#name").focus();
return;
}
//주민번호 체크
if($.trim($("#pnum").val()) == "" || $("#pnum").val().length < 6){
alert("주민번호 앞자리를 입력하세요.");
$("#pnum").focus();
return;
}
if($.trim($("#nnum").val()) == "" || $("#nnum").val().length < 7){
alert("주민번호 뒷자리를 입력하세요.");
$("#nnum").focus();
return;
}
//주민번호 유효성 체크
var jumin = $("#pnum").val() + $("#nnum").val(); //문자열 + 문자열 이기때문에 가능 (숫자면 연산됨)
if(!getFmt.test(jumin)){
alert("주민등록번호 형식에 맞게 입력하세요.");
$("#pnum").focus();
return;
}
// 생일 년/월/일 설정
var birthYear = (jumin.charAt(6) <= 2) ? "19" : "20" ;
birthYear += $("#pnum").val().substr(0,2); // .substr(0,2) - 0번째 인덱스 부터 2글자 가져온다.
$("#year").val(birthYear);
var birthMonth = $("#pnum").val().substr(2,2);
var birthDate = $("#pnum").val().substr(4,2);
$("#year").val(birthYear);
$("#month").val(birthMonth);
$("#day").val(birthDate);
// 관심분야 체크 (1개 이상 필수)
var hobbyCheck = false;
for(var i = 0 ; i < $('[name="hobby"]').length ; i++){
if( $('input:checkbox[name="hobby"]').eq(i).is(":checked") == true){
hobbyCheck = true;
break;
}
}
if(!hobbyCheck){
alert("하나 이상의 관심분야를 선택하세요.");
return;
}
// 자기소래
if(!$.trim($("#intro").val())){
alert("자기 소개를 입력하세요.");
$("#intro").val("");
$("#intro").focus();
return;
}
// 최종확인
if(confirm("회원가입을 하시겠습니까?")){
document.form1.submit();
}
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form1" method="get" action="1219.html">
<h2 align="center">회원가입</h2>
<table align="center" border="3" cellspacing="0" >
<tr>
<td colspan="5" height="30" align="center" bgcolor=#000000" span style="color:white;">회원기본정보</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="100">아이디:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="text" name="id" maxlength="12" id="tbID" > 4~12자리의 영문 대소문자와 숫자로만 입력</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td >비밀번호:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="password" maxlength="12" id="tbPwd" > 4~12자리의 영문 대소문자와 숫자로만 입력</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td >비밀번호확인:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="password" id="cpass" maxlength="12"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>메일주소:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="text" name="addr" id="mail">
예)id@domain.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>이름:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="text" name="nam" id="name"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="5" height="30" align="center" bgcolor=#000000" span style="color:white;">개인신상정보</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>주민등록번호:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="text" name="jum" id="pnum">-<input type="password" name="jumin" id="nnum">예)123456789</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td >생일:</td>
<td colspan="4">
<input type="text" autocomplete="OFF" name="nyear" id="year" style="width: 70px" readonly disabled> 년
<input type="text" autocomplete="OFF" name="nmonth" id="month" style="width: 50px" readonly disabled> 월
<input type="text" autocomplete="OFF" name="nday" id="day" style="width: 50px" readonly disabled> 일
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>관심분야:</td>
<td colspan="4"><input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="컴퓨터" >컴퓨터
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="인터넷" >인터넷
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="여행">여행
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="영화감상">영화감상
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="음악감상">음악감상
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="20" height="100">자기소개:</td>
<td colspan="4"><textarea name="my_intro" id="intro" cols="50" rows="5"></textarea></td>
</tr>
</table>
<p align="center">
<!-- <input type="button" onClick="checkz()" value="회원가입"> -->
<input type="button" id="btn1" value="회원가입">
<input type="reset" value="다시입력">
</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
| 12/18 수업 (33일차) _ 요소 추가 / 요소 복사 / 요소 대체 (1) | 2023.12.18 |
|---|---|
| 12/15 수업 (32일차) (1) | 2023.12.15 |
- .append() 메서드
선택한 요소(ex.id,)의 '마지막'에 새로운 요소나 컨텐츠를 추가.
- .prepend() 메서드
선택한 요소의 '처음'에 새로운 요소나 콘텐츠를 추가.
- .appendTo() 메서드
선택한 요소를 '해당 요소의 마지막'에 삽입.
동작은 .append()메소드와 같지만, 소스(source)와 타겟(target)의 위치가 서로 반대
- .prependTo()메서드
선택한 요소를 '해당요소의 처음'에 삽입.
동작은 .pretend()메소드와 같지만, 소스 소스(source)와 타겟(target)의 위치가 서로 반대
* 기존 요소 외부에 추가
- .before() 메서드
선택한 요소의 '바로앞에' 새로운 요소나 콘텐츠를 추가.
- .after() 메서드
선택한 요소의 '바로 뒤에' 새로운 요소나 콘텐츠를 추가.
- .insertBefore() 메서드
메소드는 선택한 요소를 '해당 요소의 앞에' 삽입.
동작은 before()메소드와 같지만, 소스(source)와 타켓(target)의 위치가 서로 반대.
- .insertAfter() 메서드
선택한 요소를 '해당 요소의 뒤'에 삽입
동작은 after()메소드와 같지만, 소스(source)와 타켓(target)의 위치가 서로 반대.
* 기존 요소를 포함하는 새로운 요소를 추가
- . wrap() 메서드
선택한 요소를 포함하는 새로운 요소를 추가.
- .wrapAll()메서드
선택한 모든 요소를 포함하는 새로운 요소를 추가
- .wrapInner()메서드
******************************************************************************************************************************************
- .clone() 메서드
선택한 요소를 복사하여 새로운 요소를 생성.
.clone()메소드는 기존의 HTML요소를 복사하여 새로운 HTML요소를 생성한다.
반드시 .append()메소드나 .appendTo()메소드와 같은 다른 메소드를 이용하여 요소를 추가해야한다.
- .replaceAll() 메서드
선택한 요소를 지정된 요소로 대체.
인수로 선택자나 제이뭐리 객체, HTML DOM요소, 배열 등을 전달받을 수 있다.
- .replaceWith() 메서드
선택한 요소를 지정된 요소로 대체.
- .remove() 메서드
선택한 요소를 DOM트리에서 삭제.
삭제되는 요소와 연관된 제이쿼리 데이터나 이벤트도 모두 함께 삭제된다.
- .detach() 메서드
선택한 요소를 DOM트리에서 삭제.
삭제되는 요소와 연관된 제이쿼리 데이터나 이벤트는 삭제되지 않고, 계속 유지된다.
- .empty() 메서드
선택한 요소의 자식 요소를 모두 삭제.
.remove()나 .detach() 메소드와 달리 선택된 요소 그 자체는 삭제되지 않음.
- .unwrap() 메서드
선택한 요소의 부모 요소를 삭제.
* 트리탐색(tree traversing) :
특정 요소로부터 다른 요소들과의 관계를 통해 선택하기 원하는 요소까지 DOM트리를 검새해 나아가는 과정을 의미한다.
- 조상(ancestor)요소 탐색 : 특정 요소의 부모(parent) 요소를 포함한 상위의 요소를 탐색
- 형제(sibling) 요소탐색
- 자손 요소 탐색
- 조상 요소 탐색 .parent()
선택한 요소의 부모 요소를 선택.
선택자를 인수로 전달하여, 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 부모 요소만을 선택할 수도 있다.
.css메소드는 선택한 요소에 인수로 전달받은 스타일을 설정한다.
- 조상 요소 탐색 .closest()
자신을 포함한 조상 요소 중 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 요소의 집합에서 가장 첫 번째 요소 선택.
요소의 집합을 구하는 방식은 .parents()메소드와 비슷하지만,
해당 요소의 조상 요소뿐만 아니라 해당 요소 자신 까지도 검사하는 점이 다르다.
- 형제 요소 탐색 .siblings()
선택한 요소의 형제(sibling) 요소 중에서 지정한 선택자에 해당하는 요소를 모두 선택.
- 형제 요소 탐색 .next()
선택한 요소의 바로 다음에 위치한 형제 요소를 선택.
- 형제 요소 탐색 .nextAll()
선택한 요소의 다음에 위치한 형제 요소를 모두 선택.
선택자를 인수로 전달하여, 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 형제 요소만을 선택할 수 도 있다.
- 형제 요소 탐색 .prev() / .prevAll() / prevUntill()
.next() / . next All(), / next Untill() 각각 정반대로 독삭하여 요소들을 선택해준다.
- 자손 요소 탐색 .children()
선택한 요소의 자식(child) 요소를 모두 선택.
선택자를 인수로 전달하여, 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 자식 요소만을 선택할 수 도 있다.
- 자손 요소 탐색 .find()
선택한 요소의 자손 요소 중에서 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 자손요소를 모두 선택.
별표 ("*")를 인수로 전달하여, 선택한 요소의 자손 요소를 모두 선택할 수도 있다.
- 기타 탐색 메서드 .add()
선택한 요소의 집합에 전달 받은 요소를 추가
- 기타 탐색 메서드 .each()
선택한 요소 집합의 요소마다 전달받은 콜백 함수를 실행함.
- .first() 메서드 / .last()메서드
first()메서드는 선택한 요소 중에서 첫번째 요소를 선택, .last()메서드는 마지막 요소를 선택
- .eq() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달받은 인덱스에 해당하는 요소를 선택
선택한 요소 집합의 맨 처음 요소를 인덱스 0으로 놓고, 앞에서 부터 검색한다.
- .filter() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달 받은 선택자에 해당하거나, 함수 호출의 결과가 참(true)인 요소를 모두 선택
:odd 선택자는 인덱스가 홀수인 요소를 모두 선택하는 선택자.
:odd 나 :even 선택자를 사용할 때는 언제나 인덱스가 0부터 시작한다는사실을 염두에 두고 사용해야함.
사용예) .filter(:odd) / .filter(:even)
- .not() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달받은 선택자에 해당하거나, 함수 호출의 결과가 참(true)일 요소를 제외한 나머지 요소를 모두 선택.
filter()메서드와는 정반대로 동작하여 요소를 선택한다.
.not() 메서드에 인수로 전달된 식별자는 '인덱스가 2보다 작은'이라는 의미를 가지는 식별자,
인덱스가 2인 요소와 2보다 큰 요소를 모두 선택해준다
- .has() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 요소를 자손요소로 가지고 있는 요소를 모두 선택.
선택한 <li>요소 중 자손 요소 <span>요소를 가지고 있는 요소만의 스타일을 변경하는 예제.
- .is() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달받은 선택자에 해당하는 요소가 하나라도 존재하면 참을 반환
예제에서 우선 선택한 <span>요소의 모든 요소를 다시 선택한다.
선택된 모든 조상 요소 중에 <ul>요쇼가 존재하는지 여부를 .is() 메소드를 통해 검사한다.
- .map() 메서드
선택한 요소 집합의 각 요소마다 지정된 콜백 함수를 실행하고, 그 반환값으로 구성된 제이쿼리 객체를 반환.
예제에서 선택한 <li>요소 집합의 각 요소마다 해당 요소의 id값을 반환하는 콜백함수를 실행한다.
콜백함수의 실행으로 반환되는 값들은 .get()메소드를 통해 하나의 배열로 반환되며, 다신 .join()메소드를 통해 하나의 문자열로 변환되어 반환된다.
- .slice() 메서드
선택한 요소 중에서 전달받은 인덱스 범위에 해당하는 요소만을 선택
선택한 <li>요소 중에서 인덱스가 1과 같거나 그 이상인 요소만의 스타일을 변경하는 예제
** 프로퍼티 설정 **
- .css() 메서드
선택한 요소의 CSS스타일을 간단하게 설정
- .attr() 메서드
선택한 요소 집합의 첫번째 요소의 지정된 속성(attribute) 값을 반환하거나, 선택한 요소의 지정된 속성을 전달받은 값으로 설정
- .prop() 메서드
선택한 요소 집합의 첫번째 요소의 지정된 프로퍼티(property) 값을 반환하거나, 선택한 요소의 지정된 프로퍼티을 전달받은 값으로 설정
- 속성과 프로퍼티의 차이점?
- 클래스 설정에 관한 메서드
| 메 서 드 | 설 명 |
| .addClass() | 선택한 요소에 인수로 전달받은 클래스를 추가함. |
| .removeClass() | 선택한 요소에서 인수로 전달받은 클래스를 제거함. |
| .toggleClass() | 선택한 요소에 클래스가 없으면 인수로 전달받은 클래스를 추가함. 전달받은 클래스가 추가되어 있으면 제거함. |
| .hasClass() | 인수로 전달받은 값이 선택한 요소의 클래스 이름과 일치하는지 확인함 |
사용자는 마우스를 움직이거나, 요소를 클릭하거나, 텍스트 박스에 글을 쓰는 등 수많은 종류의 동작을 수행.
이벤트핸들러가 연결된 특정요소에서 지정된 타입의 이벤트가 발생하면, 웹브라우저는 연결된 이벤트 핸들러를 실행한다.
특정 요소에서 발생하는 이벤트를 처리하기 위해서는 이벤트 핸들러 함수를작성.
작성된 이벤트 핸들러를 특정 요소에 연경하는 것을 이벤트의 연결 이라고함.
** 예제 1218 <.append()메서드 / prepend()메서드> **

** 예제 1218_2 <.appendTo()메서드 / prependTo()메서드> **

- 첫번째 추가 클릭시 : 선택한 요소 (id="first")'첫번째 순서입니다.' 를 마지막에 삽입
** 예제 1218_2 <.befoer()메서드 / .after()메서드 / .insertBefore() 메서드 / .insertAfter() 메서드> **


** 예제 1218_3 < . wrap() 메서드 / . wrapAll() 메서드 / .wrapInner() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_3 < . wrap() 메서드 / . wrapAll() 메서드 / .wrapInner() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_3 < 요소 복사 .clone() 메서드 / 요소 대체 .replaceAll() / 요소 대체 .replaceWith() 메서드> **


** 예제 1218_3 < .remove() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_4 < .detach() / .empty() / .unwrap() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_5 < 부모 요소 탐색 .parent() / parents() 메서드 > **

** 예제 1218_6 < 부모 요소 탐색 .parents() 메서드 > **

** 예제 1218_7 < 형제 요소 탐색 .sibling() / next() 메서드> **


** 예제 1218_8 < .add() / .each() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_8 < .first() / .last() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_8 < filter() 메서드> **

** 예제 1218_9 < 마우스 이벤트 > **

** 예제 1218 <.append()메서드 / pretend()메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
var val = 0;
$(function(){
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
$("#list").append("<li id='id" + val++ + "'>마지막에 새로 추가됩니다.</li>");
//<li id='id0'>새로 추가됩니다.<li>
});
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("#list").prepend("<li>처음에 새로 추가됩니다.</li>");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.append() 메서드 : 마지막에 추가 됩니다.</h2>
<ul id="list">
<li>첫번째 순서</li>
<li>두번째 순서</li>
<li>세번째 순서</li>
</ul>
<button id="btn1">마지막에 추가</button>
<button id="btn2">처음에 추가</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_2 <.appendTo() / pretendTo() / before() / after() / insertBefore() /insertAfter() > **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
//appendTo() / prependTo() 메서드
$("#firstBtn").on("click", function(){
$("#first").appendTo("#list");
});
$("#secondBtn").on("click", function(){
$("#second").appendTo("#list");
});
$("#thirdBtn").on("click",function(){
$("#third").appendTo("#list");
});
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
$("<b>새로 추가됩니다.</b>").prependTo(".item");
});
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//before() / after() 메서드
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("#firstRow").before("<tr><td>행 추가됩니다.</td><td></td></tr>");
});
$("#btn3").on("click", function(){
$("#firstRow").after("<tr><td colspan='2'>행 추가됩니다.</td></tr>");
});
//.insertBefore() 메서드
$("#btn4").on("click",function(){
$("<td>새로운 앞 열 추가</td>").insertBefore("#secondColumn");
});
//.insertAfter() 메서드
$("#btn5").on("click", function(){
$("<td>새로운 뒷 열 추가</td>").insertAfter("#secondColumn2");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.appendTo() 메서드</h2>
<ul id="list">
<li id="first">첫번째 순서입니다.</li>
<li id="second">두번째 순서입니다.</li>
<li id="third">세번째 순서입니다.</li>
</ul>
<button id="firstBtn">첫번째 추가</button>
<button id="thirdBtn">세번째 추가</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.prependTo() 메서드</h2>
<ul>
<li class="item">첫번째 prependTo 입니다.</li>
<li class="item">두번째 prependTo 입니다.</li>
<li>세번째 prependTo 입니다.</li>
</ul>
<button id="btn1">prtendTo 추가됩니다</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.before() / after() 메서드</h2>
<table>
<tr id="firstRow">
<td>첫번째 셀입니다.</td>
<td>두번째 셀입니다.</td>
</tr>
<button id="btn2">위에 행 추가</button>
<button id="btn3">아래에 행 추가</button>
</table>
<br /><br />
<h2>.insertBefore() 메서드</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<td>첫번째 열입니다.</td>
<td id="secondColumn">두번째 열입니다.</td>
</tr>
</table>
<button id="btn4">앞에 열 추가</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.insertAfter() 메서드</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<td>첫번째 열입니다.</td>
<td id="secondColumn2">두번째 열입니다.</td>
</tr>
</table>
<button id="btn5">뒤에 열 추가</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_3 < . wrap() 메서드 / . wrapAll() 메서드 / .wrapInner() 메서드 / .clone() 메서드 / .replaceAll() / .replaceWith() 메서드 / remove()메서드 > **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<style>
div{margin:10px}
.content{border:2px solid orange;}
.wrapper{border:2px solid green;}
.wrapper2{border:2px solid blue;}
.wrapper3{border:2px solid red;}
</style>
<script>
$(function(){
// .wrap() .wrapAll() 메서드
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
$(".content").wrap("<div class='wrapper'></div>");
});
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$(".content").wrapAll("<div class='wrapper2'></div>");
});
// .wrapInner() 메서드
$("#btn3").on("click", function(){
$(".content").wrapInner("<div class='wrapper3'></div>");
});
// .clone() 메서드
$("#btn4").on("click",function(){
$("#first").clone().appendTo("#list");
});
// .replaceAll() / replaceWith() 메서드
$("#btn5").on("click",function(){
$("#first2").replaceAll(".item");
});
$("#btn6").on("click", function(){
$(".item").replaceWith($("#first2"));
});
// .remove() 메서드
$("#btn7").on("click", function(){
$(".content2").remove(".first, .second");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.wrap() .wrapAll() wrapInner() 메서드</h2>
<div class="content">첫번째 div입니다.</div>
<div class="content">두번째 div입니다.</div>
<button id="btn1">div 추가 - wrap()</button>
<button id="btn2">div 추가 - wrapAll()</button>
<button id="btn3">div 추가 - wrapInner()</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.clone() 메서드</h2>
<ul id="list">
<li id="first">첫번째 입니다.</li>
<li>두번째 입니다.</li>
<li>세번째 입니다.</li>
</ul>
<button id="btn4">clone 복사</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.replaceAll() / replaceWith() 메서드</h2>
<ul>
<li class="item" id="first2">첫번째 입니다.</li>
<li class="item" id="second2">두번째 입니다.</li>
<li class="item" id="third2">세번째 입니다.</li>
</ul>
<button id="btn5">replaceAll 적용</button>
<button id="btn6">replaceWith 적용</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.remove() 메서드</h2>
<div>
<div class="content2 first">첫번째 입니다.</div>
<div class="content2 second">두번째 입니다.</div>
<div class="content2 third">세번째 입니다.</div>
</div>
<button id="btn7">remove() 적용</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_4 < .detach() / .empty() / .unwrap() 메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQeury</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
//body가 생성되야 메서드가 실행되기 떄문에 ready메서드(또는 $(function(){ });)로 감싸줘야한다.
var data;
// detach() 메서드
$("#btn1").on("click",function(){
data = $(".content").detach();
});
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("#container").append(data);
});
// .empty() 메서드
$("#btn3").on("click", function(){
$("#con").empty();
});
// .unwrap() 메서드
$("#btn4").on("click", function(){
$("span").unwrap();
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>detach() 메서드</h2>
<div id="container">
<div>첫번째 순서입니다.</div>
<div class="content">두번째 순서입니다.</div>
<div class="content">세번째 순서입니다.</div>
</div>
<button id="btn1">삭제</button>
<button id="btn2">복구</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.empty() 메서드</h2>
<div id="con" style="border:3px solid blue; padding:5px;">
<div>첫번째 입니다.</div>
<div>두번째 입니다.</div>
<div>세번째 입니다.</div>
</div>
<button id="btn3">자식 삭제</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>.unwrap() 메서드</h2>
<div id="con2" style="border:3px solid blue; padding:5px;">
<div><span>첫번째</span>입니다.</div>
<div><span>두번째</span>입니다.</div>
<div><span>세번째</span>입니다.</div>
</div>
<button id="btn4">부모 삭제</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_5 < .parent() / parents() 메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<style>
.con * {
display: block;
border:1px solid gray;
padding:5px;
margin:15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function(){
// 부모 요소
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
$("p").parent().css({"border":"2px solid red"});
});
// 부모 전체요소
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("p").parents("div").css({"border":"2px solid green"});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.parent() 메서드</h2>
<div class="con">
<div>div요소
<ul>ul태그
<li>li첫번째</li>
<li>li두번째
<p>p태그<span>span태그</span></p>
</li>
<li>li세번째</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<button id="btn1">부모요소</button>
<button id="btn2">부모전체요소</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_6 < .parents() 메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<style>
.container * {
display: block;
border: 1px solid lightgray;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#parents").on("click", function(){
$("#orgin").parents("div").css({"border":"2px solid red"});
});
$("#closest").on("click", function(){
$("#orgin").closest("div").css({"border":"2px solid green"});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>.parents() 메서드</h1>
<div class="container">
<div>div요소
<div>요소2
<ul>ul요소
<li>li 요소</li>
<li>li 요소
<div id="orgin">div요소(기준)
<span>span요소</span>
</div>
</li>
<li>li 요소</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<button id="parents">parents() 메서드</button>
<button id="closest">closest() 메서드</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_7 < .sibling() / next() 메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<style>
.con * {
display: block;
border: 1px solid gray;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function(){
// sibling() 메서드
$("#btn1").on("click", function(){
$("h4").siblings().css({"border":"2px solid blue"});
});
// next() 메서드
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("h4").next().css({"border":"2px solid red"});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.siblings() / next() 메서드</h2>
<div class="con">
<div>위치</div>
<h2>h2요소</h2>
<h3>h3요소</h3>
<h4>h4요소</h4>
<h5>h5요소</h5>
<h6>h6요소</h6>
<p>p 입니다.</p>
</div>
<button id="btn1">h4 형제요소 - sibling()</button>
<button id="btn2">h4 next요소 - next()</button>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_8 < .add() / .each() / .first() / .last() / .eq() / .filter() 메서드> **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<style>
.con * {
/* display: block;
border: 1px solid gray; */
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
.boldFont {
color:blue;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function(){
// .add() 메서드
$("#btn1").on("click",function(){
$("li").add("p").css({"border":"2px solid red"});
});
// .each() 메서드 (없을때는 추가, 있을때는 제거)
$("#btn2").on("click", function(){
$("li").each(function(){
$(this).toggleClass("boldFont");
});
});
// .first() 메서드
$("#btn3").on("click", function(){
$("li").first().css({"border":"2px solid brown"});
});
// .last() 메서드
$("#btn4").on("click",function(){
$("li").last().css({"border":"2px solid orange"});
});
// .eq(1) 메서드
$("#btn5").on("click", function(){
$("li").eq(1).css({"border":"2px solid red"});
});
// .eq(-1) 메서드
$("#btn6").on("click", function(){
$("li").eq(-1).css({"border":"2px solid yellow"});
});
// .filter(:odd) / .filter(:even) 메서드
$("#btn7").on("click", function(){
$("li").filter(":odd").css({"border":"2px solid blue"});
});
$("#btn8").on("click", function(){
$("li").filter(":even").css({"border":"2px solid pink"});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>.add() / .each() / .first() / .last() / .eq() 메서드</h2>
<ul class="con">ul태그
<li>li 첫번째</li>
<li>li 두번째</li>
<li>li 세번째</li>
<li>li 네번째</li>
<li>li 다섯번째</li>
</ul>
<p>추가 단락입니다.</p>
<button id="btn1">li에 p추가 - add()</button>
<button id="btn2">클래스 추가/제거 - each()</button>
<button id="btn3">.first() 적용</button>
<button id="btn4">.last() 적용</button>
<br />
<button id="btn5">.eq(1) 적용</button>
<button id="btn6">.eq(-1) 적용</button>
<button id="btn7">.filter(:odd)적용</button>
<button id="btn8">.filter(:even)적용</button>
<br />
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1218_9 < 마우스 이벤트 > **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
// 마우스 이벤트 (mouseenter / click / mouseleave )
$("#btn1").on({
mouseenter:function(){
$("#text").append("마우스가 버튼 위로 왔습니다.<br />");
},
click:function(){
$("#text").append("마우스가 버트을 클릭했습니다.<br />");
},
mouseleave:function(){
$("#text").append("마우스가 버튼 위를 벗어났습니다.<br />");
}
});
// clickText() /dblClickText() 메서드
$("#btn2").click(function(){
$("#clickText").css("color", "red");
$("#dblClickText").css("color", "black");
});
$("#btn2").dblclick(function(){
$("#clickText").css("color", "black");
$("#dblClickText").css("color", "red");
});
// focusin() / focusout() 메서드 - 클릭시 색 변한다.
$("#focus").on("focusin", function(event){
$(this).css("backgroundColor", "yellow");
});
$("#focus").on("focusout", function(event){
$(this).css("backgroundColor", "white");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>마우스 이벤트</h2>
<button id="btn1">마우스 버튼 위로 포커스를 이동해보세요.</button>
<p id="text"></p>
<br /><br />
<button id="btn2">dbChlick</button>
<p>버튼을 <span id="clickText">클릭</span>하거나
<span id="dblClickText">더블클릭</span>해보세요.
</p>
<br />
<h2>.focusin() / focusout() 메서드</h2>
<input type="text" id="focus">
</body>
</html>
| 12/19 수업 (34회차) _ keypress() / hide() / show() slideUp() / slideDown() / slideToggle() 메서드 / 제이쿼리 회원가입 (0) | 2023.12.19 |
|---|---|
| 12/15 수업 (32일차) (1) | 2023.12.15 |
제이쿼리는 자바스크립트 언어를 간편하게 사용할 수 있도록 단순화시킨 오픈소스 기반의 자바스크립트 라이브러리 이다.
문서 객체 모델(DOM)과 이벤트에 관한 처리를 손쉽게 구현할 수 있으며, 현재 가장 인기있는 자바스크립트 라이브러리 중 하나이다.
* 가장 많이 사용하는 이유 *
제이쿼리는 주요 웹 브라우저의 구 버전을 포함한 대부분의 브라우저에서 지원됨.
HTML DOM을 손쉽게 조작할 수 있으며, CSS스타일도 간단히 적용할 수 있음.
애니메이션 효과나 대화형 처리를 간단하게 정용해 줌.
같은 동작을 하는 프로그램을 더욱 짧을 코드로 구현할 수 있음.
다양한 플러그인과 참고할 수 있는 문서가 많이 존대함.
오픈 라이센스를 적용하여 누구나 자유록게 사용할 수 있음
cf ) jQuery 버전 2,3 은 모두 익스플로러 9이상에서만 동작하기 때문에 아직도 많은 웹사이트에서는 jQuery 버전1을 사용하고 있음.
* 적용
제이쿼리는 자바스크립트 라이브러리이므로, 제이쿼리 파일은 자바스크립트 파일(.js 파일)
웹페이지에서 제이쿼리를 사용하기 위해서는 제이쿼리 파일을 먼저 웹페이지에 로드해야함
* 웹페이지에 제이쿼리파일을 로드한는 방법.
- 1.제이쿼리 파일을 다운받아로드
- 2.CDN을 이용하여 로드하는 방법
* 1. 제이쿼리 파일을 다운받아 로드하는 방법
서버에 저장하여 head scrip에 포함한다.
* 2. CDN을 이용하여 로드하는 방법 (잘 사용하지 않는다.)
CDN(content Delivery Netsork)이란 웹사이트의 접속자가 서버에서 콘텐츠를 다운받아야 할 때, 자동으로 가장 가까운 서버에서 다운받도록하는 기술.
이 기술을 이용하면 특정 서버에 트래픽이 집중되지 않고, 콘텐츠 전송 시간이 매우 빨라지는 장점이 있다.
이러한 CDN을 이용하면 제이쿼리 파일을 서버에 따로 저장하지 않아도 제이쿼리를 사용할 수 있습니다.
******************************************************************************************************************************************
* jQuery 문법
문법) $(선택자).동작함수();
달러($) 기호는 제이쿼리를 의미하고, 제이쿼리에 접근할 수 있게 해주는 식별자.
선택자를 이용하여 원하는 HTML요소를 선택하고 , 동작함수를 정의하여 선택된 요소에 원하는 동작을 설정한다.
* $() 함수
$() 함수는 선택된 HTML요소를 제이쿼리에서 이용할 수 있는 형태로 생성해 주는 역할을 한다.$() 함수의 인수로는 HTML 태그 이름뿐만 아니라, CSS 선택자를 전달하여 특정 HTML 요소를 선택할 수 있음.이러한 $() 함수를 통해 생성된 요소를 제이쿼리 객체(jQuery object)라고 하며, 생성된 제이쿼리 객체의 메서드를 사용하여 여러동작을 설정할 수 있다.
* Document 객체의 ready() 메서드 (예제1215_2)
자바스크립트 코드는 웹 브라우저가 문서의 모든 요소를 로드 한 뒤에 실행되어야 합니다.
보통은 별다른 문제가 바생하지 않지만, 다음과 같은 경우에는 오류가 발행 합니다.
- 아직 생서되지 않은 HTML요소에 속성을 추가하려고 할 경우
- 아직 로드되지 않은 이미지의 크기를 얻으려고 할 경우
* Window 객체의 onload() 메서드 (예제1215_2)
자바스크립트에서는 Window 객체의 onload()메소드를 이용하여 문서가 모두 로드된 뒤에 코드가 실행되도록 설정
문법)
window.onload = function(){
자바스크립트 고드;
};
* 제이쿼리에서는 Document객체의 ready()메서드를 이용하여 같은 결과를 보장 (예제1215_2)
문법)
$(document).ready(function(){
제이쿼리 코드;
});
* jQuery Team에서는 같은 결과를 보장하는 더욱 짧은 문법을 다음과 같이 제공 (예제1215_2)
문법)
$(function(){ 제이쿼리코드 })
* CSS 선택자 (예제1215_3)
- 태그 이름을 사용하여 같은 태그이름을 가지는 HTML요소를 모두 선택할 수 있음.
자바스크립트의 getElementsByTagName() 메서드와 같은 동작을 함.
예제)
$(function(){
$("p").on("click", function() { //<p>요소를 모두 선택함
$("span").css("fontsize", "28px"); //span요소를 모두선택함
});
});
cf ) $() 함수에 전달되는 인수는 반드시 따옴표("")를 사용한 문자열 형태로 전달되어야 함.
- 아이디를 사용하여 특정 HTML요소를 선택할 수 있음.
자바스크립트의 getElementsById() 메서드와 같은 동작을 함.
* 클래스(class)를 사용하여 같은 클래스에 속하는 HTML요소를 모두 선택할 수 있음.
자바스크립트의 getElementsByClassName()메소드와 같은 동작을 함.
예제) &
* 속성(attribute)을 사용하여 속성이 조건에 맞는 특정 HTML요소를 선택할 수 있음.
- 선택한 요소 저장
제이쿼리에서는 선택한 요소들을 변수에 저장하여 사용할 수 있음
아래 예제는 문서 내의 모든 <li>요소를 선택하여 변수에 저장한 후, 해당 변수를 사용하는 예제 ( 예제 1215_4 )
저장된 요소들은 변수에 저장 될 당시의 요소들만 저장됨.
즉, 요소가 저장된 이후에 문서에 추가되거나 삭제된 요소들을 자동으로 갱신하지는 않음.
- 선택한 요소 필터링 ( 예제 1215_5 )
문서 내의 모든<li> 요소 중에서 <span>요소를 가지고 있는 요소만을 선택하는 예제
// :has 선택자 → 선택한 요소중에서 지정한 선택자와 일치하는 자손요소를 갖는 요소 모두 선택함
- input 요소 선택
입력 양식에 관련된 특정 요소를 손귑게 선택할 수 있음. 예제)
| 선 택 자 | 설 명 |
| :button | type 속성값이 " button "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :checkbox | type 속성값이 " checkbox "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :file | type 속성값이 " file "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :image | type 속성값이 " image "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :password | type 속성값이 " password "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :radio | type 속성값이 " radio "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
| :submit | type 속성값이 " submit "인 요소를 모두 선택함 |
- getter메서드와 setter메서드 (선택 요소에 접근)
선택자에 의해 선택된 요소의 값을 읽거나 설정하기 위해서는 메서드를 통해 해당 요소에 접근.
getter 메서드는 선택된 요소에 접근하여 그 값을 읽어오기 위한 메서드이며, 아무런 인수를 전달하지 않고 호출한다.
setter 메서드는 선택된 요소제 접근하여 그 값을 설정하기 위한 메서드, 대입하고자 하는 값을 인수로 전달하여 호출한다.
1. var newText = $("h1").html(); //<h1> 요소 텍스트를 읽어오는 getter메서드
2. $("#text").html(newText); // id 가 "text" 인 요소에 새로운 텍스트를 설정하는 setter 메서드
1번 라인처럼 html() 메서드에 인수를 절달하지 않고 호출하면, 해당 HTML요소에서 값을 읽어오는 getter메서드로 사용.
2번 라인처럼 html() 메서드에 인수를 절달하고 호출하면, 해당 HTML요소에서 값을 읽어오는 getter메서드로 사용.
대표적인 getter / setter 메서드
요소에 접근하여 요소의 값을 읽거나 설정할 수 있도록 해주는 대표적인 메서드.
| 메 서 드 | 설 명 |
| .html() | 해당 요소의 HTML 콘텐츠를 반환하거나 설정함. |
| .text() | 해당 요소의 텍스트콘텐츠를 반환하거나 설정함. |
| .width() | 선택한 요소 중에서 첫 번째 요소의 너비를 픽셀 단위의 정수로 반환하거나 설정함. |
| .height() | 선택한 요소 중에서 첫 번째 요소의 높이를 픽셀 단위의 정수로 반환하거나 설정함. |
| .attr() | 해당 요소의 명시된 속성의 속성값을 반환하거나 설정함. |
| .position() | 선택한 요소 중에서 첫 번째 요소에 대해 특정 위치에 존재하는 객체를 반환함 (getter메서드) |
| .val() | <form>요소의 값을 반환하거나 설정함. |
- 메서드 체이닝 (method chaining)
.eq(index)
- width() / height() 메서드
- attr() 메서드 - 선태한 요소의 특정 속성값을 반환하거나 설정하기 위해 사용함.
** 예제 1215 **

** 예제 1215_2 ( Document 객체의 ready() 메서드 / Window 객체의 onload() 메서드 ) **

** 예제 1215_3 ( CSS 선택자 ) **

** 예제 1215_3 ( CSS 선택자 ) **

** 예제 1215_4 ( ) ** li 갯수는 클릭시 <현재 체이지의 <li>태그는 총 8 개 입니다.> 나옴

** 예제 1215_5 ( ) **

** 예제 1215_6 ( ) **


** 예제 1215_6 ( ) **

** 예제 1215_6 ( ) **


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jQuery</title>
<script src="../js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
/*
$("button").on("click", function(){
$("#msg").find("li") //id 가 msg 인것의 li태그의
.eq(1) //두번째 태그 선택 (eq(index)선택자)
.html("두번째 아이템을 선택하셨습니다.") //두번째 태그 내용을 ""안의 내용으로 변경
.end()
.eq(2)
.html("세번째 아이템을 선택하셨습니다.");
});
*/
$("#getter").on("click", function(){
var size = "너비는 " + $("#box").width() + "px이고 높이는 " + $("#box").height() + "px입니다.";
$("#text").html(size);
});
$("#setter").on("click", function(){
w = $("#box").width();
h = $("#box").height();
$("#box").width(w/2).height(h/2);
var size = "너비는 " + $("#box").width() + "px 이고 높이는 " + $("#box").height() + "px 입니다.";
$("#text").html(size);
});
//*****************************************************************************************************
$("#imgchk").on("click", function(){
//var imgSrc = $("img").attr("src"); //getter
//$("img").attr("src", "../img/flower1.jpg"); //setter
var imgSrc = $("#img2").attr("src"); //위 태그를 이용하면
//alert("imsgArc : " + imgSrc);
if(imgSrc == "../img/flower2.jpg"){
imgSrc = "../img/flower1.jpg";
}
else{
imgSrc = "../img/flower2.jpg";
}
$("#img2").attr("src", imgSrc);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>메서드 체이닝</h2>
<ul id="msg">
<li>첫번째 순서 입니다.</li>
<li>두번째 순서 입니다.</li>
<li>세번째 순서 입니다.</li>
</ul>
<button>텍스트 변경</button>
<br /><br />
<h2>width() / height() 메서드</h2>
<p>버튼을 각각 클릭해보세요.</p>
<button id="getter">크기 읽어오기</button>
<button id="setter">크기 설정하기</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box" style="width:400px; height:200px; background-color:yellow;"></div>
<p id="text"></p>
<br /><br />
<h2>.attr() 메서드</h2>
<button id="imgchk">src속성변경</button><br />
<img id="img1" src="../img/flower1.jpg" style="width:320px; height:210px; border:1px solid blue;">
<br /><br />
<img id="img2" src="../img/flower2.jpg" style="width:320px; height:210px; border:1px solid blue;">
<br />
</body>
</html>
| 12/19 수업 (34회차) _ keypress() / hide() / show() slideUp() / slideDown() / slideToggle() 메서드 / 제이쿼리 회원가입 (0) | 2023.12.19 |
|---|---|
| 12/18 수업 (33일차) _ 요소 추가 / 요소 복사 / 요소 대체 (1) | 2023.12.18 |
** 예제 1214 ( 객체 ) **



* 소스
** 예제 1214_2 (문서 객체 생성하기 ) **



당신의 이름은 무엇인가요? 클릭 전.
당신의 이름은 무엇인가요? 클릭 후.
** 예제 1214_3 ( 이벤트 처리 )**


** 예제 1214_4 ( 이벤트 처리 ) **



** 예제 1214_5 ( 계산기 )**

** 예제 1214_6 ( 문서 객체 스타일 변경하기 ) **



모든 객체, 전역함수, 전역 변수들은 자동으로 window 객체의 프로퍼티가 됨.
Window객체의 메서드는 전역함수이며, window 객체의 프로퍼티는 전역 변수가 됨.
문서 객체 모델(DOM)의 요소들도 모두 window객체의 프로퍼티가 됨.
- 브라우저 새 창 열기 : window.open() 메서드
// 변수 strWindowFeatures를 통해 새롭게 여는 브라우저 창의 옵션들을 일일이 설정 가능.
var strWindowFeatures = "menubar = yes
- 브라우저 창 닫기 : close() 메서드
** 예제 1214_6 (Window 객체)**


현재 브라우저에 표시된 HTML 문서의 주소를 얻거나, 브라우저에 새 문서를 불러올 때 사용
- 현재 문서의 URL 주소
예 ) document.write("현새 문서의 주소는 " + location.href + "입니다.");
브라우저의 히스토리 정보를 문서와 문서 상태 목록으로 저장하는 객체
- 히스토리 목록 접근
이전페이지로 가기 - window.history.back(); 또는 window.history.go(-1);
다음페이지로 가기 - window.history.forward();
** 예제 1214_6 (location객체 / history객체)**


screen.width와 screen.height는 현재 사용자의 모니터 화면의 크기를 반환.
window.outerWidth와 widow.outerHeight는 현재 브라우저 창의 크기를 반환.
** 예제 1214_6 ( 사용자 화면 크기 )**

문자열에서 특정한 규칙을 가지는 문자열의 집합을 찾아내기 위한 검색 패턴.
이러한 검색패턴은 모든 종류의 문자열 검색이나 교체 등의 작업에서 사용.
문법) / 검색패턴 / 플래그
search() 메서드는 해당 문자열에서 인수로 전달받은 정규 표현식과 일치하는 첫번째 문자열의 위치를 반환해주는 자바스크립트의 String메서드이다.
- regExp 객체 : 정규 표현식을 구현한 자바스크립트 표준 내장 객체
test() 메서드 : 인수로 전달된 문자열에 특정 패턴과 일치하는 문자열이 있는지를 검색.
패턴과 일치하는 문자열이 있으면 true를, 없으면 false를 반환함.
| 식 | 기능 | 설명 |
| ^ | 시작 | 문자열의 시작을 표시 |
| $ | 끝 | 문자열의 끝을 표시 |
| . | 문자 | 한 개의 문자와 일치 |
| \d | 숫자 | 한개의 숫자와 일치 |
| \w | 문자와 숫자 | 한개의 문자나 숫자와 일치 |
| \s | 공백 문자 | 공백, 탭, 줄바꿈, 캐리지 리턴 문자와 일치 |
| [] | 문자종류, 문자범위 | [abc] 는 a또는 b 또는 c [a-z] 는 a부터 z까지 중의 하나 [1-9] 는 1부터 9까지 중의 하나 |
예)
/abc/ : 정확히 "abc"와만 일치됨.
/./ : 한자리의 문자, 예를 들어 "A", "1", "$"
/\d/d/d/ : 3자리
/[a-z]/ :
/\w/ :
/^\d/ :
/\d\d$/ :
메타문자 뒤에 수량한정자를 붙일 수 있음. 수량한정자는 문자가 몇번 반복되는냐를 나타냄
| 수량 한정자 | 기 능 | 설 명 |
| * | 0 회 이상 반복 | "a*" 는 "" , "a", "aa", "aaa" ...를 나타낸다 |
| + | 1회 이상 | "a+" 는 "a", "aa", "aaa"를 나타낸다 |
| ? | 0 또는 1회 | "a?" 는 "", "a" 를 나타낸다. |
| {m} | m회 | "a{3}"는 "aaa"만 나타낸다. |
| {m,n} | m회 이상 n회 이하 | "a{1,3}"은 "a", "aa", "aaa"를 나타낸다 |
| {ab} | 그룹화 | (ab)* 은 "","ab", "abab"등을 나타낸다. |
예)
/.+/ - 어떤 문자가 1회 이상 반복
/\w*/ - 어떤 문자나 숫자로 이루어진 문자열
/^[1-9][0-9]*$/ - 처음 숫자가 0이 아니고 전체가 숫자 (예 - 가격)
/^\d{6}-\d{7}$/ - 중간에 -이 있는 주민등록번호
/(Good)?Bye/ - "GoodBye" 또는 "Bye"
- alert()
사용자에게 간단한 메시지를 보여주고, 그것에 대한 사용자의 확인을 기다린다. (확인버튼을 누를때까지 프로그램이 멈춰있다.)
- prompt()
사용자에게 간단한 메시지를 보여주고, 사용자가 입력한 문자열을 반환함.
- confirm()
사용자에게 간단한 메시지를 보여주고, 사용자가 확인이나 취소를 누르면 그 결과를 불리언 값으로 반환함.
** 예제 1214_7 **



* 소스 *
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>자바스크립트</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 배열에 1부터 100까지 저장한 후 모두 더하기
var arrdata = [];
var gubun = "";
function insertArr(chk){
gubun = chk;
var i;
for(i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++){
arrdata[i] = i + 1;
}
if(gubun == "I"){
selectArr();
}
else if (gubun == "D"){
delArr();
}
}
function selectArr(){
var i;
for(i = 0 ; i < arrdata.length ; i++){
document.write(arrdata[i] + " ");
}
addArr();
}
function addArr(){
var i, sum=0;
for(i = 0 ; i < arrdata.length ; i++){
sum += arrdata[i];
}
if(gubun == "I"){
document.write("<p>배열 데이터 덧셈 연산결과 : " + sum + "</p>");
}
else if(gubun == "D"){
document.write("<p>홀수번째 데이터 초기화 완료 : " + sum + "</p>");
}
document.write("<a href='1214_8.html'>돌아가기</a>");
}
function delArr(chk){
//홀수번째 0으로 초기화
var i;
for(i = 0 ; i < arrdata.length ; i++){
if(i % 2 == 0) //if(arrdata[i] % 2 != 0){
arrdata[i] = 0;
}
selectArr();
}
</script>
<!-- 1.생성,조회,연산을 우선 적용하고 2.홀수번째 0으로 초기화 적용 -->
<input type="button" value="배열 생성.조회.연산" onclick="insertArr('I')" />
<br />
<input type="button" value="배열의 홀수번째 0으로 초기화" onclick="insertArr('D')" />
</body>
</html>
| 12/13 수업 (30일차) _ for in 문 / label 문 / 배열 / 함 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
|---|---|
| 12/12 수업 (29일차) (0) | 2023.12.12 |
| 12/11 수업 (28일차) _ (1) | 2023.12.11 |
| 12/08 수업 (27일차) _ 자바스크립트란? / 식별자 / 타입 / 변수 / 연산자 (2) | 2023.12.08 |
- 해당 객체의 열거할 수 있는 모든 프로퍼티는 순회할 수 있도록 해줌.
- 문법 ) for(변수 in 객체){
객체의 열거할 수 있는 모든 프로퍼티의 개수만큼 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 실행문; }
프로그램 내의 특정 영역을 식별할 수 있도록 해주는 식별자
label문을 사용하면 continue문과 break 문의 동작이 프로그램의 흐름을 특정 영역으로 이동
- continue 문 : 해당 루프의 나머지 부분을 건너뛰고, 바로 다음 표현식으로 넘어가게함
문법1. continue;
문법2. continue 라벨이름;
- break 문 : 반복문을 완전히 종료시키고 다음위치의 실행문으로 프로그램의 흐름을 이동
문법1. break;
문법2. break 라벨이름;
* 예제 1213_2 (label 문) * - label문은 잘 사용하지 않는다. (문법정도만 알아두기)

* leble 을 break와 continue 사용

* 예제 1213_2 (switch문) *

- 배열의 특징
배열 요소의 타입이 고정되어 이지 않으므로, 같은 배열에 있는 배열 요소끼리의 타입이 서로 다를 수 있다.
배열 요소의 인덱스가 연속적이지 않아도 되며, 때문에 특정 배열 요소가 비어 있을 수 있음
자바스크립트에서 배열은 Array객체로 다뤄진다.
- 배열의 참조
배열의 각 요소를 참조하고 싶을 때는 []연산자를 사용함. 문법 : 배열이름[인덱스]
배열 요소의 개수를 배열의 길이라고 함.
배열의 길이는 length 프로퍼티에 자동으로 갱신됨.
cf) 삭제예) delete arr[2]; //배열의 3번째 요소를 삭제함, 배열의 길이는 변하지 않는다.
- 배열의 요소 추가
문법)
1. arr.push(추가할 요소); // push메소드를 이용하는 방법
2.arr[arr.length] = 추가할 요소; // length 프로퍼티를 이용하는 방법
3.arr[특정인덱스] = 추가할 요소; // 특정 인덱스를 지정하여 추가하는 방법
push()메서드와 length프로퍼티를 이용한 추가방법은 모두 배열의 끝에 새로운 요소가 추가된다.
- 배열 요소 접근
모든 요소에 차례대로 접근하고 싶을 때는 for/in 과 같은 반복문을 사용하여 접근
- Array객체
배열은 정렬된 값들의 집합으로 정의되며, Array객체로 다뤄짐
- 희소 배열
배열에 속한 요소의 위치가 연속적이지 않은 배열을 의미함.
희소배열의 경우 배열의 length 프로퍼티 값보다 배열 요소의 개수가 언제나 적음
- 다차원 배열
배열요소가 또 다른배열인 배열을 의미함
2차원배열이란 배열 요소가 1차원 배열인 배열을 의미함
- 연관 배열 (associative array)
숫자로 된 인덱스 대신에 문자열로 된 키(key)를 사용해 배열처럼 사용.
Array 객체가 아닌 기본 객체로 실제배열이 아님
- 문자열을 배열처럼 접근
문자열은 변하지 않는 값이므로, 읽기 전용 배열로 다룰 수 있음
하나의 특별할 목적으로 작업을 수행하도록 설계된 독립적인 블록을 의미함.
필요할 때마다 호출하여 해당 작업을 반복하여 수행할 수 있음.
- 함수의 정의는 function키워드로 시작되며, 다음과 같은 구성요소를 가짐
1. 함수의 이름
2. 괄호안에 쉼표(,)로 구분되는 함수의 매개변수 (parameter)
3. 중괄호 ({})로 둘러싸인 자바스크립트 실행문
- 문법)
function 함수이름(매개변수1, 매개변수2...)
{
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행하고자 하는 실행문;
}
* 예제 1213_3 (배열) *

* 예제 1213_3 (배열의 활용) *

* 예제 1213_3 (배열 요소 접근 <for in 문 활용>) *

* 예제 1213_3 (희소배열/다차원배열) *

* 예제 1213_3 (연관배열) *

* 소스
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>자바스크립트-배열</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>배열</h3>
<script>
//
var arrList = [1, true, "JavaScript"];
var arrObj = Array(1, true, "JavaScript");
var arrNewObj = new Array(1, true, "JavaScript");
document.write(arrList + "<br />");
document.write(arrObj + "<br />");
document.write(arrNewObj + "<br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h2>배열의 활용</h2>
<script>
//배열의 요소 추가 , 삭제
var arr = ["JavaScript"];
var ele = arr[0];
arr[1] = 10;
arr[2] = ele;
document.write("배열의 요소는 [" + arr + "] 입니다.<br />");
document.write("배열의 길이는 " + arr.length + "입니다.<br />");
delete arr[1];
document.write("배열의 요소는 [" + arr + "] 입니다.<br />");
document.write("배열의 길이는 " + arr.length + "입니다.<br /><br />");
//배열의 요소 추가
arr.push("Script");
arr[arr.length] = 100;
document.write("배열의 요소는 [" + arr + "] 입니다.<br />");
document.write("배열의 길이는 " + arr.length + "입니다.<br />");
arr[20] = "자바스크립트";
document.write("배열의 요소는 [" + arr + "] 입니다.<br />");
document.write("배열의 길이는 " + arr.length + "입니다.<br />"); //길이 : 21
document.write("arr[10] : " + arr[10] + "<br />") // undefined : 값이 없기에 타입이 정해지지 않아서
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>배열 요소 접근</h3>
<script>
arr = [1, true, "Javascript"];
var result = "<table border=1><tr>";
for(var idx in arr){
result += "<td>" + arr[idx] + "</td>";
}
result += "</tr></table>";
document.write(result);
document.write("<br /><br />");
document.write("typeof arr : " + (typeof arr) + "<br />");
document.write("typeof arr[0] : " + (typeof arr[0]) + "<br />");
document.write("typeof arr[1] : " + (typeof arr[1]) + "<br />");
document.write("typeof arr[2] : " + (typeof arr[2]) + "<br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>희소배열 / 다차원배열</h3>
<script>
//희소배열
arr = new Array();
arr[99] = "JavaScript"
document.write("배열의 길이는 " + arr.length + "입니다.<br />");
//다차원 배열
arr = new Array(3);
var row, column;
for(row = 0 ; row < 3 ; row++){
arr[row] = new Array(4);
for(column = 0 ; column < arr[row].length ; column++){
arr[row][column] = "[" + row + "," + column + "]";
document.write(arr[row][column] + " ");
}
document.write("<br />");
}
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>연관배열 / 문자열을 배열처럼 접근</h3>
<script>
//연관 배열
arr = [];
arr["하나"] = 1;
arr["참"] = true;
arr["자바스크립드"] = "JavaScript";
document.write(arr["참"] + "<br />");
document.write("arr.length : " + arr.length + "<br />");
document.write("arr[0] : " + arr[0] + "<br /><br />");
//문자열을 배열처럼 접근
var str = "안녕하세요.";
document.write("str.charAt(2) : " + str.charAt(2) + "<br />");
document.write("str[2] : " + str[2] + "<br />");
</script>
</body>
</html>
하나의 특별할 목적으로 작업을 수행하도록 설계된 독립적인 블록을 의미함.
필요할 때마다 호출하여 해당 작업을 반복하여 수행할 수 있음.
- 함수의 정의는 function키워드로 시작되며, 다음과 같은 구성요소를 가짐
1. 함수의 이름
2. 괄호안에 쉼표(,)로 구분되는 함수의 매개변수 (parameter)
3. 중괄호 ({})로 둘러싸인 자바스크립트 실행문
- 문법)
function 함수이름(매개변수1, 매개변수2...)
{
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행하고자 하는 실행문;
}
- 반환(return)문
함수는 반환문을 포함할 수 있음. 호출자는 함수에서 실행된 결과를 전달 받을 수 있음.
- 값으로서의 함수
함수가 변수에 대입될 수도 있으며, 다른 함수의 인수로 전달될 수 도 있음.
- 변수의 유효 범위
유효범위에 따라 -> 지역변수(lical variable) / 전역변수(global variable ) 로 구분됨.
cf) 선언되지 않은 변수에 대한 typeof 연산자의 결과값은 undefined을 반환.
· 지역변수
함수 내에서 선언된 변수를 가리킴
함수 내에서만 유효하며, 함수가 종료되면 메모리에서 사라짐
함수의 매개변수 또한 함수 내에서 정의되는 지역변수처럼 동작함
· 전역변수
함수 외부에서 선언된 변수
프로그램의 어느 영역에서나 접근 가능, 페이지가 닫히면 메모리 삭제
함수내부에서 var 키워드를 사용하지 않고 변수 선언하면 → 전역변수로 선언됨
cf) 전역변수와 같은이름의 지역변수 선언시 함수 내에서는 지역변수만 호출
함수 내에서 같은 이름의 전역변수를 호출하려면 window. 붙여준다.
- 매개변수
함수 정의시 매개변수의 타입을 따로 명시하지않으며, 함수 호출 시 인수(argument)로 전달된 값에 대해 어떠한 타입검사도 하지 않음
함수를 호출 할 때 함수의 매개변수보다 적은 인수가 전달되더라도 오류가 발생하지 않음.
(나머지 매개변수에 자동으로 undefined값을 설정)
* 예제 1213_4 (자바스크립트 함수) *

* 예제 1213_4 ( 값으로서 함수 / 변수유효범위 / 함수내에서 전역변수 사용법 window. / 매개변수 ) *
- head

- body

* 소스 *
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>자바스크립트(함수)</title>
<script>
function addNum(x, y){
document.write("addNum 함수 호출<br />");
return x + y;
}
function addNum2(x, y){
document.write("addNum2(x, y) : " + (x + y) + "<br />");
}
function sqr(x){
return x*x;
}
function localNum(){
var num = 10; //지역변수 / var 없음면 전역변수로 된다.
num2 = 20; //var선언 안하면 전역변수
document.write("함수 내부에서 변수 num의 타입은 " + (typeof num) + "입니다.<br />");
document.write("함수 내부에서 변수 num2의 타입은 " + (typeof num2) + "입니다.<br />");
}
var num = 10;
function globalNum(){
var num = 20;
document.write("함수내에서 지역변수 num의 값은 " + num + "입니다.<br />");
document.write("함수내에서 전역변수 num의 값은 " + window.num + "입니다.<br />");
}
function addNum3(x, y, z){
return x+y+z;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>자바스크립트 함수</h3>
<script>
document.write("addNum(x, y) : " + addNum(2,3));
document.write("<br /><br />");
document.write("addNum() : " + addNum());
document.write("<br /><br />");
addNum2(13, "일 입니다.<br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h4>값으로서의 함수</h4>
<script>
//값으로서의 함수
var sqrNum = sqr;
document.write("sar(4) : " + sqr(4) + "<br />");
document.write("sqrNum(5) : " + sqrNum(5) );
</script>
<br /><br />
<h4>변수 유효 범위 (지역변수/전역변수)</h4>
<script>
//변수 유효 범위 (지역변수/전역변수)
localNum();
document.write("함수 호출이 끝난 뒤 변수 num의 타입은 " + (typeof num) + "입니다.<br />");
document.write("함수 호출이 끝난 뒤 변수 num2의 타입은 " + (typeof num2) + "입니다.<br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h4>함수내에서 전역변수 사용시 앞에 window. 사용</h4>
<script>
//함수내에서 전역변수 사용시 앞에 window. 사용
globalNum();
//매개변수
document.write("<br /><br />")
document.write("1 : " + addNum3(1, 2, 3) + "<br />");
document.write("1 : " + addNum3(1, 2) + "<br />");
document.write("1 : " + addNum3(1) + "<br />");
document.write("1 : " + addNum3() + "<br />");
</script>
</body>
</html>
* 예제 1213_5 메소드 오버로딩 해보자 * → 맨 마지막의 메소드만 호출된다. ( 결과 : alert창의 값4가 네번나옴)


- 함수 정의보다 더 많은 수의 인수가 전달되었을때 arguments객체를 이용하여
함수로 전달된 인수의 총 개수를 확인하거나, 각각의 인수에도 바로 접근할 수 있다.
- 전달받은 인수의 개수에 상관없이 정상적인 계산을 수행할 수 있다.
- Arguments객체는 배열과 비슷하지만 Array객체는 아니므로, 인덱스와 . length프로퍼티만을 가지고 있을 뿐, 모든 것을 배열처럼 다룰 수는 없다.


- 문자열에서 위치 찾기 메서드
String 인스턴스에서 특정 문자나 문자열이 처음으로 등장하는 위치 또는 마지막으로 등장하는 위치를 반환한다.
.indexOf()
.lastIndexOf()
전달 받은 특정 문자나 문자열을 찾을 수 없을 때는 -1을 반환한다..
- 문자열에서 지정된 위치에 있는 문자 반환
.charAt()
.
- 문자열 추출 메서드
String 인스턴스에서 전달받은 시작 인덱스부터 종료 인덱스 바로 앞까지의 문자열만을 추출하여 만든 새로운 문자열을 반환한다.
.slice(a, b) → a : 시작인덱스 / b : 끝인덱스 +1 <a부터 b-1인덱스 까지 추출>.substring() → 슬라이스와 동일.substr(a, b) → a : 시작인덱스 / b : 문자갯수
str.slice(-4, -2); //음수로 전달된 인덱스는 문자열의 뒤에서부터 시작함 (뒤는 1부터 시작)
- 문자열 주위의 공백 제거 메서드
String인스턴스의 양끝에 존재하는 모든 공백과 줄 바꿈 문자를 제거한 새로운 문자열 반환한다.
.trim()
- 문자열 분리 메서드
String인스턴스를 구분자를 기준으로 나눈 후 , 나눈 문자열을 하나의 배열로 반환한다.
.split(); //()안에 들어가는 기준으로 나눈다.
split("") : 한문자씩 나눔 (공백도 한문자로 취급한다.)
split(" ") : 띄어쓰기를 기준으로 나눔 (나뉜 후 띄어쓰기부분만 사라짐)
split(!) : 느낌표를 기준으로 나눔 (나뉜 후 !는 없다. !이외 공백이나 다른요소들을 그대로 유지)
Split메서드는 인수로 구분자를 전달하지 않으며, 전체 문자열을 하나의 배열 요소로 가지는 길이가 1일 배열을 반환
- 문자열의 대소문자 변환 메서드
String인스턴스의 모든 문자를 대문자나 소문자로 변환한 새로운 문자열을 반환함.
.toUpperCase(); // 전부 대문자로 변환
.toLowerCase(); // 전부 소문자로 변환
Array 객체에 정의된 배열과 관련된 작업을 할 때 사용하는 메서드
Array.prototype 메서드
push() 메서드 : 하나 이상의 요소를 가장 마지막에 추가
- pop() 메서드
배열의 가장 마지막 요소를 제거하고, 그 제거된 요소를 반환함.
pop() 메서드를 실행할 때마다 배열의 길이를 1 씩 줄어들게됨.
cf) delete 는 배열의 길이는 변하지 않고 해당위치의 요소를 삭제 / pop 해당 요소를 제거하고 배열도 줄어듬
- shift() 메서드
배열의 가장 마지막 요소가 아닌 첫 요소를 제거하고, 그 제거된 요소를 반환한다.
실행할 때 마다 배열의 길이가 1 씩 줄어들게됨.
- reverse() 메서드
배열 요소의 순서를 뒤집는다.
- splice() 메서드
배열 요소를 제거하거나 새로운 배열요소를 추가하여 내용을 변경한다.
첫번째 인수 : 새로운 요소가 삽입될 위치의 인덱스
인수 : 제거할 요소의 개수
그후 인수들 : 모두 배열 요소로서 지정된 인데스부터 차례대로 삽입
이 메소드는 배열에서 제거된 요소를 배열의 형태로 반환하며, 아무요소도 제거되지 않았으면 빈 배열 반환.
* 예제 1213



* 소스 *
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>자바스크립트</title>
<script>
function addNum(){
var sum = 0,i;
for(i = 0 ; i < arguments.length ; i++){
sum += arguments[i];
}
return sum;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>arguments 객체</h3>
<script>
// argument 객체
document.write("addNum(1,2,3) : " + addNum(1,2,3) + "<br />");
document.write("addNum(1,2) : " + addNum(1,2) + "<br />");
document.write("addNum(1) : " + addNum(1) + "<br />");
document.write("addNum() : " + addNum() + "<br />");
document.write("addNum(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10) : " + addNum(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10) + "<br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>String 메소드 - 위치찾기 / 지정된위치의 문자 반환 / 문자열 추출</h3>
<script>
var str = "abcEDFabc";
//문자열에서 위치찾기
document.write("indexOf('abc') : " + str.indexOf("abc") + "<br />");
document.write("indexOf('abcd') : " + str.indexOf('abcd') + "<br />");
document.write("indexOf('abc', 3) : " + str.indexOf("abc", 3) + "<br />");
document.write("lastindexOf('abc') : " + str.lastIndexOf("abc") + "<br />");
document.write("indexOf('d') : " + str.lastIndexOf("d") + "<br />");
document.write("indexOf('c') : " + str.lastIndexOf("c") + "<br /><br />");
//문자열에서 지정된 위치의 문자 반환
document.write("str.charAt(0) : " + str.charAt(0) + "<br />");
document.write("str.charAt(10) : " + str.charAt(10) + "<br /><br />");
//문자열 추출
str = "abcDEFabc";
document.write("slice(2, 6) : " + str.slice(2, 6) + "<br />");
document.write("slice(-4, 2) : " + str.slice(-4, -2) + "<br />");
document.write("slice(2) : " + str.slice(2) + "<br />");
document.write("substring(2, 6) : " + str.substring(2, 6) + "<br />");
document.write("substr(2, 3) : " + str.substr(2, 4) + "<br /><br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>String 메소드2 - 공백제거 / 문자열분리 / 문자열의 대소문자 변환</h3>
<script>
//공백제거
var temp = " java script ";
document.write("[" + temp + "],length : " + temp.length + "<br />");
document.write("[" + temp.trim() + "], length : " + temp.trim().length + "<br /><br />");
//문자열 분리
str = "자바스크립트는 너무 멋져요! 그리고 유용해요.";
document.write("str.split() : " + str.split() + "<br />");
document.write("str.split('') : " + str.split("") + "<br />");
document.write("str.split(' ') : " + str.split(" ") + "<br />");
document.write("str.split('!') : " + str.split("!") + "<br /><br />");
const arr = str.split(" "); //const : 상수정의
document.write("arr.length : " + arr.length + "<br />");
document.write("arr[0] : " + arr[0] + "<br />");
document.write("arr[1] : " + arr[1] + "<br />");
document.write("arr[2] : " + arr[2] + "<br />");
document.write("arr[3] : " + arr[3] + "<br /><br />");
str = "Javascript";
document.write("toUppercase() : " + str.toUpperCase() + "<br />");
document.write("toLowercase() : " + str.toLowerCase() + "<br /><br />");
</script>
<br /><br />
<h3>Array 메소드3 - Array메서드</h3>
<script>
// Array 메서드 - push
var arr1 = [1, true, "Java Script"];
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + "<br />");
arr1.push("자바스크립트");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + "<br />");
document.write("arr1 : " + arr1 + " <br />");
arr1.push(2, "거짓");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + "<br />");
document.write("arr1 : " + arr1 + "<br /><br />");
//pop() 메서드
document.write("arr1.pop() : " + arr1.pop() + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.pop() : " + arr1.pop() + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.pop() : " + arr1.pop() + " <br />");
document.write("arr1 : " + arr1 + " <br /><br />");
//shift() 메서드
document.write("arr1.shift() : " + arr1.shift() + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.shift() : " + arr1.shift() + " <br />");
document.write("arr1.length : " + arr1.length + " <br />");
document.write("arr1 : " + arr1 + " <br /><br />");
</script>
</body>
</html>
문서 객체 모델 HTML문서에 접근하기 위한 일종의 인터페이스.
이 객체 모델은 문서 내의 모든 요소를 정의하고, 각각의 요소에 접근하는 방법을 제공

- 객체 모델을 이용한 작업
새로운 HTML요소나 속성을 추가
존재하는 HTML요소나 속성을 제거
HTML문서의 모든 HTML요소를 변경
HTML문서의 모든 HTML속성을 변경
HTML문서의 모든 CSS스타일을 변경
HTML문서의 새로운 HTML이벤트 추가
HTML문서의 모든 HTML이벤트에 반응
HTML DOM은 HTML문서를 조작하고 접근하는 표준화된 방법을 정의함.
웹페이지 그자체를 의미하며, 웹페이지에 존재하는 HTML 요소에 접근하고자 할 때는 반드시 Document객체부터 시작해야한다.
document.getELementsById
- 아이디 (id) 를 이용한 선택
- Name 속성을 이용한 선택
getElementsByName() 은 HTML요소의 name속성을 이용해 HTML요소를 선택
name 속선값이 같은 모든 요소를 선택한다.
- CSS선택자(selector)를 이용한 선택
quarySelectorAll() 메서드는 CSS선택자(아이디, 클래스, 속성, 속성값 등)를 이용해 HTML 요소를 선택
quarySelectorAll() 메소드는 익스플로럴8 과 그 이전 버전은 지원하지 않음.
- HTML 객체 집합(object coloection)을 이용한 선택
객체 집합(object collection)을 이용하여 HTML용소를 선택
- DOM 요소의 내용변경
HTML 요소의 내용(content)이나 속성값 등을 손쉽게 변경.
HTML 요소의 내용을 변경하는 가장 쉬운 방법은 innerHTML 프로퍼티를 이용.
- DOM 요소의 스타일 변경
예 )
var str = document.getElementById("text"); //아이디가 "str"인요소를 선택함
function changeRedColor(){ str.style.color = "red";}
https://tcpschool.com/javascript/js_dom_document


* 소스
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>DOM요소</title>
<script>
//모든 li요소를 선택하여 텍스트 색상 변경
function fn_tag(){
var selectedItem = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
var i;
for(i = 0 ; i < selectedItem.length ; i++){
selectedItem.item(i).style.color = "orange"; //선택된 요소의 텍스트 색상 변경.
}
}
//아이디를 이용하여 선택한 후 텍스트 변경(단, 아이디가 여러개인 경우 첫번쨰만 적용됨)
function fn_id(){
var selectItem = document.getElementById("even");
selectItem.style.color = "red";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>모든 li 요소 선택</h2>
<ul>
<li id="even">월요일</li>
<li>화요일</li>
<li name="first">수요일</li>
<li>목요일</li>
<li name="first">금요일</li>
<li id="even">토요일</li>
<li id="even">일요일</li>
</ul>
<input type="button" value="li태그로 선택" onclick="fn_tag()" />
<input type="button" value="id가 even선택" onclick="fn_id()" />
<script>
// name을 이용한
var selectI = document.getElementsByName("first");
for( i = 0 ; i < selectI.length ; i++){
selectI.item(i).style.color = "blue";
}
// title 요소 선택
var title = document.title;
document.write(title + "<br /><br />");
</script>
<h2>DOM 요소의 스타일 변경</h2>
<p id="text">이부분의 스타일이 변경됩니다.</p>
<input type="button" value="빨간색 변경" onclick="redColor()" />
<input type="button" value="검정색 변경" onclick="blackColor()" />
<script>
var str = document.getElementById("text");
//스크립트를 이곳에 쓴 이유
//document.getElementById("text")는 <p id="text">이부분의 스타일이 변경됩니다.</p>이 선언된 후 사용되기 때문
function redColor(){
str.style.color = "red";
}
function blackColor(){
str.style.color = "black";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
| 12/14 수업 (31일차) (0) | 2023.12.14 |
|---|---|
| 12/12 수업 (29일차) (0) | 2023.12.12 |
| 12/11 수업 (28일차) _ (1) | 2023.12.11 |
| 12/08 수업 (27일차) _ 자바스크립트란? / 식별자 / 타입 / 변수 / 연산자 (2) | 2023.12.08 |
: if else 문을 삼항 연산자를 이용해 간단히 표현가능
문법)표현식?반환값1:반환값2;
문법)switch (조건값){
case1: 조건 값이 값1일 떄 실행하고자 하는 실행문;
break;
case2: 조건 값이 값2일 떄 실행하고자 하는 실행문;
break;
...
dufault:
{ 조건값이 어떠한 case절에도 해당하지 않을 때 실행하고자 하는 실행문; }
- default 절의 위치가 반드시 switch 문의 맨 마지막일 필요는 없음
** 문제 1212 **
/*
문제)과목 점수를 입력을 받아 학점을 출력하는 프로그램
과목점수는 0~100점 이며, 범위가 초과되면 "0~100점 사이 값을 입력하세요." 라고 화면에 출력.
(화면에 출력 document.write 사용)
과목점수가 정상 입력되었을 경우.
90~100 : A, 80~89 : B, 70~79 : C, 60~69 : D, 나머지 : F 로 학점(grade)를 구하고
A인 경우 "잘했습니다."
B인경우 "잘했습니다."
C인 경우 "조금만 노력하면 잘 할수 있습니다."
D인 경우 "좀 더 노력하세요"
F인 경우 "많이 노력하기 바랍니다."
입력예)과목점수를 입력하세요.
85
출려계)잘했습니다.
당신의 학점은 B입니다. (단, B는 <b>태그 이용)
단, 출력은 document.write로 사용.
*/

* 소스 *
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>학점 환산 프로그램</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var score = parseInt(prompt("점수를 입력하세요."));
var grade="";
if(score < 0 && 100 < score){
document.write("0~100점 사이 값을 입력하세요.");
}
else{
if(score >= 90){
grade = "A";
document.write("아주 잘했습니다.<br />");
}
else if(score >= 80){
grade = "B";
document.write("잘했습니다.<br />");
}
else if(score >= 70){
grade = "C";
document.write("조금만 노력하면 잘 할수 있습니다.<br />");
}
else if(score >= 60){
grade = "D";
document.write("좀 더 노력하세요<br />");
}
else{
grade = "F";
document.write("많이 노력하기 바랍니다.<br />");
}
document.write("당신의 점수는 <b>" + grade + "</b>입니다.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>** 1212_2 예제 (switch문 오늘 요일 출력) **

** 1212_2 문제 1 (커피 주문) **
/*
문제)커피를 주문하는 과정 중 어떤 커피를 주문 할 지 입력을 받은 후 출력하는 프로그램
입력예)무슨 커피 드릴까요?
아이스아메리카노
출력예)아이스아메리카노 1500월 입니다.
단, 아이스아메리카노(icecoffee) : 1500
카페라떼 : 4500
바닐라라떼 : 5500
나머지는 '000은(는) 없습니다.'
출력시 금액이 있는 경우가 정상적인 경우로 판다.
*/

* 1212_2 문제 2 (요일별 영업) *
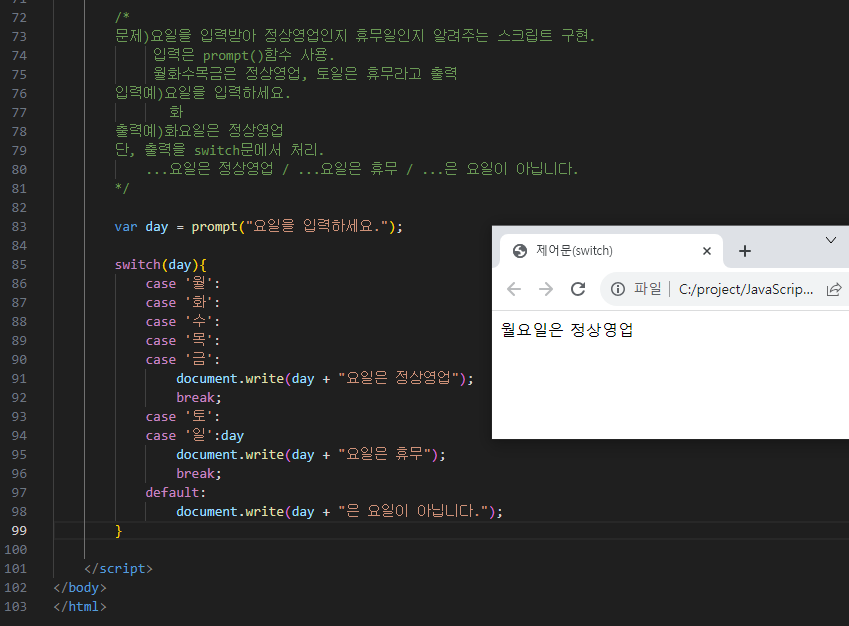
/*
문제)요일을 입력받아 정상영업인지 휴무일인지 알려주는 스크립트 구현.
입력은 prompt()함수 사용.
월화수목금은 정상영업, 토일은 휴무라고 출력
입력예)요일을 입력하세요.
화
출력예)화요일은 정상영업
단, 출력을 switch문에서 처리.
...요일은 정상영업 / ...요일은 휴무 / ...은 요일이 아닙니다.
*/
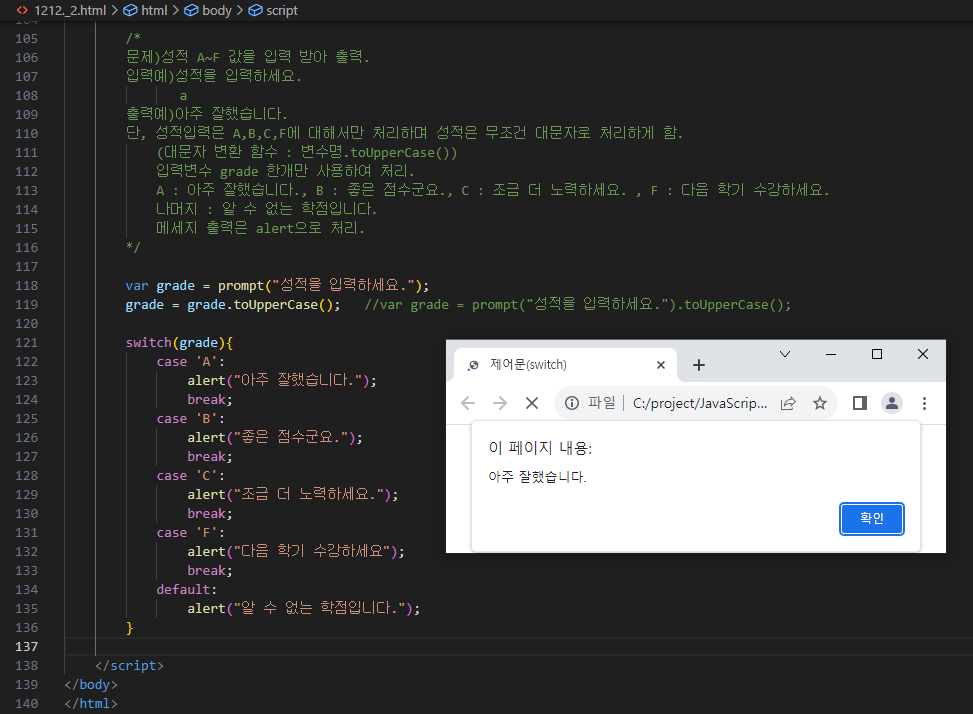
** 1212_2 문제 3 (성적) **
/*
문제)성적 A~F 값을 입력 받아 출력.
입력예)성적을 입력하세요.
a
출력예)아주 잘했습니다.
단, 성적입력은 A,B,C,F에 대해서만 처리하며 성적은 무조건 대문자로 처리하게 함.
(대문자 변환 함수 : 변수명.toUpperCase())
입력변수 grade 한개만 사용하여 처리.
A : 아주 잘했습니다., B : 좋은 점수군요., C : 조금 더 노력하세요. , F : 다음 학기 수강하세요.
나머지 : 알 수 없는 학점입니다.
메세지 출력은 alert으로 처리.
*/
* 소스 1212_2 *
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>제어문(switch)</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var day;
var week = new Date().getDay(); //0(일요일)~6(토요일)
/*
switch(week){
case 0:
day = "일요일";
break;
case 1:
day = "월요일"; break;
case 2:
day = "화요일";
break;
case 3:
day = "수요일";
break;
case 4:
day = "목요일";
break;
case 5:
day = "금요일";
break;
case 6:
day = "토요일";
break;
default:
day = "없는 요일";
}
document.write("<h1>오늘은 <b>" + day + "</b>입니다.<h1");
*/
/* 1
문제)커피를 주문하는 과정 중 어떤 커피를 주문 할 지 입력을 받은 후 출력하는 프로그램
입력예)무슨 커피 드릴까요?
아이스아메리카노
출력예)아이스아메리카노 1500월 입니다.
단, 아이스아메리카노(icecoffee) : 1500
카페라떼 : 4500
바닐라라떼 : 5500
나머지는 '000은(는) 없습니다.'
출력시 금액이 있는 경우가 정상적인 경우로 판다.
var type = prompt("무슨 커피 드릴까요?");
var price="";
//var price="" 초기값을 세팅하지 않으면 if(price != undefined) 또는 0으로 세팅 후 (price != 0)으로 가능
switch(type){
case ("아이스아메리카노"):
case ("icecoffee"):
price = 1500;
break;
case "카페라떼":
price = 4500;
break;
case "바닐라라떼":
price = 5500;
break;
default:
document.write(type + "은(는) 없습니다.");
}
if(price != ""){document.write(type + " " + price + "원 입니다.");}
*/
/* 2
문제)요일을 입력받아 정상영업인지 휴무일인지 알려주는 스크립트 구현.
입력은 prompt()함수 사용.
월화수목금은 정상영업, 토일은 휴무라고 출력
입력예)요일을 입력하세요.
화
출력예)화요일은 정상영업
단, 출력을 switch문에서 처리.
...요일은 정상영업 / ...요일은 휴무 / ...은 요일이 아닙니다.
var day = prompt("요일을 입력하세요.");
switch(day){
case '월':
case '화':
case '수':
case '목':
case '금':
document.write(day + "요일은 정상영업");
break;
case '토':
case '일':day
document.write(day + "요일은 휴무");
break;
default:
document.write(day + "은 요일이 아닙니다.");
}
*/
/* 3
문제)성적 A~F 값을 입력 받아 출력.
입력예)성적을 입력하세요.
a
출력예)아주 잘했습니다.
단, 성적입력은 A,B,C,F에 대해서만 처리하며 성적은 무조건 대문자로 처리하게 함.
(대문자 변환 함수 : 변수명.toUpperCase())
입력변수 grade 한개만 사용하여 처리.
A : 아주 잘했습니다., B : 좋은 점수군요., C : 조금 더 노력하세요. , F : 다음 학기 수강하세요.
나머지 : 알 수 없는 학점입니다.
메세지 출력은 alert으로 처리.
*/
var grade = prompt("성적을 입력하세요.");
grade = grade.toUpperCase(); //var grade = prompt("성적을 입력하세요.").toUpperCase();
switch(grade){
case 'A':
alert("아주 잘했습니다.");
break;
case 'B':
alert("좋은 점수군요.");
break;
case 'C':
alert("조금 더 노력하세요.");
break;
case 'F':
alert("다음 학기 수강하세요");
break;
default:
alert("알 수 없는 학점입니다.");
}
</script>
</body>
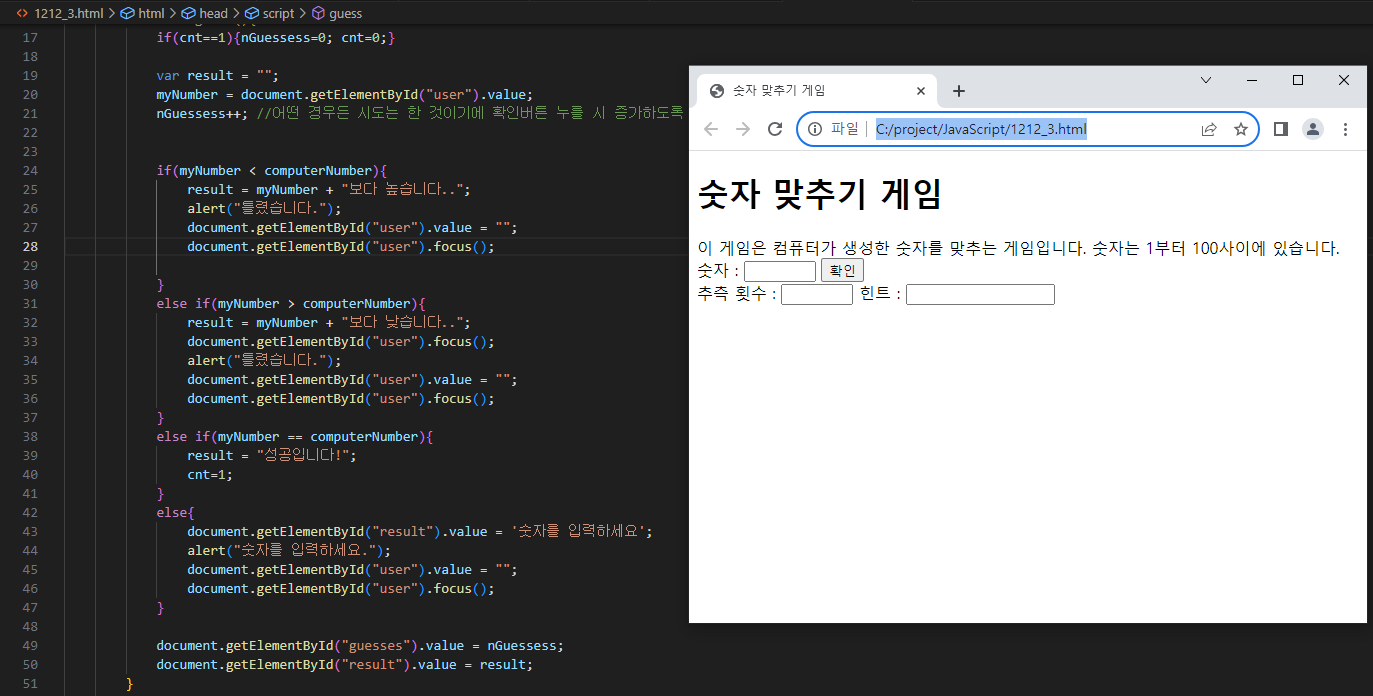
</html>** 1212_3 문제 (숫자 맞추기 게임)**
* <head>에 함수 정의 해보기 *
<body>
<h1>숫자 맞추기 게임</h1>
이 게임은 컴퓨터가 생성한 숫자를 맞추는 게임입니다. 숫자는 1부터 100사이에 있습니다.<br />
숫자 : <input type="text" id="user" size="5" />
<input type="button" value="확인" onclick="guess()" /><br />
추측 횟수 :
<input type="text" id="guesses" size="5">
힌트 : <input type="text" id="result" size="16" />
</body>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>숫자 맞추기 게임</title>
<script>
/*
입력값이 낮을 경우는 '낮습니다.', 높을 경우는 '높습니다.', 맞은 경우는 '성공입니다.'
*/
var computerNumber = 53;
var nGuessess = 0;
var cnt = 0;
//myNumber = document.getElementById("user").value;
//-> 헤드가 먼저 실행되기 때문에 document.getElementById("user").value 아직 없다. 따라서 바디 안의 무언가 가지고오려면 함수 안에서 하는 것이 좋다.
function guess(){
if(cnt==1){nGuessess=0; cnt=0;}
var result = "";
myNumber = document.getElementById("user").value;
nGuessess++; //어떤 경우든 시도는 한 것이기에 확인버튼 누를 시 증가하도록 후 맨 아래에 값 대입
if(myNumber < computerNumber){
result = myNumber + "보다 높습니다..";
alert("틀렸습니다.");
document.getElementById("user").value = "";
document.getElementById("user").focus();
}
else if(myNumber > computerNumber){
result = myNumber + "보다 낮습니다..";
document.getElementById("user").focus();
alert("틀렸습니다.");
document.getElementById("user").value = "";
document.getElementById("user").focus();
}
else if(myNumber == computerNumber){
result = "성공입니다!";
cnt=1;
}
else{
document.getElementById("result").value = '숫자를 입력하세요';
alert("숫자를 입력하세요.");
document.getElementById("user").value = "";
document.getElementById("user").focus();
}
document.getElementById("guesses").value = nGuessess;
document.getElementById("result").value = result;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>숫자 맞추기 게임</h1>
이 게임은 컴퓨터가 생성한 숫자를 맞추는 게임입니다. 숫자는 1부터 100사이에 있습니다.<br />
숫자 : <input type="text" id="user" size="5" />
<input type="button" value="확인" onclick="guess()" /><br />
추측 횟수 :
<input type="text" id="guesses" size="5">
힌트 : <input type="text" id="result" size="16" />
</body>
</html>
* 반복문 : 같은 명령을 일정횟수만큼 반복하여 수행하도록 제어하는 실행문
while 문
do / while 문
for문
for / in 문
for / of 문
cf) 하나의 태그에 열고닫고 <br /> <input />
** 문제 1212_5 (구구단표 작성해보기) **

** 문제 1212_6 (prompt / innerHTML 두가지로 구구단 출력해보자) **
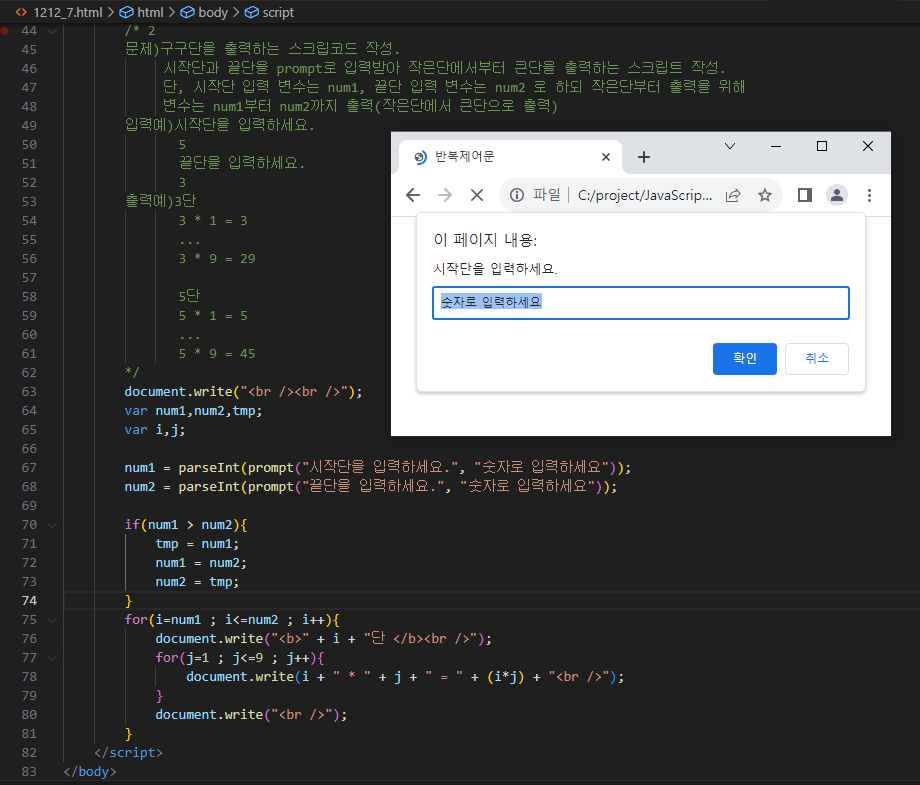
/*
문제) 구구단을 작은 수와 큰 수 순서로 입력받아 구구단 출력하는 프로그램
입력예)시작단을 입력하세요.2
끝단을 입력하세요.3
출력예)2단
2 * 1 =2
...
2 * 9 = 18
3단
3 * 1 = 3
...
3 * 9 = 27
단, 입력받은 값은 숫자로 변환함.
1. prompt 사용하여 구구단출력
2. html imput=text에서 입력받아 버튼 클릭시 구구단 출력
시작단 : num1 , 끝단 : num2 버튼 클릭시 호출함수는 gugu()
<p id="tab"></p> : 이부분에 구구단 출력
*/
* 방법1

* 방법 2
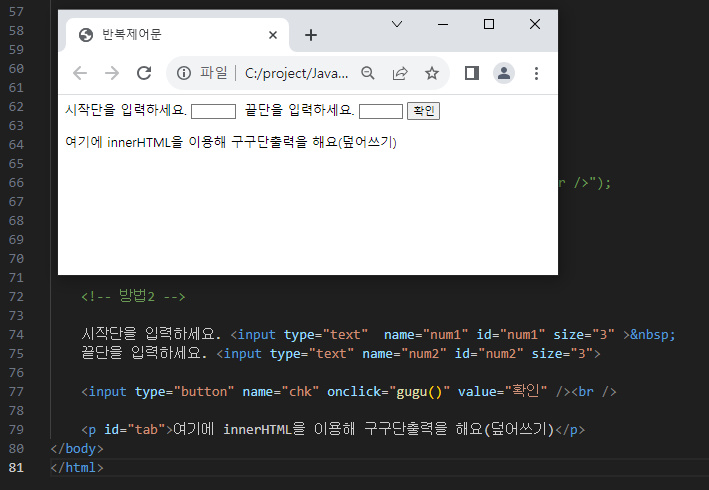

→방법2 <head>
<script> 속 함수
* 소스
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>반복제어문</title>
<script>
/*
문제) 구구단을 작은 수와 큰 수 순서로 입력받아 구구단 출력하는 프로그램
입력예)시작단을 입력하세요.2
끝단을 입력하세요.3
출력예)2단
2 * 1 =2
...
2 * 9 = 18
3단
3 * 1 = 3
...
3 * 9 = 27
단, 입력받은 값은 숫자로 변환함.
1. prompt 사용하여 구구단출력
2. html imput=text에서 입력받아 버튼 클릭시 구구단 출력
시작단 : num1 , 끝단 : num2 버튼 클릭시 호출함수는 gugu()
<p id="tab"></p> : 이부분에 구구단 출력
*/
function gugu(){
var i,j;
var result = ""; //누적하려면 초기값 세팅해줘야한다.
var n1 = document.getElementById("num1").value;
var n2 = document.getElementById("num2").value;
for(i = n1; i<=n2 ; i++){
result += "<br />" + i + "단<br />";
for(j=1 ; j<10 ; j++){
result += i + ' * ' + j + " = " + i*j + "<br />"
}
}
/*
//위의 포문과 같은 방법
for(i=n1 ; i<=n2 ; i++){
document.getElementById("tab").innerHTML += "<br ?>" + i + "단<br />";
for(j=1 ; j<10 ;j++){
document.getElementById("tab").innerHTML += i + ' * ' + j + " = " + i*j + "<br />";
}
}
*/
// document.getElementById("tab").innerHTML = result;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 방법1. -->
<!-- <script>
num1 = parseInt(prompt("시작단을 입력하세요."));
num2 = parseInt(prompt("끝단을 입력하세요."));
var i,j;
for(i = num1; i<=num2 ; i++){
document.write("<br />" + i + "단<br />");
for(j=1 ; j<10 ; j++){
document.write(i + ' * ' + j + " = " + (i*j) + "<br />");
}
}
</script> -->
<!-- 방법2 -->
시작단을 입력하세요. <input type="text" name="num1" id="num1" size="3" >
끝단을 입력하세요. <input type="text" name="num2" id="num2" size="3">
<input type="button" name="chk" onclick="gugu()" value="확인" /><br />
<p id="tab">여기에 innerHTML을 이용해 구구단출력을 해요(덮어쓰기)</p>
</body>
</html>** 문제 1212_7 (3의 배수를 제외한 숫자 출력_continue / continue사용 x) **
/* 1212_7
문제) for문을ㅣ용하여 1~100까지 출력하며 3의 배수는제외하고출력하는 스크립트 작성(continue문 사용)
출력예)1 2 4 5 7 8 10 11 ..... 100
*/

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>반복제어문</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
/* 1
문제) for문을ㅣ용하여 1~100까지 출력하며 3의 배수는제외하고출력하는 스크립트 작성(continue문 사용)
출력예)1 2 4 5 7 8 10 11 ..... 100
*/
var i;
// for(i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++){
// if(i%3==0){
// continue;
// }
// document.write(i+" ");
// }
//위와 동일한 결과로 continue 사용하지 않고 결과 출력
for(i=1 ; i < 100 ; i++){
if(i%3==0){
document.write(i+" ");
}
}
</script>
<br /><br />
<h1>for/ in 문</h1>
<script>
var arr = [3,4,5];
for(var i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write("<br /><br />");
for(var i in arr){
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
/* 2
문제)구구단을 출력하는 스크립코드 작성.
시작단과 끝단을 prompt로 입력받아 작은단에서부터 큰단을 출력하는 스크립트 작성.
단, 시작단 입력 변수는 num1, 끝단 입력 변수는 num2 로 하되 작은단부터 출력을 위해
변수는 num1부터 num2까지 출력(작은단에서 큰단으로 출력)
입력예)시작단을 입력하세요.
5
끝단을 입력하세요.
3
출력예)3단
3 * 1 = 3
...
3 * 9 = 29
5단
5 * 1 = 5
...
5 * 9 = 45
*/
document.write("<br /><br />");
var num1,num2,tmp;
var i,j;
num1 = parseInt(prompt("시작단을 입력하세요.", "숫자로 입력하세요"));
num2 = parseInt(prompt("끝단을 입력하세요.", "숫자로 입력하세요"));
if(num1 > num2){
tmp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = tmp;
}
for(i=num1 ; i<=num2 ; i++){
document.write("<b>" + i + "단 </b><br />");
for(j=1 ; j<=9 ; j++){
document.write(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i*j) + "<br />");
}
document.write("<br />");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 해당 객체의 열거할 수 있는 모든 프로퍼티는 순회할 수 있도록 해줌.
문법 ) for(변수 in 객체){
객체의 열거할 수 있는 모든 프로퍼티의 개수만큼 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 실행문; }
** 문제 1212_7 (구구단출력) **
| 12/14 수업 (31일차) (0) | 2023.12.14 |
|---|---|
| 12/13 수업 (30일차) _ for in 문 / label 문 / 배열 / 함 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
| 12/11 수업 (28일차) _ (1) | 2023.12.11 |
| 12/08 수업 (27일차) _ 자바스크립트란? / 식별자 / 타입 / 변수 / 연산자 (2) | 2023.12.08 |
** 1208_7 (리스너 / 자바스크립트 함수 호출) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>연산자</title>\
<script>
function over(obj){
obj.src = "./img/computer2.jpeg" ;
}
function out(obj){
obj.src = "./img/computer1.jpeg";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--연산자-->
<h1>연산자</h1>
<script>
var x = 3, y = 5;
var a = "abc", b = "bcd";
document.write((x > y) + "<br />"); //false
document.write((a <= b) + "<br />"); //true(알파벳 a보다 b가 큼. 변수 맨 앞자리부터 체크)
document.write((x < a) + "<br />"); //false(숫자와 문자열 비교 불가)
x = 3, y = '3', z = 3;
document.write((x == y) + "<br />"); //true(값이 같으므로)
document.write((x === y) + "<br />"); //false(값은 같으나 타입이 다르므로)
document.write((x === z) + "<br />"); //true(값과 타입이 같으므로)
</script>
<br /><br />
<h1>delete 연산자</h1>
<script>
var arr = [1,2,3];
document.write("삭제 전 : " + arr + "<br />");
delete arr[2];
document.write("삭제 후 : " + arr + "<br />");
document.write("arr[2] : " + arr[2] + "<br />");
document.write("arr.length : " + arr.length + "<br />");
</script>
<br />
<h2><a href="javascript:void(0)">링크는 동작하지 않습니다.</a></h2>
<h2><a href="javascript:void(document.body.style.backgroundColor='yellow')">링크는 동작하지 않지만 HTML문서 배경은 변경됨.</a></h2>
<br /><br />
<!--이벤트 리스너 속성-->
<h3>이미지 위에 마우스를 올려 보세요.</h3>
<img src="./img/computer1.jpeg" alt="컴퓨터1" width="300" height="200" onmouseover="this.src='./img/computer2.jpeg'" onmouseout="this.src='./img/computer1.jpeg'" />
<br /><br />
<!--(head의)자바스크립트 함수 호출-->
<h3>이미지 위에 마우스를 올려 보세요.2</h3>
<img src="./img/computer1.jpeg" alt="컴퓨터2" width="300" height="200" onmouseover="over(this)" onmouseout="out(this)" />
</body>
</html>
→ 마우스 올리면 computer2로 이미지 바뀜
- 프로그램의 순차적인 흐름을 제어해야 할 때 사용하는 실행문, 제어문에는 조건문과 반복문.
- 조건문 : if 문 / if else 문 / else if 문/ else문 / switch 문
문법 ) if(표현식){ 표현식의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
if(표현식){ 표현식의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
else{ 표현식의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
if(표현식1){ 표현식1의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
else if(표현식2){ 표현식2의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
else{ 표현식의 결과가 참일 때 시행하고자 하는 실행문; }
** 1211 (예제/문제/문제/문제) **





** 1211_2 (문제/문제) **


* 위 문제의 cal 함수를 .js 파일로 빼서 사용해보기


-> 원래있던 cal 함수 주석처리 후
<script src="./js/sample2.js"></script> 입력하면 같은 결과 나옴다.
* 소스 코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>자바스크립트-제어문</title>
<script>
function cal(){
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
/* 1
문제) prompt()함수를 이용하여 점수를 입력받아 if~else를 사용하여 A~F까지 학점을 출력하는 스크립트 코드작성.
입력예) 점수를 입력하세요.
90
출력예) 90점은 A입니다.
단, 90~100 : A, 80~89 : B, 70~79 : C, 60~69 : D, 나머지 F
document.write()는 한번만 실행.
var score = prompt("점수를 입력하세요.");
if(score < 60){
result = "F";
}
else if(score < 70){
result = "D";
}
else if(score < 80){
result = "C";
}
else if(score < 90){
result = "B";
}
else{
result = "A";
}
document.write(score + "점은 " + result + "입니다.");
*/
/* 2
문제)짝홀수 맞추기 게임
숫자를 입력받고 계산하기 버튼 클릭 후 해당하는 함수에서 처리하는 순서
1. 입력값을 number1변수에 대입
document.폼네임.해당이름.value (예 : var tmp = document.fff.num1.value;)
2. 숫자가 입력되지 않았을 때 처리 (2번까지만 실행하고 해당 함수는 처리 끝.)
alert으로 "값을 입력하세요."
실행 후 커서를 해당 위치로 가게 함.(document.폼네임.해당이름.focus())
3. 숫자가 입력되었는지 확인
숫자입력 확인은 isNaN(입력변수) true면 숫자가 아님.
숫자가 아니면 alert으로 "숫자만 입력 가능합니다. 다시 입력하세요."
실행 후 커서를 해당 위치로 가게 하고 처리 끝
4. 여기 실행 조건은 값이 입력되었고, 입력값이 숫자인 경우 실행.
입력 값을 숫자로 변경한 후 짝/홀수 체크해서 alert으로 "짝수입니다."또는 "홀수입니다."라고 출력.
단, 서버 프로그램은 1211.html 로 하고, 서버 전송 방식은 get으로 함.
*/
function cal(){
var number1 = document.form1.num1.value; //name으로 조회
var number1 = document.getElementById("num1").value;
if(number1==""){ //if(document.form1.num1.value=="")
alert("값을 입력하세요");
document.form1.num1.focus();
return;
}
if(isNaN(number1)){
alert("숫자만 입력 가능합니다. 다시 입력하세요." );
document.form1.num1.value = "";
document.form1.num1.focus();
return;
}
number1 = parseInt(number1);
if(number1%2 == 0){
alert("짝수입니다.");
}
else{
alert("홀수입니다.");
}
if(confirm("서버로 보내시겠습니까?")){
//확인버튼 선택시 처리
document.form1.submit();
}
}
</script>
<h1>짝홀수 맞추기 게임</h1>
값을 입력하세요.
<form action="1211.html" name="form1" method="get">
숫자 : <input type="text" id="num1" name="num1" size="5" />
<input type="button" name="result" onclick="cal()" value="계산하기" />
</form>
</body>
</html>** 1211_3 (로그인 성공/실패) **

* 실행은 1211_3실행


** 1211_4 (자바스크립트_학점매기기게임) **
* 두개의 함수를 하나의 함수로 처리 *

| 12/14 수업 (31일차) (0) | 2023.12.14 |
|---|---|
| 12/13 수업 (30일차) _ for in 문 / label 문 / 배열 / 함 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
| 12/12 수업 (29일차) (0) | 2023.12.12 |
| 12/08 수업 (27일차) _ 자바스크립트란? / 식별자 / 타입 / 변수 / 연산자 (2) | 2023.12.08 |
HTML로는 웹의 내용을 작성하고, CSS로는 웹을 디자인하며, 자바스크립트로는 웹의 동작을 구현함.
특별한 준비나 컴파일 없이 보통의 문자형태로 작성할 수 있고, 실행도 할 수 있음
* 자바스크립트의 특징
- 자바스크립트는 객체 기반의 스크립트 언어
- 자바스크립트는 동적이며, 타입(데이터)을 명시할 필요가 없는 인터프리터 언어
- 자바스크립트는 객체 지향형 프로그래밍과 함수형 프로그래밍을 모두 표현 할 수 있음
* 자바스크립트를 사용하여 웹 프로그래밍에서 할 수 있는 일
- HTML 의 내용을 변경 할 수 있음
- HTML 속성을 변경 할 수 있음
- HTML 스타일을 변경 할 수 있음
* 자바스크립트 문법
- 실행문은 세미콜론 (;)으로 구분 (한 행에 한 문장씩 작성할 경우 세미콜론 생략 가능)
- 자바스크립트는 대소문자를 구분함
- 변수나 함수의 이름, 예약어 등을 작성하거나 사용할 때에는 대소문자를 정확히 구분해서 사용
사용예)
var javascript = 10;
var javaScript = 20; // javascript와 javaScript는 서로 다른 변수로 인식
var Script = 30; // 변수선언은 var키워드로 사용 할 수 있으므로 var는 동작안함
* 자바언어와 자바스크립트 특징 비교 *
| 특징 | 자바 언어 | 자바스크립트 |
| 언어 종류 | 소스파일을 컴파일하여 실행하는 언어 | 브라우저가 소스 코드를 직접 해석하여 실행하는 인터프리터 언어 |
| 실행 방식 | 자바 가상 머신 위에서 실행 | 브라우저 위에서 실행 |
| 작성 위치 | 별도의 소스 파일에 작성 | HTML 파일 안에 삽입 가능 |
| 변수 선언 | 변수의 타입을 반드시 선언 해야함 | 변수의 타입을 선언하지 않아도 사용 가능 |
식별자는 변수나 함수의 이름을 작성할 때 사용하는 이름을 의미함
자바스크립트에서 식별자는 영문자(대소문자), 숫자, 언더바(_), $만 사용할 수 있음.
(숫자와 식별자를 구별하기 위해 숫자로 시작할 수 없음)
* 식별자 작성 방식 *
- Camel Case 방식
식별자가 여러 단어로 이루어질 경우 첫번 째 단어는 모두 소문자로 , 그 다음 단어부터는 첫 문자만 대문자로 작성하는 방식
- Underscore Case 방식 (자바스크립트에서 많이 사용)
단어들을 소문자로만 작성하고, 단어들은 언더바(_)로 연결하는 방식
사용예)
var firstVar = 10; //Camel Case 방식
Function my_first_func //Underscore Case 방식
{
var firstLocalVar = 20; //Camel Case 방식
}
cf) 자바스크립트에서 하이픈(-)은 뺄셈을 위해 예약된 키우드로 식별자를 작성 할때는 사용할 수 없음
* 키워드 - 미리 예약된 단어 즉 예약어라고 하여, 프로그램 내에서 식별자로 사용할 수 없음
* 주석 -웹 브라우저의 동작에 전형 영향을 미치지 않음 / 문법 - 1.한줄주석 : //주석문 | 2. 여러줄주석 : /* 주석문 */
* 자바스크립트 출력
- window.alert() 메서드
- HTML DOM요소를 이용한 innerHTML 프로퍼티
- document.write() 메서드
- console.log() 메서드 (보통 디버깅용)
- window.alert() 메서드 (가장 많이 사용) - 브라우저와는 별도의 대화 상자를 띄워 사용자에게 데이터를 전달함
ex)
<script>
function alertDialogBox() { alert("확인을 누를때까지 다른 작업을 할 수 없어요!");
</script>
cf) window 객체의 모든 메서드나 프로퍼티를 사용할 때는 window 라는 접수사를 생략할 수 있음
- document.write()메소드
document.write()메소드는 웹 페이지가 로딩될 때 실행되면, 웹 페이지에 가장 먼저 데이터를 출력함.
document.write()메소드는 대부분 테스트나 디버깅을 위해 사용됨
예)
<button onclick="document.write(4*5)">
-> //document.write 버튼을 누르면 20값이나오고 그 전의 body 는 날아감. (JAVASCRIPT 1208_2)
// 자바스크립트 html 는 head 실행 후 body 실행
- HTML DOM요소를 이용한 innerHTML 프로퍼티
document 객체의 getElementById()나 getElementsByTagName()등의 메서드를 사용하여 HTML요소를 선택함.
innerHTML 프로퍼티를 이용하면 선택된 HTML요소의 내용(content)이나 속성 (attribute)값을 손쉽게 변경할 수 있음.

버튼을 눌러보세요 -> alert창 뜸
버튼을 눌러보세요. -> document창 뜨고 그 전 body는 날아감
* 자바 스크립트 적용
HTML문서에 자바스크립트 코드를 적용하는 방법
1. 내부 자바스크립트 코드로 적용
2. 외부 자바스크립트 파일로 적용
- 내부 자바스크립트 코드 : (헤드 바디 모두 올 수 있음)
자바스크릷트 코드는 <script>태그를 사용하여 HTML문서안에 삽입할 수 있음
문법 :
<script>
document.getElementById("text").~~~
</script>
- 외부 자바스크립트 파일 : (헤드에 와야함)
자바스크립트 코드는 HTML문서의 내부뿐만 아니라 외부 파일로 생성하여 삽입 할 수 있음
외부에 작성된 자바스크립트 파일은 .js확장자를 사용하여 저장함.
자바스크립트 파일(.js)을 적용하고 싶은 모든 웹 페이지에 <script>태그를 사용해 외부 자바스크립트 파일을 포함
** 예제1) 1208_4 <head>태그에 코드삽입 **

타입(data type)이란 프로그램에서 다룰 수 있는 값의 종류를 의미함
기본타입은 원시 타입과 객체 타입으로 구분함
- 원시타입 : 숫자(number), 문자열(string), 불리안(boolean), 심볼(symbol), undefined / 심복타입은 익스플로러에서 지원하지 않음.
- 객체타입 : 객체(object)
예제) 자바스크립트의 데이터 타입은 마지막에 넣은 변수의 타입을 따라 결정된다.
var num = 10;
var myName = "홍길동";
var str;
- 숫자(number)
정수와 실수를 따로 구분하지 않고, 모든 수를 실수 하나로만 표현함.
- 문자열(string)
문자열은 큰따옴표(" ")나 작은 따옴표(' ')로 둘러싸인 문자의 집합을 의미
예)
var firstStr = "이것도 문자열입니다.";
var secondStr = '이것도 문자열입니다';
var thirdStr = "나의 이름은 '홍길동'이야"; //따옴표속에 같은 종류의 따옴표 올 수 없다 (다른종류의 따옴표 사용해야함)
var fourthStr = '나의 이름은 "홍길동"이야';
- 불리언(boolean)
참(true)와 거짓(false)을 표현함.
var fisrtNum = 10;
var secondNum = 11;
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = (fNum == sNum); //false
- typeof 연산자
피연산자의 타입을 반환하는 피연산자가 단 하나 뿐인 연산자이다.
typeof 10; /number 타입
typeof "문자열"; //sting 타입
typeof true; //boolean 타입
typeof undefined; //undefined 타입
typeof null; //object 타입
cf) 변수선언을 했지만 초기값세팅이 되지 않은 경우 -> undefined
- null과 undefined
null은 object타입이며, 아직 값이 정해지지 않은 것을 의미함
undifined란 null과는 달리 타입이 정해지지 않은 것을 의미함
undifined는 초기화되지 않은 변수나 존재하지 않은 값에 접근할때 반환됨
예)
var num; //초기화하지 않았으므로 undefined값을 반환함
var str; //object 타입의 null값
typeof secondNum; //정의되지 않은 변수에 접근하면 undefined 값을 반환함.
- 객체 (object)
기본타입은 객체이며, 객체란 실생활에서 우리가 인식할 수 있는 사물을 의미
객체는여러 프로퍼티나 메서드를 같은 이름을 묶어놓은 일종의 집합체
예)
var dog = {name:"해피", age:3}; //객체생성
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML = "강아지의 이름은" + dog.name + "이고, 나이는" + dog.age + "살 입니다.";
- 타입변환(type conversion)
자바스크립트는 타입검사가 매우 유연한 언어로 변수의 차입이 정해져 있지 않으며, 같은 변수에 다른 타입의 값을 다시 대입할 수도 있음.
예)
var num = 20; //Number 타입의 20
num = "이십" //String타입의 "이십"
var num; //한 변수에 여러번 대입할 수 는 있지만, 변수의 재선언은 할 수 없습니다. + 재선언문은 무시됩니다.
- 묵시적 타입 변환(implicit type conversion)
자바스크립트는 특정 타입의 값을 기대하는 곳에 다른 타입의 값이 오면, 자동으로 타입을 변환하여 사용. 즉, 문자열 값이 와야 할 곳에 숫자가 오더라도 알아서 숫자를 문자열로 변환.
예)
10 + "문자열"; // 문자열 연결을 위해 숫자 10이 문자열로 변환됨.
"3" * "5"; // 곱셈 연산을 위해 두 문자열이 모두 숫자로 변환됨.
1 - "문자열"; // NaN : Not a Number으로 정의되지 않는 값이나 표현 할 수 없는 값
// NaN은 number타입의 값으로0으로 나누거나, 숫자로 변환 할 수 없는 피연산자로 산술 연산을 시도하는 경우에 반환 되는 읽기 전용
- 명시적 타입 변환(explicit type conversion)
자바스크립트는 묵시적 타입 변환을 많이 사용하지만, 명시적으로 타입변환 방법 제공
명시적 타입 변환을위해 자바 스크립트가 제공하는 전역함수
.Number() .String() .Boolean() .Object() .parseInt() .parseFloat()
예)
Number("10"); // 숫자 10
String(true); // 문자열 "true"
Boolean(0); // 불리언 false
Object(3); //new Number(3)와 동일한 결과로 숫자3
- 불리언 값을 문자열로 변환
String()함수와 toString 메서드를 사용할 수 있음.
예제)
String(true); //문자열"true"
false.toString(); //문자열"false"
- 날짜를 문자열이나 숫자로 변환
String()함수와 toString()메서드를 사용, 날짜 (Date) 객체는 문자열과 숫자로 모두 변환 할 수 있는 유일한 타입
| 메소드 | 설 명 |
| getDate () | 날짜 중 일자를 숫자로 반환함.(1~31) |
| getDay () | 날짜 중 요일을 숫자로 반환함. ( 0(일요일)~6(토요일) ) |
| getFullYear () | 날짜 중 연도를 4자리 숫자로 반환함. (yyyy년) |
| getMonth () | 날짜 중 월을 숫자로 반환함. ( 1월(0) ~ 12월(11) ) |
| getTime () | 1970년 1월 1일부터 현재까지의 시간을 밀리초(millisecond) 단위의 숫자로 반환함. |
| getHours () | 시간 중 시를 숫자로 반환함. (0~23) |
| getMinutes () | 시간 중 분을 숫자로 반환함. (0~59) |
| getSeconds () | 시간 중 초를 숫자로 반환함. (0~59) |
| getMilliseconds () | 시간 중 초를 밀리초 (millisecond) 단위릐 숫자로 반환함. (0~999) |
- 문자열을 숫자로 변환
Number()함수를 사용함, 문자열을 숫자로 변환해 주는 두개의 전역 함수를 별도로 제공
| 함 수 | 설 명 |
| parseInt() | 문자여을 파싱하여 특정 진법의 정수를 반환함. |
| parseFloat() | 문자열을 파싱하여 부동 소수점 수를 반환함. |
** 변수 **
- 변수의 선언과 초기화
데이터(data)를 저장할 수 있는 메모리 공간을 의미하여, 그 값이 변경될 수 있음.
var키워드를 사용하여 변수를 선언함.
선언되지 않은 변수를 사용하려고 하거나 접근하려고 하면 오류가 발생.
단, 선언되지 않은 변수를 초기화할 경우에는 자동으로 선언을 먼저 한 후 초기화를 진행.
선언된 변수는 나중에 초기화 할 수도 있고, 선언과 동시에 초기화 할 수 도 있습니다.
쉼표(,) 연산자를 이용하여 여러 변수를 동시에 선언하거나 초기화 할 수 있음.
예제)
var month // month라는 이름의 변수 선언
date = 25; //date라는 이름의 변수를 묵시적으로 선언
var month, date; //여러 변수를 한번에 선언
var hours =7, minutes = 15; //여러변수를 선언과 동시에 초기화
month = 10, date = 5;
- 변수의 타입과 초기값
변수는 타입이 정해져 있지 않으며, 같은 변수에 다른 타입의 값을 다시 대입할 수 도 있음.
한 변수에 다른 타입의 값을 여러 번 대입할 수는 있지만, 한 번 선언된 변수를 재선언 할 수는 없음.
- 변수의 이름
변수의 이름은 식별자이며, 변수의이름
영문자(대소문자), 숫자, 언더바(_), $만 사용할 수 있음.
숫자와의 구분을 빠르게 하기 위해 숫자로는 시작할 수 없음.
대소문자를 구분하며, 자바스크립트 언어에서 예약된 키워드는 이름으로 사용할 수 없음.
** 연산자 **
| 산술연산자 | +, -, *, /, % 연산자 우선순위 1순위는 소괄호 |
| 대입연산자 | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %= |
| 증감연산자 | ++, -- (전치, 후치) |
| 비교연산자 | >, >=, <, <= == (값이 같으면 참을 반환), ===(값이 같고 타입이 같으면 참을 반환), != (값이 같지 않으면 참), !== (값이 같지 않거나, 타입이 다르면 참) |
| 논리연산자 | &&, ||, ! |
| 기타연산자 | 문자결합, 삼항, 쉼표, delete, typeof, instanceof, void연산자 - 문자결합 1) 피연산자가 둘 다 숫자이면, 산술 연산인 덧셈을 수행 2) 피연산자가 하나라도 문자열이면, 문자열 결합을 수행 - 삼항 : 표현식 ? 반환값1 : 반환값2 - 쉼표 : 여러 변수를 동시에 갱신할 경우 - delete : 객체의 프로퍼티 또는 배열의 요소등을 삭제함(삭제 성공시 true, 실패시 false) 배열의 요소 삭제시 - 배열의 요소만 삭제하고, 배열의 크기 유지(크기 줄이지 않는다.) |
typeof - 피연산자의 타입을 반환함
instanceof - 피연산자의 객체가 특정 객체의 인스턴스인지 아닌지를 확인함.
void - 어떤 타입의 값이 오던지 상관없이 언제나 undefined 값만을 반환.
** 예제) 1108_5 숫자 타입 **


** 예제) 1108_6 **

** 예제) 1108_7 **


링크를 동작하지 않습니다. -> 선택시 아무 효과 X
링크를 동작하지 않지만 HTML문서 배경은 변경됩니다. -> 선택시 배경 변경
소스 ↓
| 12/14 수업 (31일차) (0) | 2023.12.14 |
|---|---|
| 12/13 수업 (30일차) _ for in 문 / label 문 / 배열 / 함 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
| 12/12 수업 (29일차) (0) | 2023.12.12 |
| 12/11 수업 (28일차) _ (1) | 2023.12.11 |
** html 연습문제 1208 (table태그 / form태그 / imput태그 / textarea / select / div) **

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>연습문제</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="join.html" name="form1" method="get">
<table align="center" bordercolor="#CCDDFF" border="1" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<th colspan="2" bgcolor="#CCDDFF">회원 기본 정보</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center" bgcolor="#EEEEEE">아이디:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="my_id" width="15" /><span>4~12자의 영문 대소문자와 숫자로만 입력</span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">비밀번호:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_password" width="15" /><span>4~12자의 영문 대소문자와 숫자로만 입력</span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">비민번호확인:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_password_confirm" width="15" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">메일주소:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_mail" width="20" /><span>예) id@domain.com</span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">이름:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_name" width="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th colspan="2" bgcolor="#CCDDFF">개인 신상 정보</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">주민등록번호:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_address" width="20" /><span>예) 134561234567</span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">생일:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="my_year" size="4" maxlength="4">년
<select name="my_month">
<option value="1" selected>1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
<option value="4">4</option>
<option value="5">5</option>
<option value="6">6</option>
<option value="7">7</option>
<option value="8">8</option>
<option value="9">9</option>
<option value="10">10</option>
<option value="11">11</option>
<option value="12">12</option>
</select>월
<select name="my_day">
<option value="1" selected>1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
<option value="4">4</option>
<option value="5">5</option>
<option value="6">6</option>
<option value="7">7</option>
<option value="8">8</option>
<option value="9">9</option>
<option value="10">10</option>
<option value="11">11</option>
<option value="12">12</option>
<option value="13">13</option>
<option value="14">14</option>
<option value="15">15</option>
<option value="16">16</option>
<option value="17">17</option>
<option value="18">18</option>
<option value="19">19</option>
<option value="20">10</option>
<option value="21">21</option>
<option value="22">22</option>
<option value="23">23</option>
<option value="24">24</option>
<option value="25">25</option>
<option value="26">26</option>
<option value="27">27</option>
<option value="28">28</option>
<option value="29">29</option>
<option value="30">30</option>
<option value="31">31</option>
</select>일
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">관심분야:</th>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="My_hobby" value="conputer" />컴퓨터
<input type="checkbox" name="My_hobby" value="internet" />인터넷
<input type="checkbox" name="My_hobby" value="trip" />여행
<input type="checkbox" name="My_hobby" value="movie" />영화감상
<input type="checkbox" name="My_hobby" value="music" />음악감상
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#EEEEEE">자기소개:</th>
<td>
<textarea name="my_intro" cols="50" rows="5" style="resize:none"></textarea>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br />
<div align="center">
<input type="submit" value="회원 가입" />
<input type="reset" value="다시 입력" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>** 예제 1207_15 (평행이동 변환하기) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>평행 이동 변환하기</title>
<style>
/*
div{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px dotted black;
background-color: yellow;
}
div#box2{
transform:translate(100px, 50px);
}
*/
/* 2번 회전 변환
div{width:100px; height:100px; border:1px dotted black;
background-color: lightgreen; margin: 30px;}
div#box1{transform:rotate(45deg);}
div#box2{transform:rotate(-90deg)}
*/
/* 3변 기울기 변환 */
div{width:100px; height:100px; border:1px dotted black;
background-color: lightgreen; margin: 50px;}
div#box1{transform:skewX(50deg);}
div#box2{transform:skewY(-30deg);}
div#box3{transform:skew(20deg, 10deg);}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
<div id="box1">
박스1
</div>
<div id="box2">
박스2
</div>
-->
<!--2번 회전 변환
<div>
기본박스(0deg)
</div>
<div id="box1">
박스 1(45deg)
</div>
<div id="box2">
박스 2(90deg)
</div>
-->
<!--3번 기울기 변환-->
<div>
기본박스(0deg)
</div>
<div id="box1">
박스1
</div>
<div id="box2">
박스2
</div>
<div id="box3">
박스3
</div>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1208_2 (애니메이션 속성) **

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>애니메이션 속성</title>
<style>
/* 1번 무한반복 좌우로 이동하는 박스
@keyframes 애니메이션 이름 지정
div{
width:100px; height:100px;
background: red;
position:relative;
animation:boxmove 5s linear infinite alternate;
}
@keyframes boxmove{
from{left: 0px;}
to{left:300px;}
}
*/
/* 2번 웹문서가 로드된 후 일정 시간 후에 애니메이션 시작 */
/* 3번 애니메이션 진행방향 설정
div{
width:100px; height:50px;
background: red;
position: relative;
animation: boxmove 5s linear infinite; //alternate;
}
#box1 {animation-delay: 3s; animation-direction: reverse;}
#box2 {animation-delay: 5s; animation-direction: alternate-reverse;}
@keyframes boxmove{
from{left: 0px;}
to{left:300px;}
}
*/
/* 4번 애니메이션 반복횟수 설정(iteration, count 속성)
div{
width:100px; height:50px;
background: red;
position: relative;
animation: boxmove 5s;
}
#box1 {animation-delay: 3s; animation-direction: reverse;
animation-iteration-count: 2;}
#box2 {animation-delay: 5s; animation-direction: alternate-reverse;
animation-iteration-count: 5;}
@keyframes boxmove{
from{left: 0px;}
to{left:300px;}
}
*/
/* 5번 애니메이션 타이밍 설정 */
div{
width:100px; height:50px;
background: red;
position: relative;
animation: boxmove 5s alternate;
}
#box1 {animation-delay: 1s;
animation-iteration-count: 3;
animation-timing-function: ease;}
#box2 {animation-delay: 2s;
animation-iteration-count: 3;
animation-timing-function: linear;}
#box3 {animation-delay: 3s;
animation-iteration-count: 3;
animation-timing-function: ease-out;}
@keyframes boxmove{
from{left: 0px;}
to{left:300px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 1번 무한반복 좌우로 이동하는 박스
<div>애니메이션 박스</div>
<p><strong>참고 : </strong>잘 이동하는지 확인합니다.</p>
//-->
<!-- 2번 웹문서가 로드된 후 일정 시간 후에 애니메이션 시작 3번//
<div id="box1">애니메이션 박스1</div>
<div id="box2">애니메이션 박스2</div>
<p><strong>참고 : </strong>잘 이동하는지 확인합니다.</p>
-->
<!-- 4번 애니메이션 반복횟수 설정(iteration, count 속성)
<div id="box1">애니메이션 박스1</div>
<div id="box2">애니메이션 박스2</div>
<p><strong>참고 : </strong>잘 이동하는지 확인합니다.</p>
-->
<!-- 5번 애니메이션 타이밍 설정-->
<div id="box1">애니메이션 박스1</div>
<div id="box2">애니메이션 박스2</div>
<div id="box3">애니메이션 박스3</div>
<p><strong>참고 : </strong>잘 이동하는지 확인합니다.</p>
</body>
</html>
| 12/07 수업 (25일차) _ 선택자 / (2) | 2023.12.07 |
|---|---|
| 12/06 수업 (24일차) _ Table 태그 속성 / Img 태그 / Input태그 / Form 태그 / 레이아웃 구성 태그 - div, span / CSS란? (1) | 2023.12.06 |
| 12/04 수업 (23일차) _ HTML설치 / Web이란? / HTML태그 / CSS적용 List 태그 / Table태그 (2) | 2023.12.04 |
- CSS의 효과가 적용될 태그를 지정
예) h1 {color:blue;font:12px;}
* Id 선택자
- id속성은 전체 문서에서 하나의 태그를 식별하기 위해서만 사용됨 / 우선순위가 가장 높다.
- css선택자에서는 #을 사용해서 id임을 표시
<style type="text/css">
#memo{color:red;}
</sytle>
<div id="memo">
red
</div>→ id값이 memo인 태그의 컨텐츠를 빨간색으로 표시하도록 함.
* Class 선택자 *
- class속성은 일련의 태그를 그룹핑해서 하나처럼 제어하기 위해서 사용
- class 속성에는 공백으로 구분된 여러개의 class가 표시될 수 있음
- css선택자에서는 '.'을 사용해서 class임을 표시
- 예) </style>
<div class="red">red</div>
<p class >
.red{ }
* type 선택자 *
- 특정 태그명을 가진 엘리먼트 전체를 제어하기 위해서 사용
- css선택자에서는 태그의 이름을 사용함
* 하위 선택자 *
- 특정 엘리먼트의 하위에 나오는 엘리면트를 선택하는데 사용
- 부모가 먼저 나오고 자식이 나중에 나옴
- 공백을 통해서 부모와 자식을 구분
* 하나의 CSS선언을 여러 개의 선택 자에 적용 *
- 하나의 css선언을 여러 엘리먼트 셀렉터에 적용하고 싶을 때 사용 / 선택자와 선택자를 ,(콤마)로 구분
- 예제)
- h1과 #link 선택자 사이에 ,(콤마)를 두어 글씨의 색을 붉은색으로 지정
* 스타일링 링크 꾸미기 *
- 링크는 4가지의 상태를 가지고 있고, 각 상태에 따라소 시각적으로 다른모양을 가질 수 있음
| 방문하지 않은 링크 | a:link{} |
| 방문했던 링크 | a:visited{} |
| 마우스르 오버한 링크 | a:hover{} <!--a:link와 a:visited 뒤에 와야함--> |
| 마우스를 누른 상태의 링크 | a:active{} <!--a:hover뒤에 와야함--> |
* 두개의 클래스 적용 *
** 예제 1207.html (id, class선택자) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>id, class선택자</title>
<!--overflow:hidden (내용이 넘치면 자름. 자른 부분은 안보임.)
float:left (정렬-왼쪽)-->
<style>
#memo{
color:red;
font-size:30px;
}
#memo2{
color:orange;
font-size:50px;
}
#header{
width:800px;
margin:0 auto;
background:red;
}
#wrap{
width:800px;
margin:0 auto;
overflow:hidden;
}
#aside{
width:200px;
height:100px;
float:left;
background:blue;
overflow:scroll;
overflow:hidden;
}
#content{
width:600;
float:left;
background-color:green;
}
.red{
color:red;
}
.intro{
color:blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
<h1>id 선택자</h1>
<div id="memo">
red
</div>
<div id="memo2">
red2
</div>
-->
<!--id가 순서대로 적용
<div id="header">
<h1>#header 태그 적용</h1>
</div>
<div id="wrap">
<div id="aside">
<h1>#aside 태그 적용#aside 태그 적용#aside 태그 적용#aside 태그 적용#aside 태그 적용</h1>
</div>
<div id="content">
<h1>#contect 태그 적용</h1>
</div>
</div>
-->
<!--클래스 선택자-->
<div class="red">red</div>
<p class="red intro">Hello World</p>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_2.html (하위 선택자) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>하위 선택자</title>
<style>
#navigation li a{
color:orange;
}
h1, #link{
color:red;
}
a:link{
color:red;
}
a:visited{
color:aqua;
}
a:hover{
color:greenyellow;
}
a:active{
color:orange;
}
.select{
color:pink;
font-size:30px;
}
.header{background-color:blue;color:orange}
.item{color:yellow;}
li.select2{
color:brown;
}
input[type="text"]{
background:orange;
}
h3, #link{
color:blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--하나의 CSS선언을 여러 개의 선택 자에 적용 시작-->
<div id="navigation">
<ul>
<li>홈</li>
<li><a href="http://www.daum.net">제품소개</a></li>
<li>고객센터</li>
</ul>
</div>
<ul>
<li>홈</li>
<li><a href="http://www.sist.co.kr">제품소개</a></li>
<li>고객센터</li>
</ul>
<h1>하나의 CSS선언을 여러개의 선택자에 적용</h1>
<a id="link" href="http://www.daun.net">잘되나요?</a>
<!--하나의 CSS선언을 여러 개의 선택 자에 적용 끝-->
<!--스타일링 링크 꾸미기 시작-->
<p>
<a href="https://www.jejusi.go.kr">링크 상태 모두 체크</a>
</p>
<!--스타일링 링크 꾸미기 끝-->
<br /><br />
<ul>
<li class="select">사과</li>
<li>바나나</li>
<li class="select">오렌지</li>
<li>키위</li>
</ul>
<!--header/item 두개의 클래스 적용해보자-->
<p><h1 class="header item">즐거운 하루 되세요</h1></p>
<!--태그 하위 클래스 선택-->
<ul>
<li class="select2">사과</li>
<li>바나나</li>
<li>오렌지</li>
<li>키위</li>
</ul>
<h3 class="select2">나는 하위가 아닙니다.</h3>
<br />
<input type="text" name="name1" size="20" />
<input type="password" name="name2" size="20" />
<br /><br />
<a id="link" href="http://www.daun.net">잘 됩니까.....</a>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_3.html (스타일링 테이블 꾸미기 _ css외부파일방식 적용) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>스타일링 테이블(표) 꾸미기 (css외부파일방식 적용)</title>
<link type="text/css" href="./style/style.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>순서</th>
<th>과목명</th>
<th>토픽수</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>웹서비스 만들기</td>
<td>12</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>HTML수업</td>
<td>13</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td>
<td>HTML수업</td>
<td>9</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>4</td>
<td>CSS수업</td>
<td>15</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
table{
border:1px solid gray;
border-collapse:collapse;
}
th{
background-color: #d0d0d0;
font-weight:bold;
}
th, td{
border:1px solid gray;
padding:5px;
}

** iframe **
- 웹페이지 안에서 다른 웹페이지를 표시하고자 할 때 사용됨.
** 예제) 1207_4,5 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>iframe 테스트</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>첫번째 iframe 페이지</h1>
<p>첫번째 나눈 단락</p>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>iframe 적용</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>iframe 적용</h1>
<iframe src="1207_4.html" width="300" height="150"></iframe>
<h3>iframe 적용 끝</h3>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_6.html (textarea) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<!--textarea 안에있는 것은 텍스트로 인식-->
<!--가끔 <>(꺽쇠)를 태그로 인식할때는 < >로 써준다.-->
<textarea rows="5" cols="50">
<html>
<body>
<h1>This is a header.</h1>
</body>
</html>
</textarea>
<br />
<iframe src="" name="iframe1"></iframe>
<p><a href="http://www.daum.net" target="iframe1">여기를 클릭하면 어디에 보일까요??</a></p>
<p><b>참고 : </b>링크를 클릭하면 iframe안에서 홈페이지가 열립니다.</p>
</body>
</html>

** 예제 1207_7 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/*body{
width:500;
margin:10px auto;
}*/
#middle{overflow:hidden;}
#left{
float:left;width:150px;background-color:orange;
}
#right{
float:right;width:350;background:brown;
}
#top{
width:150;background:green;
}
#bottom{
background:violet;
}
h1, p {width:300px;}
.ell{
white-space:nowrap;
overflow:hidden;
text-overflow:ellipsis;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="top">"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표</div>
<div id="middle">구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
<div id="left"> 1.0은 규모에 맞게 세 종류로 최적화했다. ▲방대하고 복잡한 작업에 적합한 가장 유용하고 규모가 큰 모델 '제미나이 울트라(Gemini Ultra)' ▲다양한 작업에서 확장하기에 가장 적합한 모델 '제미나이 프로(Gemini Pro)' ▲ 온디바이스(on-device) 작업에 가장 효율적인 모델 '제미나이 나노(Gemini Nano)'다.
</div>
<div id="right"> 따르면 특히 제미나이 울트라의 성능은 대형언어모델(LLM) 연구개발 평가에서 주로 사용되는 32개의 벤치마크 중 30개에서 기존의 최신 기술을 뛰어넘는 결과를 보여준 것으로 전해졌다.
</div>
</div>
<div id="bottom"> 물리학, 역사, 법률, 의학, 윤리 등 총 57개의 주제를 복합적으로 활용해 세계 지식과 문제 해결 능력을 평가하는 MMLU(대규모 멀티태스크 언어 이해) 테스트에서 90.04%의 점수를 기록한 제미나이 울트라는 전문가 인력보다 높은 결과를 기록한 최초의 모델이라는 설명이다.또한 제미나이 울트라는 고도의 추론 능력이 요구되는 다양한 영역에 걸친 멀티모달 작업으로 구성된 새로운 MMMU 벤치마크에서 59.4%의 최상위 점수를 획득했다.
</div>
<!--
<h1 class="ell">"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</h1>
<p class="ell"> 규모에 맞게 세 종류로 최적화했다. ▲방대하고 복잡한 작업에 적합한 가장 유용하고 규모가 큰 모델 '제미나이 울트라(Gemini Ultra)'
▲다양한 작업에서 확장하기에 가장 적합한 모델 '제미나이 프로(Gemini Pro)' ▲ 온디바이스(on-device) 작업에 가장 효율적인 모델 '제미나이 나노(Gemini Nano)'다.
따르면 특히 제미나이 울트라의 성능은 대형언어모델(LLM) 연구개발 평가에서 주로 사용되는 32개의 벤치마크 중 30개에서
기존의 최신 기술을 뛰어넘는 결과를 보여준 것으로 전해졌다.
물리학, 역사, 법률, 의학, 윤리 등 총 57개의 주제를 복합적으로 활용해 세계 지식과 문제 해결 능력을 평가하는 MMLU(대규모 멀티태스크 언어 이해) 테스트에서
90.04%의 점수를 기록한 제미나이 울트라는 전문가 인력보다 높은 결과를 기록한 최초의 모델이라는 설명이다.
또한 제미나이 울트라는 고도의 추론 능력이 요구되는 다양한 영역에 걸친 멀티모달 작업으로 구성된 새로운 MMMU 벤치마크에서 59.4%의 최상위 점수를 획득했다.
</p>
-->
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_8 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>html5 책갈피 기능</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<center>
<h2>< 책갈피 기능 ></h2>
</center>
</header>
<section>
<article>
<p>
<a href="#user">[이름]</a>
<a href="#addr">[주소]</a>
<a href="#tel">[전화번호]</a>
<a href="#foot">[참고]</a>
</p>
</article>
</section>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p><a name="user">홍길동</a></p>
<a href="#top">[TOP]</a>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<P><a id="addr" name="addr">서울 마포구 월드컵</a></P>
<a href="#top">[TOP]</a>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p><a id="tel">02-123-4567</a></p>
<a href="#top">[TOP]</a>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p id="foot">기타</p>
<a href="#top">[TOP]</a>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
<p>"각 분야 전문가보다 해박"…구글, 멀티모달 AI 모델 '제미나이' 발표
구글은 제미나이는 구글 딥마인드와 구글 리서치 등 구글 조직 전반에 걸친 대규모 협업의 결과"라며 "구글 역사상 가장 큰 과학적 및 기술적 노력 중 하나"라고 소개했다.
</p>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_9 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>html5 input type</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form1" action="1207_8.html" method="get">
date : <input type="date" name="name1" /><br />
datetime-local : <input type="datetime-local" name="name2" /><br />
month : <input type="month" name="name3" /><br />
time : <input type="time" name="name4" /><br />
week : <input type="week" name="name5" /><br />
color : <input type="color" name="name6" /><br />
e-mail : <input type="email" name="name7" pattern=".@gmail.com"
placeholder="example@gamil.com" required/><br />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
</html>


** 예제 1207_10 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--optgroup label은 타이틀의 역할-->
<h3>전공 분야를 선택하세요.</h3>
<form name="form1" action="1207.html" method="get">
<label>그룹별 선택항목을 제공
<select name="major">
<optgroup label="computer">
<option value="software">SoftWare</option>
<option value="robot">Robot</option>
<option value="system">System</option>
</optgroup>
<optgroup label="language">
<option value="korea" selected>Korea</option>
<option value="english">English</option>
<option value="china">China</option>
<option value="germany">Germany</option>
</optgroup>
<optgroup label="business">
<option value="service">Service</option>
<option value="education">Education</option>
<option value="communication">Communication</option>
<option value="marketing">Marketing</option>
</optgroup>
</select>
<br />
<input type="submit" value="선택">
<input type="reset" value="다시선택">
</label>
</form>
<br /><br /><br />
<h3>선택사항을 직접 입력하세요.</h3>
<form name="form2" action="1207.html" method="get">
<label>전공분야를 입력하세요.
<input type="text" name="major" list="majorlist">
<datalist id="majorlist">
<option value="SoftWare">소프트웨어</option>
<option value="Robot">로봇</option>
<option value="System">시스템</option>
<option value="Service">서비스</option>
<option value="Education">교육</option>
</datalist>
<br />
<input type="submit" value="완료">
<input type="reset" value="다시작성">
</label>
</form>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_11 **

** 문제 1207_12 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{ margin:0; padding: 0;}
body{background-color: #F5F6F7;}
div{margin-top: 60px;margin-left: 38%;}
ul,li{ list-style: none;}
li{margin-bottom: 20px; text-align: left;}
.box{width: 450px; height: 50px; border: 1px solid #666; padding: 10px;}
.pbox{width: 120px; height: 50px; border: 1px solid #666; padding: 10px;}
.necessary{font-size: small; color:red;}
button{background:#00C850; color:white; width: 450px; border: 1px solid #666; height:50px; font-size: x-large; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li><span>아이디<span><br />
<input type="text" name="name1" placeholder="아이디를 입력하세요." class="box"/>
</li>
<li><span>패스워드</span><br />
<input type="password" name="name2" placeholder="패스워드를 입력하세요." class="box" /><br />
<span class="necessary">필수 정보입니다.</span>
</li>
<li><span>패스워드 확인</span><br />
<input type="password" name="name3" placeholder="패스워드를 다시 입력하세요." class="box" /><br />
<span class="necessary">필수 정보입니다.</span>
</li>
<li><span>생년월일</span><br />
<input type="date" name="name4" placeholder="연도-월-일" class="box" /><br />
<span class="necessary">태어난 년도 4자리를 정확하게 입력하세요.</span>
</li>
<li>전화번호<br />
<input class="pbox" type="text" name="name5" maxlength="4" />-
<input class="pbox" type="text" name="name6" maxlength="4" />-
<input class="pbox" type="text" name="name7" maxlength="4" /><br />
<span class="necessary">필수 정보입니다.</span>
<li>
<li><span>성별</span><br />
<input type="radio" name="name8" value="남자" />남자
<input type="radio" name="name8" value="여자" />여자
</li>
<li><span>취미생활</span><br />
<input type="checkbox" name="name9" value="독서" />독서
<input type="checkbox" name="name9" value="산책" />산책
<input type="checkbox" name="name9" value="TV시청" />TV시청
</li>
<li><button>가입하기</button></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_13 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p{
background-color:yellow; color:red;
font-weight:bold; font-size:16px;
}
p.pad{
color:purple;
padding:20px;
}
p.mar{
color:green;
margin:30px;
}
p.mp{
color:blue;
padding:5%;
margin:5%;
}
body{font-family:consolas}
h3.none{border-style:none;}
h3.hidden{border-style:hidden}
h3.dootted{border-style:dotted}
h3.dashed{border-style:dashed}
h3.solid{border-style:solid;}
h3.double{border-style:double;}
h3.groove{border-style:groove;}
h3.ridge{border-style:ridge;}
h3.inset{border-style:inset;}
h3.outset{border-style:outset;}
h3.mix{border-style:dotted dashed solid double;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--padding : 박스의 안쪽 여백, margin : 박스의 바깥쪽 여백
<p>박스의 안쪽 여백과 바깥쪽 여백 지정</p>
<p class="pad">(1) 안쪽 여백 지정 - padding 20px</p>
<p class="mar">(2) 바깥쪽 여백 지정 - margin 30px</p>
<p class="mp">(3) 안쪽, 바깥쪽 여백 지정 - padding 5% margin 5%x</p>
-->
<h1>border-style 예제</h1>
<h3 class="none">no border</h3>
<h3 class="hidden">hidden border</h3>
<h3 class="dotted">dotted border</h3>
<h3 class="dashed">dashed border</h3>
<h3 class="solid">solid border</h3>
<h3 class="double">double border</h3>
<h3 class="groove">groove border</h3>
<h3 class="ridge">ridge border</h3>
<h3 class="inset">inset border</h3>
<h3 class="outset">outset border</h3>
<h3 class="mix">mix border</h3>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1207_14 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body{font-weight:bold; font-size:12px;}
.boxshadow1{
background-color:yellow;
border:5px solid blue;
box-shadow:10px 10px 10px teal;
}
.boxshadow2{
background-color:orange;
border:5px solid red;
box-shadow:20px 20px 20px red;
}
.boxshadow3{
background-color:silver;
border:5px solid black;
box-shadow:20px 20px 30px - 20px maroon;
}
.boxshadow4{
background-color:lime;
border:5px solid olive;
box-shadow:10px 10px 0px 10px fuchsia inset;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="boxshadow1">박스 그림자 스타일링 예제1</h1>
<h1 class="boxshadow2">박스 그림자 스타일링 예제2</h1>
<h1 class="boxshadow3">박스 그림자 스타일링 예제3</h1>
<h1 class="boxshadow4">박스 그림자 스타일링 예제4</h1>
</body>
</html>
** 문제 1207_15 **
- 열병합 (colspan) : column span 약자로, 셀(가로줄)을 합치는 개수를 지정
- 행병합 (rowspan) : 행합치기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Table 연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--열병합-->
<table border="1" width="250" height="100">
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="3"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
← 결과
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Table 연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--행병합-->
<table border="1" width="258" height="100">
<tr>
<td rowspan="3"></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
← 결과
** 실습문제2 **

실행 후 결과가 위와 같이 나오도록.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Table 연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--Table 실습문제2-->
<table border="2">
<tr>
<th>1열</th>
<th>2열</th>
<th>3열</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="2">1행 1열</td>
<td>1행 2열</td>
<td>1행 3열</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2행 2열</td>
<td>2행 3열</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">3행 1열</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>** 이미지 출력 태그 img **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>img 태그연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><img src="https://t1.kakaocdn.net/gamepub/daumgame/banner/content/gametop_content_1701251409983_36.jpg" alt="첫번째 이미지" /></p>
<p><img src="https://t1.kakaocdn.net/gamepub/top/2018/code/game_c_371.jpg" alt="두번째 이미지" /></p>
<p><img src="https://t1.kakaocdn.net/gamepub/top/2018/code/game_w_333.jpg" alt="세번째 이미지" /></p>
<p><img src="./img/game.png" alt="네번째 이미지" /></p>
</body>
</html>** 실습_개인 홈페이지 만들기1 **
아래 이미지와 같이 나오도록.

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>개인 홈페이지 만들기1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>My HomePage</h2>
<p><img src="./img/computer.jpg" width="250" height="150" alt="" />
<strong>컴퓨터 프로그래머</strong>를 꿈꾸며 열심히 공부하고 있는 KYH입니다.</p>
<h3>현재 학습하고 있는 과목</h3>
<p>
<ul>
<li>C언어</li>
<li>JAVA 언어</li>
<li>웹프로그래밍 <a href="http://www.daum.net" target="_blank">W3C사이트</a></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p><h3>이번 학기 시간표</h3></p>
<p>
<table border="1">
<caption>시간표</caption>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>월요일</th>
<th>화요일</th>
<th>수요일</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1교시</th>
<th>C언어</th>
<th>JAVA언어</th>
<th>JAVA언어</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>2교시</th>
<th>C언어</th>
<th>JAVA언어</th>
<th>JAVA언어</th>
</tr>
</table>
</p>
</body>
</html><input>태그는 사용자가 다양하게 폼 태그에 입력할 수 있는 공간을 만들어줌.
예) <input type="">
| type | 태그 모양을 다양하게 변경할 수 있음. text, radio, checkbox (0개 이상 선택가능) , password, button, hidden, submit, reset 등이 있음 cf) radio, checkbox 은 name이 같은것끼리 그룹으로 묶인다.(name은 되도록 중복되지 않게 사용한다.) <input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="cpu" />cpu 값은 value값이 넘어간다(프론트에서 서버에요청할때 맨뒤 변수 cpu에 해당하는 값) / 화면에 출력되는것은 맨 뒤의 cpu |
| name | 해당 type의 이름을 지정 |
| readonly | 태그를 읽기전용으로 지정 예) <input readonly> |
| maxlength | 해당 태그 최대 글자 수를 지정 |
| required | 해당 태그가 필수태그로 지정됨. 필수 태그를 입력하지 않고 submit버튼을 누르면 에러메시지가 브라우저에서 출력됨(HTML5추가) |
| autofocus | 웹 페이지가 로딩되자마자 이 속성을 지정한 태그로 포커스가 이동됨 (HTML5추가) |
| placeholder | 태그에 입력할 값에 대한 힌트를 줌 (HTML5추가) |
| pattern | 정규표현식을 사용하여 특정범위 내의 유효한 값을 입력받을 때 사용함 (HTML5추가) |
cf) HTML 에서는 = 앞뒤로 뜨어쓰기 하지 않는 것이 좋다.
* type
- input type="button" / input type="sublmit" / input type="reset"
<p><h1>button, submit, reset</h1></p>
<input type="reset" value="다시입력" />
- input type="image"
이미지:<input type="image" src="folwer.png">
- input type="file"
상대경로 : ./ 내폴더 밑에 | ../ 내 위에폴더 밑에
** 실습 (input type 종류) **
** select option **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>input type 종류</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><h1>imput type 종류</h1></p>
이름 : <input type="text" name="my_name" size="20" /><br>
비밀번호 : <input type="password" name="my_pwd" size="20"><br />
<input type="text" name="my_name2" size="20" value="수정불가" readonly />
<p><h1>type radio</h1></p>
아침메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<br /><br />
점심메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food2" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<br /><br />
저녁메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food3" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<p><h1>type checkbox</h1></p>
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="cpu" checked>cpu
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="memory" />memory
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="hdd" />하드디스크
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="cdrom" />cdrom
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="grapic" />그래픽카드
<p><h1>select option</h1></p>
<table>
<tr>
<td><h2>가장 재미있는 것을 선택해 주세요.</h2></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<select name="item1">
<option value="html1">HTML</option>
<option value="javaScript">자바스크립트</option>
<option value="CSS">CSS</option>
</select>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<select name="item2" size="3">
<option value="html">HTML</option>
<option value="javaScript">자바스크립트</option>
<option value="CSS">CSS</option>
</select>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<form> : 폼만들기 폼 태그의 속성에서 사용자가 입력한 자료를 서버로 어떤 방식으로 넘길 지와 어떤 프로그램을 이용해 처리할지 지정한다.
method : 사용자가 입력한 내용을 서버로 어떻게 넘겨줄 것인지 지정
get - 주소 표시줄에 입력 값이 그대로 드러남
post - 표준 입력으로 데이터를 전송, 입력 길이에 제한이 없으며, 입력한 내용이 드러나지 않음 (http프로토콘 내 에 담아서감)
name : 한 문서 안에 여러 개의 form이 있을 경우를 위해 이름 지정
action : form태그 안의 내용을 처리해 줄 서버 프로그램 지정.
target : action태그에서 지정한 스크립트 파일을 다른 창에서 열기.
accept-charset : 폼 전송에 사용할 문자 인코딩을 지정.(utf-8)
<form action="search.jsp" name="search_info" mathod="post"
<input type="text" title="검색">
<input type="submit" value="검색">
</form>
** GET방식 / POST방식 **
서버에 특정 서비스를 요청을하기 위해 클라이언트에서 작성한 값을 넘기는 방식
GET방식 : 클라이언트 데이터를 URL뒤에 붙여서 보낸는방식(?key=value&key=value...)
보안에 취약, 길이제한이 있음.(256byte), 전송속돈는 POST보다 빠름
POST방식 : URL에 노출하지 않고 데이터를 body에 포함시킴(URL에 노출되지 않아 기본 보안.)
전송길이에 제한이 없음.(사용예 - 회원가입시 사용자 입력값)
** 예제1206_4 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><h1>button, submit, reset</h1></p>
<input type="button" value="로그인" />
<input type="submit" value="회원가입" />
<input type="reset" value="다시입력" />
<br /><br />
<p><h1>input type=image</h1></p>
이미지 : <input type="image" src="./img/flower.jpg" width="100" height="100"/>
<p><h1>imput type=file</h1></p>
파일명 : <input type="file" name="fileName" />
</body>
</html>
** 예제1206_5 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form1" action="1206_4.html" method="get"> <!--"post"-->
<input type="text" name="id" title="검색" />
<input type="submit" value="검색" />
<input type="reset" value="다시입력" />
</form>
</body>
</html>** 예제 1206_6 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>form 연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form1" action="1206_5.html" method="post"> <!--"get"-->
<p><h1>imput type 종류</h1></p>
이름 : <input type="text" name="my_name" size="20" /><br>
비밀번호 : <input type="password" name="my_pwd" size="20"><br />
<input type="text" name="my_name2" size="20" value="수정불가" readonly />
<p><h1>type radio</h1></p>
아침메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<br /><br />
점심메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food2" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food2" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<br /><br />
저녁메뉴 : <input type="radio" name="food3" value="치킨" checked>치킨
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="피자">피자
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="짜장면">짜장면
<input type="radio" name="food3" value="짬뽕">짬뽕
<p><h1>type checkbox</h1></p>
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="cpu" checked>cpu
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="memory" />memory
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="hdd" />하드디스크
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="cdrom" />cdrom
<input type="checkbox" name="computer" value="grapic" />그래픽카드
<p><h1>select option</h1></p>
<table>
<tr>
<td><h2>가장 재미있는 것을 선택해 주세요.</h2></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<select name="item1">
<option value="html1">HTML</option>
<option value="javaScript">자바스크립트</option>
<option value="CSS">CSS</option>
</select>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<select name="item2" size="3">
<option value="html">HTML</option>
<option value="javaScript">자바스크립트</option>
<option value="CSS">CSS</option>
</select>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br /><br />
<input type="submit" value="회원가입" />
<input type="reset" value="다시입력" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
** 예제 1206_7 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="form1" action="1206_6.html" method="get">
<table>
<tr>
<td>이름 : </td>
<td><input type="text" name="name1" repuired></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>비빌번호 : </td>
<td><input type="password" name="name2"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>연락처 : </td>
<td><input type="text" name="name3" size=5>-<input type="text" name="name4" size="5">-<input type="text" name="name5" size="5"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>사진 : </td>
<td><input type="file" name="name6" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>성별 : </td>
<td><input type="radio" name=name7 value="남">남
<input type="radio" name=name7 value="여">여</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>사용언어 : </td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="name8" value="한글" />한글
<input type="checkbox" name="name8" value="영어" />영어
<input type="checkbox" name="name8" value="일어" />일어
<input type="checkbox" name="name8" value="중국어" />중국어
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>자기소개 : </td>
<td><textarea rows="5" cols="30" name="info">간단하게 입력하세요.</textarea></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>국적 : </td>
<td><select name="name9">
<option value="한국">한국</option>
<option value="미국">미국</option>
<option value="중국">중국</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>좋아하는 음식 : </td>
<td><select name="name10" size="4">
<option value="김치">김치</option>
<option value="불고기">불고기</option>
<option value="파전">파전</option>
<option value="비빔밥">비빔밥</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<input type="submit" value="제출" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Div : 블록요소를 가지고 있음, 줄바꿈이 발생.
span : 줄바꿈이 발생하지 않음.
** 예제1206_8 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--div, span-->
<p>block</p>
<ul>
<li>item1</li>
<li>item2</li>
<li>item3</li>
</ul>
<div>111111</div><div>222222</div><div>333333</div><div>444444</div><div>555555</div>
<span>item1</span>
<span>item2</span>
<span>item3</span>
<span>item4</span>
<span>item5</span>
</body>
</html>
HTML이 정보를 표현한다면 CSS는 HTML을 시각적으로 꾸며주는 역할(정보와 디자인을 분리)
특정 태그를 선택하여, 해당 태그의 속성을 변경하는 목적으로 사용됨.
* CSS적용방식(3가지)
- .inline방식 : 엘리먼트에 스타일을 직접 기술하는 방식 / 셀렉트가 필요없음 / CSS 선언이 분명해서 style tag방식에 비해 엘리먼트에 영향을 주고 있는 CSS를 추적하기 쉬움./ 코드가 많아지고, 정보와 디자인의 분리라는 CSS취지와 벗어남.
- style tag방식 : style 태그에 기술하는 방식 / inline방식 대비 경제적으로 코딩할 수 있음 / 정보와 디자인의 분리라는 CSS의 취지에 부합 (현재 페이지에 공통으로 들어가는 것들에 사용)
- .외부 파일 방식 : CSS를 별도의 파일로 분리해서 링크하는 방식 / 문법적으로는 style tag와 동일 / 파일의 교체로 디자인을 변경할 수 있다는 점에서 유지 보수가 편리 (전체 페이지에 공통으로 들어가는 것들에 사용)
| 속성 | 설명 |
| class | 요소의 클래스 이름 . |
| id | 요소의 아이디 # |
| style | 요소에 대한 인라인 |
| title | 요소에 대한 추가정보, 툴 팁으로 표시됨. |
- 외부 link를 이용해서 css파일을 가져오는 방법이다.
- rel : 현재 문서와 외부 리소스 사이의 관계를 알려줘야한다.
- href 에 # 주는건 다른 링크를 준다는 의미
출처: https://heidong.tistory.com/85 [풀스택 개발자:티스토리]
button - 그냥 버튼
submit = submit을 감싸는 form태그속 정보를 보낸다.
reset - reset을 감싸는 form태그 속 정보를 리셋
| 12/08 수업 (26일차) _ 평행이동 / 애니메이션 (1) | 2023.12.08 |
|---|---|
| 12/07 수업 (25일차) _ 선택자 / (2) | 2023.12.07 |
| 12/04 수업 (23일차) _ HTML설치 / Web이란? / HTML태그 / CSS적용 List 태그 / Table태그 (2) | 2023.12.04 |
비주얼스튜디오 다운로드 -> 비주얼스튜디오코드 무료다운로드 (windows x64 사용자 설치 관리자) 설치

실행 후 왼쪽 맨밑 확장 -> Korean 설치 후 오른쪽아래 재실행

* c - prject - HTML새폴더 만들기

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

위 입력 후
실행 - > 디버깅 없이 실행 -> chrome
Web(웹) 이란? , 사전적인 의미로 거미줄이란 뜻으로 it에서는 WWW (World Wide Web) 의 약자
** Web의 동작원리 **
- 브라우저에 ( http:// ) www.naver.com 이라는 는 일종의 url을 치면 브라우저는 서버에 url을 요청하고 서버는 저장되어있던 네이버의 HTML, CSS, Java Script파일 등의 구성파일을 보내면 브라우저에 나타냄.
** 클라이언트 - 서버 구조 **
- 클라이언트(Client)란?
서비스를 사용하는 사용자 혹은 사용자의 단말기를 가리키는말. (서비스를 요청하는 입장)
- 서버(Server)란?
서비스를 제공하는 컴퓨터이며, 다수의 클라이언트를 위해 존재하기 때문에 일반적으로 매우 큰 용량과 성능을 가지고 있음.
(서비스를 요청받고 서비스를 제공하는 입장)
웹이란? 1개 이상의 사이트가 연결되어 있는 인터넷 서비스의 한가지 형태.
인터넷이란? 1개 이상의 네트워크가 연결되어 있는 형태
- 프로토콜(Protocol) : 네트워크상에서 약속한 통신규약 (Http, FTP, SMTP, POP, DHCP)
- IP(Internet Protocol) : 네트워크상에서 컴퓨터를 식별할 수 있는 주소 (ip와 DNS는 1:1맵핑)
- DNS(Domain Name Service) : IP주소를 인간이 쉽게 외우도록 맵핑한 문자열
- Port : IP주소가 컴퓨터를 식별할 수 있게 해준다면, Port번호는 해당컴퓨터의 구동되고 있는 프로그램을 구분 할 수 있는 번호
| - Example - http://www.daum.net/about/introduce * http - 프로토콜 * www.daum.net - 컴퓨터주소(DNS를 통한 IP주소로 변경) -> 예) <255.255.255.255> * about/introduce - Information path |
* cmd 명령 프롬프트에 ipconfig검색하면 내컴퓨터 ip 알 수 있음
* cmd 명령 프롬프트에 ping 주소 입력하면 DNS와 맵핑된 ip 알 수 있음
** HTML 이란? **
<!DOCTYPE html> //1)doctype (생략가능)
<html lang = "ko"> //2)<html> 태그
<head> //3)<head>태그
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>HTML 기본구조</title>
</head>
<body> //4)<body>태그
<h1>Hello, HTML</title>
</body>
</html>
Hyper Text Markup Language의 약자로 웹문서를 기술하는 언어, 웹문서를 표현하기 위해 태그들로 구성되어 있음.
1)doctype - 브라우저 선언문, 반드시 상단 웹표준과 관련
2)<html> 태그 - lang속성은 문서가 작성된 언어
3)<head>태그 - 브라우저 화면에 표시되지 않음, 문서의 기본설정 ( 보통 이페이지가 무슨페이지인지 설명 or body정보를 추가or보완)
4)<body>태그 - 브라우저 화면에 나타나는 내용, 태그들 대부분이 해당
* Visual studio code 에서 '! (느낌표) 하고 엔터' 치면 html기본 코드 제공
* HTML 요소 구조
HTML 요소(element)는 여러 속성을 가질 수 있으며, 이러한 속성(attribute)은 해당요소에 대한 추가적인 정보를 제공함.
HTML 요소는 시작 태그로 시작해서 종료 태그로 끝남
//HTML요소
<p class="para">TCPschool.com</p>
//<p class="para"> - 시작태그
// p-태그이름
// class - 속성명
//"para" - 속성 값
//TCPschool.com - 내용
//</p> - 종료태그
<b /> : 화면상 엔터키(줄바꿈)
* css 란?
Cascading Style Sheets의 약자로, HTML문서를 디자인적으로 예쁘게 만들어 정보를 가지고 있고, CSS는 화면상의 레이아웃 등을 컨트롤 하는 문서
a { background-color : yellow ; font-size : 16px ; }
//a - 선택자
//{} - 선언시작,끝
//background-color - 속성명
//yellow - 속성값
//font-size - 속성명
//16px - 속성값
** HTML 태그 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>html연습</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>h1 태그입니다.</h1>
<h2>h2 태그입니다.</h2>
<h3>h3 태그입니다.</h3>
<h4>h4 태그입니다.</h4>
<h5>h5 태그입니다.</h5>
<h6>h6 태그입니다.</h6>
<p>주로 본문에 사용되는 태그로서 단락을 구분합니다.</p>
<p>주로 본문에 사용되는 태그로서 단락을 구분합니다.</p>
<p>주로 본문에 사용되는 태그로서 단락을 구분합니다. <br /> 행바꿈 태그입니다.</p>
<p>주로 <b>본문</b>에 사용되는 태그로서 단락을 구분합니다. <br /> 행바꿈 태그입니다.</p>
<p><a href="http://www.daum.net">다음 웹사이트로 이동</a></p>
<p><i>KOREA</i></p>
<p>KOREA<sup>SEOUL</sup></p>
<p><ins>KOREA</ins></p>
<p><del>DELETE</del></p>
</body>
</html>
* 결과

** CSS 적용 **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
h1 {
font-size:60px;
color:green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>안녕하세요. 월요일입니다.</h1>
</body>
</html>

* 리스트 태그 - ol, ul, li
<ol> : 숫자나 알파벳 등 순서가 있는 목록
<ul> : 순서가 필요 없는 목록
<li> : list item의 약자
* 리스트 태그 - dl, dt, dd (dl안에 dt/dd 태그 올수 있다.)
<dl> : 사전처럼 용어를 설명하는 목록을 만들때
<dt> : 정의되는 용어의 제목을 넣을때
<dd> :
** 실습 (리스트) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>메뉴 리스트</p>
<ul>
<li>menu1</li>
<li>menu2</li>
<li>menu3</li>
<li>menu4</li>
<li>menu5</li>
</ul>
<p>지역 리스트</p>
<ol>
<li>서울</li>
<li>경기</li>
<li>충청</li>
<li>강원</li>
<li>제주</li>
</ol>
<ol>
<li><a href="http://www.google.com" target="_blank">구글</href></li>
<li><a href="http://www.daum.net" target="_self">다음</href></li>
</ol>
<br /><br />
<!--리스트 태그 dl, dt, dd-->
<dl>
<dt>메뉴 리스트</dt>
<dd>menu1</dd>
<dd>menu2</dd>
<dd>menu3</dd>
<dd>menu4</dd>
<dd>menu5</dd>
<dt>지역 리스트</dt>
<dd>서울</dd>
<dd>경기</dd>
<dd>충청</dd>
<dd>강원</dd>
<dd>제주</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>
** Table 태그 **
** 테이블만들기 **
<table> : 테이블을 만드는 태그
<th> : 테이블의 헤더 부분을 만드는 태그
<tr> : 테이블의 행을 만드는 태그
<td> : 테이블의 열을 만드는 태그 (왼쪽정렬기본)
** 테이블 디자인 변경 **
border : 테이블의 테두리 (border="1") - 숫자가 높을수록 테두리가 두꺼워짐
bordercolor : 테이블의 테두리 색상 - default 검정색
width : 테이블 가로 크기
height : 테이블 세로 크기
align : 정렬 (테이블안에 있는 값들을 정렬시키는 기능)
bgcolor : 배경색
colspan : 가로합병(열 합병)
rowspan : 세로합병(행 합병)
** 실습 (테이블) **
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<!--
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>테이블테스트</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1" bordercolor="red" bgcolor="#FCFA76">
<tr>
<th>번호</th>
<th>이름</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1</th>
<th>첫번째 순서</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>2</th>
<th>두번째 순서</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
-->
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Table 실습문제1</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>영화제목</th>
<th>연도</th>
<th>감독</th>
<th>평가</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>라이프오브파이</th>
<th>2013</th>
<th>이안</th>
<th>8.68</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>레미제라블</th>
<th>2012</th>
<th>톰후퍼</th>
<th>8.28</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>장고: 분노의 추적자</th>
<th>2012</th>
<th>타란티노</th>
<th>8.29</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
| 12/08 수업 (26일차) _ 평행이동 / 애니메이션 (1) | 2023.12.08 |
|---|---|
| 12/07 수업 (25일차) _ 선택자 / (2) | 2023.12.07 |
| 12/06 수업 (24일차) _ Table 태그 속성 / Img 태그 / Input태그 / Form 태그 / 레이아웃 구성 태그 - div, span / CSS란? (1) | 2023.12.06 |
** 예제 1204 (Vector) **
package etc;
import java.util.Vector;
public class MySample1204 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 벡터
Vector v = new Vector(5);
v.add("1");
v.add("2");
v.add("3");
print(v);
//빈 공간 없애기.(용량과 크기가 같게)
v.trimToSize();
System.out.println("v.trimToSize()...");
print(v);
//벡터 용량 증가
v.ensureCapacity(6);
System.out.println("v.ensureCapacity...");
print(v);
v.setSize(7); //총 7개 중 3개가 이미 값이 있으므로 4개는 null로 채움
System.out.println("v.setSize()...");
print(v); //6개를 다사용해서 2배로늘어난다. -> capacity : 12
//벡터의 data만 삭제됨. 기존 벡터의 size는 유지.
v.clear();
System.out.println("v.clear()...");
print(v);
}
public static void print(Vector v) {
System.out.println(v);
System.out.println("size : " + v.size());
System.out.println("capacity : " + v.capacity());
}
}- 스택은 마지막에 저장한 데이터를 가장먼저 꺼내게 되는 LIFO(Last In First Out)
- 큐는 처음에 저장한 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내게 되는 FIFO(First In First Out)
- 큐는 인터페이스 -> 큐를 상속받은 LinkedList클래스
| Stack 메소드 | 설 명 |
| boolea empty() | Stack이 비어 있는지 알려줌 |
| Object peek() | Stack 의 맨 위에 저장된 객체 반환 //다음주소값이 null이면 가장 위에있는 객체 |
| Object pop() | 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 꺼낸다. |
| Object push(Object item) | Stack 에 객체를 저장 |
| int search(Object o) | 주어진 객체를 찾아 위치를 반환, 실패시 -1반환(위치는 1부터 시작) |
| Queue 메소드 | 설 명 |
| boolean add(Object o) | Queue에 추가 (성공하면 true)반환 |
| Object remove() | Queue 에서 객체를 꺼내 반환 |
| Object element() | 삭제없이 요소를 읽어옴 |
| boolean offer(Object o) | 객체를 저장. 성공하면 true |
| Object poll() | 객체를 꺼내서 반환 (비어있으면 null반환) |
| Object peek() | 삭제없이 욧를 읽어옴 (비어있으면 null반환) |
| 생성자 또는 메소드 | 설 명 |
| LinkedList(); | LinkedList 객체생성 |
| boolean add(Object) | 지정된 객체를 LinkedList끝에 추가, 성공 true 실패false |
| void add(int index, Object element) | 지정된 위치에 객체 추가 |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) | 지정된 위치에 주어진 컬렉션에 포함된 모든 요소를추가, 성공 true 실패false |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 지정된 객체가 LinkedList에 포함되었는지 알려줌 |
| boolean containsAll(Collection o) | 지정된 컬렉션의 모든 요소가 포함되었는지 알려줌 |
| Object get(int index) | 지정된 위치의 객체를 반환 |
| boolean isEmpty() | LinkedList가 비어 있는지 알려줌. 비어있으면 true |
| boolean remove (Object o) | 지정된 객체 제거, 성공 true 실패false |
| int size() | LinkedList에 저장된 객체 수 반환 |
| boolean retainAll(Collection c) | 지정된 컬렉션의 모든 요소가 포함되어 있는지 확인 |
| Object set(int index, Object element) | 지정된 위치에 객체를 주어진 객체로 바꿈 |
** 예제 MySample1204_2 **
package etc;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class MySample1204_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stack / Queue
Stack st = new Stack();
Queue q = new LinkedList(); //Queue인터페이스의 구혀네인 LinkedList사용
st.push("0");
st.push("1");
st.push("2");
q.offer("3");
q.offer("4");
q.offer("5");
System.out.println("Stack()------------");
while(!st.empty()) {
System.out.println(st.pop());
}
System.out.println("Queue()------------");
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
}
}** 예제 MySample1204_3 **
package etc;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MySample1204_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList 와 LinkedList비교 (시간)
ArrayList a = new ArrayList(2000000);
LinkedList t = new LinkedList();
System.out.println("순차적으로 추가...");
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + add1(a));
System.out.println("LinkedList : " + add1(t) + "\n");
System.out.println("중간에 추가...");
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + add2(a));
System.out.println("LinkedList : " + add2(t) + "\n");
System.out.println("중간 삭제...");
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + remove2(a));
System.out.println("LinkedList : " + remove2(t) + "\n");
System.out.println("순차적으로 삭제...");
System.out.println("ArrayList : " + remove1(a));
System.out.println("LinkedList : " + remove1(t) + "\n");
}
//순차적으로 추가
public static long add1(List list) { //모든클래스의 부모인 List로 매개변수 받음
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //현재 시간을 밀리세컨드단위
for(int i = 0 ; i < 1000000 ; i++) {
list.add(i + "");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end - start;
}
//중간에 추가
public static long add2(List list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) {
list.add(500, "X");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end - start;
}
//순차적으로 삭제
public static long remove1(List list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = list.size()-1 ; i >= 0 ; i --) {
list.remove(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end - start;
}
//중간 삭제
public static long remove2(List list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) {
list.remove(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end - start;
}
}
결론 : 순차적으로 추가/삭제하는 것은 ArrayList가 LinkedList 보다 빠르다.
결론 : 중간 데이터를 추가/삭제하는 것은 LinkedList가 ArrayList보다 빠르다.
** 예제 MySample1204_4 **
package etc;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MySample1204_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// File 클래스
//절대경로와 상대경로
File directory = new File("./tmep"); //상대경로 (./temp -> 상대경로의미) | ./ -> 현재디렉토리(.) 아래에있는(/) temp 라는 의미.
//File directory = new File("C:\\project\\JAVA\\MyProject\\temp"); //절대경로(풀경로를 다적어준다.)
directory.mkdir(); //디렉토리 생성
//temp디렉토리에 temp_file.txt 파일 생성
File file = new File(directory, "temp_file.txt"); //아직 파일이 만들어지지 않음.
file.createNewFile();
//생성file 객체가 디렉토리인지 파일인지 확인
if(directory.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println(directory.getName() + "은 디렉토리 입니다.");
}
if(file.isFile()) {
System.out.println(file.getName() + "은 파일입니다.");
System.out.println("파일 경로 : " + file.getPath());
System.out.println("파일 크기 : " + file.length() + "(bytes)");
System.out.println("쓰기 가능 여부 : " + file.canWrite());
System.out.println("읽기 가능 여부 : " + file.canRead());
}
//파일 삭제
if(file.delete()) {
System.out.println(file.getName() + "이 삭제되었습니다.");
}
//디렉토리 삭제
if(directory.delete()){
System.out.println(directory.getName() + "디렉토리가 삭제되었습니다.");
}
}
}** 예제 MySample1204_5 **
package etc;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
public class MySample1204_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// // File객체를 이용하여 Scanner생성
// File file = new File("./temp/source_data.txt");
//
// Scanner scn = new Scanner(file);
//
// //파일의 내용을 라인 단위로 출력
// System.out.println(file.getName() + "파일의 데이터 내용.");
//
// while(scn.hasNextLine()) {
// System.out.println(scn.nextLine());
// }
//
// scn.close(); //->파일은 사용하고나면 닫아줘야한다.
// //BufferedReader 이용
// File file = new File("./temp/source_data.txt");
// FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
// BufferedReader buffReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
//
// //파일 내용을 라인 단위로 출력
// System.out.println(file.getName() + "파일 데이터 내용.");
// String data = null;
//
// while((data = buffReader.readLine()) != null) {
// System.out.println(data.toString());
// }
//
// //입력스트림 종료
// reader.close();
// buffReader.close();
String filePath = "./temp/source_data.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(!file.exists()) { //파일의 존재하는지 확인 후 해당파일이 없는경우 파일생성
file.createNewFile(); //신규생성
}
//BufferedWriter 생성
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file, true));
//파일에 쓰기
writer.newLine();
writer.write("앗 월요일이다.");
writer.newLine();
writer.write("즐거운 점심시간입니다.");
writer.newLine();
//버퍼 및 스트림 정리
writer.flush(); //버퍼에 남은 데이터를 모두 쓰기
writer.close(); //스트림 종료
}
}
| 12/01 수업 (22일차) _ SimpleDateFormat / 컬렉션 프레임웍 (Collections Framework) / (2) | 2023.12.01 |
|---|---|
| 11/30 수업 (21회차) _ java.lang패키지 / String 클래스 / Calendar클래스 (2) | 2023.11.30 |
| 11/29 수업 (20회차) _ 예외 처리 (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
** 예제 etc pakage MySample1201 **
package etc;
public class MySample1201 {
final static int RECORD_NUM = 10;
final static String TABLE_NAME = "회원정보";
final static String[] CODE1 = {"010", "011", "017" ,"018", "019"};
final static String[] CODE2 = {"남자","여자"};
final static String[] CODE3 = {"10대","20대","30대","40대","50대"};
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < RECORD_NUM ; i++) {
//INSERT INTO 회원정보 VALUES ('017', '여자', '20대', 101);
System.out.println("INSERT INTO 회원정보 VALUES (" +
"'" + getRandArr(CODE1) +
"', '" + getRandArr(CODE2) +
"', '" + getRandArr(CODE3) +
"', " + getRand(100, 200) + ");"); //100~200사이 값 랜덤
}
}
public static String getRandArr(String[] arr) {
return arr[getRand(arr.length-1)]; //배열에 저장된 값 중 하나를 반환하는 용도.
}
public static int getRand(int n) {
return getRand(0,n);
}
public static int getRand(int from, int to) {
System.out.println("form : " + from + ", to : " + to);
System.out.println("abs : " + (Math.abs(to-from)+1) + ", min : " + Math.min(from, to));
return (int)(Math.random()*(Math.abs(to-from)+1)) + Math.min(from, to);
}
}** 예제 etc pakage MySample1201_2 (SimpleDateFormat) **
package etc;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class MySample1201_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// SimpleDateFormat (날짜 데이터를 원하는 형태로 다양하게 출력)
Date today = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat s1, s2, s3, s4;
SimpleDateFormat s5, s6, s7, s8, s9;
s1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
s2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yy년 MMM dd일 E요일");
s3 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.sss");
s4 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss a");
s5 = new SimpleDateFormat("오늘은 올해의 D번째 날입니다.");
s6 = new SimpleDateFormat("오늘은 이달의 d번째 날입니다.");
s7 = new SimpleDateFormat("오늘은 올해의 w번째 주입니다.");
s8 = new SimpleDateFormat("오늘은 이달의 W번째 주입니다.");
s9 = new SimpleDateFormat("오늘은 이달의 F번째 E요일 입니다.");
System.out.println(s1.format(today));
System.out.println(s2.format(today));
System.out.println(s3.format(today));
System.out.println(s4.format(today));
System.out.println(s5.format(today));
System.out.println(s6.format(today));
System.out.println(s7.format(today));
System.out.println(s8.format(today));
System.out.println(s9.format(today));
/*
* y : 년 | M : 월 | d : 일 | E : 요일 | a : 오전/오후
* H : 시간 | m : 분 | s : 초
*/
String patternKorea = "yyyy-MM-dd";
String patternUSA = "MM-dd-yyyy";
String patternUK = "dd-MM-yyyy";
String pattern1 = "E요일 HH시 mm분 ss초";
SimpleDateFormat p1 = new SimpleDateFormat(patternKorea);
SimpleDateFormat p2 = new SimpleDateFormat(patternUSA);
SimpleDateFormat p3 = new SimpleDateFormat(patternUK);
SimpleDateFormat p4 = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern1);
System.out.println("현재 날짜 : " + today);
System.out.println("한국형(년월일) : " + p1.format(today));
System.out.println("미국형(년월일) : " + p2.format(today));
System.out.println("영국형(년월일) : " + p3.format(today));
System.out.println("1형(년월일) : " + p4.format(today));
}
}
실행 결과 →
데이터를 저장하는 클래스들을 표준화 설계한 것
데이터를 다루고 표현하기 위한 단일화된 구조
* 컬렉션 프레임웍의 핵심 인터페이스
| 인터페이스 | 특징 |
| List | 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합, 데이터의 중복을 허용 구현클래스 : ArrayList, LinkedList, Stack, Vector 등 |
| Set | 순서를 유지하니 않는 데이터의 집합, 데이터의 중복을 허용하지 않음 구현클래스 : HashSet, TreeSet |
| Map | 키(key)와 값의 쌍으로 이루어진 데이터들의 집함 순서는 유지되지 않으며, 키는 중복을 허용하지 않고, 값은 중복을 허용 구현클래스 : HashMap, TreeMap, Hashtable, Properties |
- 키란(key) ?
- 데이터 집합 중에서 어떤 값(value)을 찾는데 열쇠 (key) 가 됨으로 키 (key) 는 중복을 허용하지 않음
배열과 비슷하지만 배열보다 편리한 기능을 많이 가지고 있음.
배열의 경우 크기를 한번 지정하면 사이즈가 고정이되어 변경할 수 없지만
리스트의 경우 자료를 넣는 많큼 자동적으로 사이즈가 늘어나기 때문에 동적으로 활용하기에 유리함.
* 대표 함수
| 함수 | 설명 |
| add | List 에 자료를 넣을 때 사용하는 함수 예) ArrayList<String>list = new ArrayList<String>(); //<>는 타입 넣어줌 list.add("사과") list.add( 1, "바나나" ) //숫자에 해당하는 곳에 바나나자료 넣어준다. |
| get | List의 데이터를 가져올 때 사용. 예) list.get(1) |
| size | List의 길이를 리턴하는 함수 예) list.size() |
| contains | List에 해당값이 있느면 true, 없으면 false를 리턴. 예) list.contains("사과") |
| remove | List에서 삭제가 성공하면 true, 실패하면 false 리턴. 예) list.remove("사과") / list.remove(0) //0번째 인덱스에 있는 값 삭제 |
* Colletion 인터페이스에 정의된 메서드
.
.
.....
컬렉션 프레임웍에서 가장 많이 사용되는 컬렉션 클래스
특징 - List 인터페이스르르 구현하기 떄문에 데이터의 저장순서가 유지되고 중복을 허용함
Object 배열을 애용해서 데이터를 순차적으로 저장
배열에 순서대로 저장되며, 배열에 더 이상 저장할 공간이 없으면 보다 큰 새로운 배열을 생성해서 기존의 배열 내용을 새로운 배열로 복사한 다음에 저장
* ArrayList의 생성자와 메서드
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| ArrayList() | 크기가 10인 ArrayList생성 |
| boolean add(Object o) | ArrayList의 마지막에 객체 추가 , 성공 true |
| void add (int index, Object element) | 지정된 위치에 객체 저장 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 지정된 객체가 ArrayList에 포함되어 있는지 확인 |
| Object get(int index) | 지정된위치에 저장된 객체 반환 |
| Object remove(int index) | 지정된 위치에 있는 객체 제거 |
| boolean retainAll(Collection c) | ArrayList에 저장된 객체 중에서 주어진 컬렉션과 공통된 것들만을 남기고 나머지는 삭제 |
ArrayList 크기(길이)가 10인 ArrayList가 생겨도 값이 5개만 들어오면 크기가 5로 바뀜.
** 예제 etc pakage MySample1201_3 (ArrayList) **
package exec;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class MySample1201_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>(10);
list1.add("A");
list1.add("B");
list1.add("C");
list1.add("D");
System.out.print("list1 초기 상태 : ");
System.out.println(list1 + " - size : " + list1.size());
System.out.println("\n인덱스1에 B 추가");
list1.add(1, "B");
System.out.print("B추가 후 : ");
System.out.println(list1 + " - size : " + list1.size());
System.out.println("\n인덱스2의 값 삭제");
list1.remove(2);
System.out.print("인덱스2삭제 후 : ");
System.out.println(list1 + " - size : " + list1.size());
System.out.println("\n인덱스 2번째 위치 값 불러오기 : " + list1.get(2));
System.out.println();
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList(10); //타입<String>쓰지않으면, ArrayList에 객체를 넣을 수 있다.
list2.add(new Integer(5)); //5를 넣지안고 Integer객체에 5를 넣은 이유
list2.add(new Integer(4));
list2.add(new Integer(2));
list2.add(new Integer(0));
list2.add(new Integer(1));
list2.add(new Integer(3));
System.out.println("list2 : " + list2);
ArrayList list3 = new ArrayList(list2.subList(1, 4)); //인덱스 1번째부터 (4-1) 위치까지 가져오는 것
System.out.println("list3 : " + list3);
print(list2, list3);
Collections.sort(list2); //<T> : 어떠한 데이터탑입도 다 받는다는 의미
Collections.sort(list3);
print(list2, list3);
//list2에 list3 전체가 포함되어 있는지 확인(true.false)
System.out.println("list2.containsAll(list3) - " + list2.containsAll(list3));
System.out.println("list3.containsAll(list2) - " + list3.containsAll(list2));
}
static void print(ArrayList list1, ArrayList list2) {
System.out.println("list1 : " + list1);
System.out.println("list2 : " + list2);
System.out.println();
}
}** 문제 etc pakage MySample1201_4 (ArrayList) **
// ArrayList
/*
* 문제)5명의 사람이름을 입력받아서 ArrayList에 저장한 후에 '김'씨 성을 가진 사람을 모두 출력하는 프로그램.
* 입력예)홍길동
* 이둘리
* 김길동
* 김둘리
* 최길동
* 출력예)[김길동] [김둘리]
* 김씨 성을 가진 분은 모두 2명입니다.
* 단, 입력시 nextLine() 사용하며, '김'으로 시작한 것을 찾는 메서드는 get(i) 가져와서 startsWith("김")->true, false
*/
package exec;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySample1201_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList
/*
* 문제)5명의 사람이름을 입력받아서 ArrayList에 저장한 후에 '김'씨 성을 가진 사람을 모두 출력하는 프로그램.
* 입력예)홍길동
* 이둘리
* 김길동
* 김둘리
* 최길동
* 출력예)[김길동] [김둘리]
* 김씨 성을 가진 분은 모두 2명입니다.
* 단, 입력시 nextLine() 사용하며, '김'으로 시작한 것을 찾는 메서드는 get(i) 가져와서 startsWith("김")->true, false
*/
ArrayList<String> name = new ArrayList<String>(5);
int cnt = 0; //몇명인지 체크
int i;
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("5명의 이름을 입력해 주세요.");
for(i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ ) {
name.add(scn.nextLine());
}
String str;
for(i = 0 ; i < name.size() ; i++) {
str = name.get(i); //str쓰지않고 name.get(i)를 직접 사용가능
if(str.startsWith("김")) {
cnt++;
System.out.print("[" + name.get(i) + "] ");
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("김씨 성을 가진 분은 모두 " + cnt + "입니다.");
}
}** 문제 etc pakage MySample1201_5 (ArrayList) **
package exec;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySample1201_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList 문제
/*
* 문제)5명의 별명을 입력받아 ArrayList에 저장하고 이들 중 별명의 길이가 제일 긴 별명을 출력하는 프로그램
* 입력예)세일러문
* 크루지
* 놀부
* 순대렐라
* 달려라하니
* 출력예)가장 길이가 긴 별명은 > 달려라하니
* 단, 별명의 길이는 모두 다르게 입력함.
*/
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<String> nick = new ArrayList<String>(5);
int i, maxnickIndex = 0;
int tmp = 0;
System.out.println("5명의 이름을 입력하세요.");
for(i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {
nick.add(scn.nextLine());
if(nick.get(i).length() > tmp) {
tmp = nick.get(i).length();
maxnickIndex = i;
}
// for(i = 0 ; i < nick.size() ; i++) {
// if(nick.get(i).length() > tmp) {
// tmp = nick.get(i).length();
// maxnickIndex = i;
// }
}
System.out.println("가장 길이가 긴 별명은 > " + nick.get(maxnickIndex));
// //선생님 풀이
// ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
// int[] lengthArr = new int[5];
// int max = lengthArr[0];
// int i;
//
// for(i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {
// list.add(scn.nextLine());
// }
//
// for(i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {
// lengthArr[i] = list.get(i).length();
//
// if(max < lengthArr[i]) {
// max = lengthArr[i];
// }
// }
//
// for(i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {
// if(max == list.get(i).length()) {
// System.out.println("가장 길이가 긴 별명은 > " + list.get(i));
// break;
// }
// }
}
}** 문제 etc pakage MySample1201_6 (ArrayList) **
package etc;
public class Student {
private int grade;
private int ban;
private int num;
private String name;
private int korean;
private int english;
private int math;
private int totalScore;
private double avg;
private int ranking;
public Student() {
this(0,0,0,"",0,0,0);
}
public Student(int grade, int ban, int num, String name, int korean, int english, int math) {
setGrade(grade);
setBan(ban);
setNum(num);
setName(name);
setKorean(korean);
setEnglish(english);
setMath(math);
setTotalScore(getKorean() + getEnglish() + getMath());
setAvg((double)getTotalScore() / 3);
setRanking(0);
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public int getBan() {
return ban;
}
public void setBan(int ban) {
this.ban = ban;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getKorean() {
return korean;
}
public void setKorean(int korean) {
this.korean = korean;
}
public int getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english) {
this.english = english;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getTotalScore() {
return totalScore;
}
public void setTotalScore(int totalScore) {
this.totalScore = totalScore;
}
public double getAvg() {
return avg;
}
public void setAvg(double avg) {
this.avg = avg;
}
public int getRanking() {
return ranking;
}
public void setRanking(int ranking) {
this.ranking = ranking;
}
public String toString() {
String value = "등수 : " + getRanking() + "\n";
value += getGrade( ) + "학년" + getBan() + "반 " +
getNum() + "번 " + getName() + "\n";
value += "국어 : " + getKorean() + ", 영어 : " + getEnglish() + ", 수학 : " + getMath() + "\n";
value += "총점 : " + getTotalScore() + "\n";
value += "평균 : " + String.format("%.1f", getAvg()) + "\n";
return value;
}
}package etc;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class MySample1201_6 {
public static int randomRange(int min, int max, Random random) {
if(min > max) {
return min;
}
//난수발생 - min부터 max값 사이 난수 발생
return random.nextInt((max+1)-min)+min;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
//학생 리스트 작성
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
//랜덤 점수 입력
int i;
for(i = 1 ; i <= 20 ; i++) {
list.add(new Student(1,1,1, "홍길동"+i,
randomRange(40, 100, random),
randomRange(40, 100, random),
randomRange(40, 100, random)));
}
//등수 산정 전 출력
System.out.println("###########################");
System.out.println("등수 산정 전 출력");
System.out.println("###########################");
for(i = 0 ; i < list.size() ; i++) {
Student student = list.get(i);
System.out.println(student);
}
//등수를 적용하기 위해 내림차순 정렬
int j;
Student tmp;
for(i = 0 ; i < (list.size()-1) ; i++) {
for(j = i+1 ; j < list.size() ; j++) {
if(list.get(i).getTotalScore() < list.get(j).getTotalScore()) {
tmp = list.get(i);
list.set(i, list.get(j));
list.set(j, tmp);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
//등수 산정한 후 출력
System.out.println("###########################");
System.out.println("등수 산정 후 출력");
System.out.println("###########################");
int ranking = 0; //등수
int order = 0; //동일 등수 증가 값
Student student;
//등수 산정 및 출력
for( i = 0 ; i < list.size() ; i++) {
student = list.get(i);
if(i == 0) {
//등수 포기 값으로 1로 설정
ranking++;
//동일 등수 증가 값도 1로 설정
order++;
}
else {
//총점이 같다면
if(list.get(i-1).getTotalScore() == student.getTotalScore()) {
//동일 등수시 증가값만 적용(등수 ranking 바로 앞과 동일)
order++;
}
else {
//총점이 틀리면(이전 등수에 동일 등수 증가 값을 더함)
ranking += order;
//동일 등수 증가 값 초기화
order = 1;
}
}
//등수 부여
student.setRanking(ranking);
//출력
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
| 12/04 수업 (23일차) _ Vector / Stack & Queue / LinkedList (1) | 2023.12.04 |
|---|---|
| 11/30 수업 (21회차) _ java.lang패키지 / String 클래스 / Calendar클래스 (2) | 2023.11.30 |
| 11/29 수업 (20회차) _ 예외 처리 (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
** 예제 MySample1130 (예외처리 속 예외처리) **
package exec;
public class MySample1130 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리
try {
System.out.println("외부 try");
try {
System.out.println("내부 try");
Exception e = new Exception();
throw e;
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("내부 try~catch exception : " + e);
System.out.println("예외 던기지 한번 더");
throw e;
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("외부 try~catch exception : " + e);
}
System.out.println("예외처리 끝");
}
}** 예제 MySample1130_2 (사용자 예외처리 = 클래스 예외처리) **
package exec;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySample1130_2 {
static Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
static void ticketing(int age) throws AgeException{ //ticketing 호출하는 쪽에서 예외처리 해야한다.
if(age < 20) {
//AgeException e = new AgeException("나이 입력 오류");
//throw e;
//위 두줄을 한줄로
throw new AgeException("나이 입력 오류");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리 - 사용자 예외처리 (=클래스 예외처리)
/*
* 문제)20살 미만이 입력될 경우 계속해서 입력을 받고 20살 이상이 입력되면 "티켓발행 성공"이라고 출력하고 프로그램 종료
*/
System.out.print("나이를 입력하세요.>");
int age =scn.nextInt();
try {
ticketing(age);
}
catch(AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main() 메소드 끝.");
}
}
class AgeException extends Exception{ //Exception 상속 받아야함 (안받으면 Object상속받음)
AgeException(){
this("나이 입력 오류");
}
AgeException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
//문제)20살 미만이 입력될 경우 계속해서 입력을 받고 20살 이상이 입력되면 "티켓발행 성공"이라고 출력하고 프로그램 종료
//문제)20살 미만이 입력될 경우 계속해서 입력을 받고 20살 이상이 입력되면 "티켓발행 성공"이라고 출력하고 프로그램 종료
package exec;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySample1130_2 {
static Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
static void ticketing(int age) throws AgeException{ //ticketing 호출하는 쪽에서 예외처리 해야한다.
if(age < 20) {
//AgeException e = new AgeException("나이 입력 오류");
//throw e;
//위 두줄을 한줄로
throw new AgeException("나이 입력 오류");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //Thread.sleep(1000); 사용하기위해 throws 해준다.
// 예외처리 - 사용자 예외처리 (=클래스 예외처리)
/*
* 문제)20살 미만이 입력될 경우 계속해서 입력을 받고 20살 이상이 입력되면 "티켓발행 성공"이라고 출력하고 프로그램 종료
*/
while(true) {
System.out.print("나이를 입력하세요.>");
int age = scn.nextInt();
try {
ticketing(age);
System.out.println("티켓 발행 성공");
break;
}
catch(AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//예쁘게 보이기위해 Thread.sleep(1000); 와 throws InterruptedException 사용해줌
//위 e.printStackTrace(); 대신 아래문자열로 사용 가능
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
Thread.sleep(1000); //1초 대기
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class AgeException extends Exception{ //Exception 상속 받아야함 (안받으면 Object상속받음)
AgeException(){
this("나이 입력 오류");
}
AgeException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}** 예제 MySample1130_3 (예외처리)**
package exec;
//예외처리가 어디서 일어나는지 알아보기 위해 쓰인다.(흔하게 쓰이진 않음)
public class MySample1130_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리 (연결된 예외처리)
try {
install();
}
catch(InstallException e) {
System.out.println("1111111111111111111111111");
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("2222222222222222222222222");
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
System.out.println("*************************");
}
}
static void install() throws InstallException{
try {
startInstall();
copyFiles();
}
catch(SpaceException e) {
InstallException ie = new InstallException("설치중 예외발생11");
//InstallException의 원인 예외를 SpaceException으로 지정
ie.initCause(e); //지정된 예외를 예외로 등록
throw ie;
//
}
catch(MemoryException e) {
InstallException ie = new InstallException("설치중 예외발생22");
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
}
finally {
deleteTempFiles();
}
}
static void startInstall() throws SpaceException, MemoryException{
if(!enoughSpace()) {
throw new SpaceException("설치 공간이 부족함.");
}
if(!enoughMemory()) {
throw new MemoryException("메모리가 부족함");
}
}
static void copyFiles() {
System.out.println("설치에 필요한 파일들을 복사.");
}
static boolean enoughSpace() {
System.out.println("설치시 필요한 공간이 충분한지 확인.");
return false;
}
static boolean enoughMemory() {
System.out.println("설치시 필요한 메모리 확인");
return true;
}
static void deleteTempFiles() {
System.out.println("설치 후 설치시 사용한 임시파일 삭제.");
}
}
class InstallException extends Exception{
InstallException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
- 가장 기본이 되는 클래스들을 포함하고 있으며, import문 없이도 사용가능
Object클래스 : 모든 클래스의 최고 조상
| Object 클래스의 메소드 | 설명 |
| public Boolean equals(Object obj) | 객체 자신과 객체 obj가 같은 객체인 기 (같으면 true) |
| public Class getClass() | 객체 자신의 클래스 정보를 담고 있는 Class 인스턴스를 반환 |
| public int hachCode() | 객체 자신의 해시코드를 반화 |
| public String toString() | 객체 자신의 정보를 문자열로 반환 |
Object클래스에 equals메소드는 참조변수가 같은 객체를 참조하는 판다.
String 클래스의 epuals메소드는 주소값이 아닌 내용을 비교하도록 오버라이딩 되어있음.
| public String toString{ reurn getCalss().getName() + "@" + integer.toHexString(hashCode()); //실행예) Card@19e0bfd } |
** 예제 MySample1130_4 **
package exec;
class Value{
int value;
Value(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public class MySample1130_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//java.lang 패키지
Value v1 = new Value(20);
Value v2 = new Value(20);
if(v1.equals(v2)) {
System.out.println("v1과 v2가 같습니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("v1과 v2가 다릅니다.");
}
v1 = v2;
if(v1.equals(v2)) {
System.out.println("v1과 v2가 같습니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("v1과 v2가 다릅니다.");
}
}
}** 예제 MySample1130_5 **
package exec;
public class MySample1130_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//equals 메소드 오버라이딩
Person p1 = new Person(102345677722L);
Person p2 = new Person(102345677722L);
if(p1 == p2) {
System.out.println("p1과 p2가 같습니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("p1과 p2가 다릅니다.");
}
if(p1.equals(p2)) {
System.out.println("p1과 p2가 같다.*");
}
else {
System.out.println("p1과 p2가 다르다.*");
}
}
}
class Person{
long id;
Person(long id){
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) { //Object 참조형을 받는다는 의미 - Object클래스 상속받는 모든 객체를 매개변수로 받을 수 있다.
if(obj instanceof Person) {
if(this.id == ((Person)obj).id)
return true;
else
return false;
//if절 4줄을 아래 한 줄로 표현 가능
//return this.id == ((Person)obj).id;
}
else
return false;
}
}** 예제 MySample1130_6 **
package exec;
public class MySample1130_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Card c1 = new Card();
Card c2 = new Card("heart", 10);
System.out.println("c1.toString : " + c1.toString());
System.out.println("c2.toString : " + c2.toString());
String str = new String("korea");
String str1 = "korea";
System.out.println("str : " + str);
System.out.println("str.toString : " + str.toString());
System.out.println("str1 : " + str1);
System.out.println("str1.toString : " + str1.toString());
}
}
class Card{
String kind;
int number;
Card(){
this("spade", 1);
}
Card(String kind, int number){
this.kind = kind;
this.number = number;
}
void test() {
Card c = new Card();
System.out.println(c.toString());
}
public String toString() {
return "kind : " + this.kind + ", number : " + this.number;
}
}- 문자열을 위한 클래스로 문자열을 저장하고 이를 다루는데 필요한 메서드 제공
| 메서드 설명 | 예제 | 결과 |
| int comareTo(String str) | int l = "aaa".compareTo("aaa"); | i = 0 |
| String cocat(String str) | String s1 = "Hello"; String s2 = s1.concat(" World"); |
s2 = "Hello World" |
| boolean equals(Object obj) | String s = "Hello"; String s2 = s.equals( "Hello" ); |
s2 = ture; |
| int indexOf(int ch) | String s = "Hello"; int idx1 = s.indexOf('o'); ()에 숫자가 들어가면 문자열에서 숫자에 해당하는 문자반환 ()에 문자가 들어가면 그 문자가 있는 위치 번호 반환 |
Index1 =4 |
| int length() | String s = "Hello"; int length = s.length(); |
lenght = 5 |
| String[] split(String regex) | String animals = "dog,cat,bear" String[] arr = animals.split(","); |
arr[0] = "dog" arr[1] = "cat" arr[2] = "bear" |
** 예제 MySample1130_6 **
package exec;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class MySample1130_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc"; //문자열 리터럴 "abc"의 주소가 str1에 저장
String str2 = "abc"; //문자열 리터럴 "abc"의 주소가 str2에 저장
//(결과는 str1과 str2는 문자열 "abc"를 같이 바라봄)
System.out.println("String str1 = \"abc\";");
System.out.println("String str2 = \"abc\";");
System.out.println(str1); //.toString()메소드 생략되어있음
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println("str1 == str2 : " + (str1 == str2)); //String객체는 == 연산자 할 때 객체가 가지고 있는 값을 비교함.
System.out.println("str1.equals(str2) : " + str1.equals(str2)); //String타입은 .equals로 비교하는 것이 좋음
System.out.println();
String str3 = new String("\"abc\""); //새로운 String인스턴스 생성
String str4 = new String("\"abc\""); //새로운 String인스턴스 생성
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
System.out.println("str3 == str4 : " + (str3 == str4));
System.out.println("str3.equals(str4) : " + str3.equals(str4));
System.out.println();
/*
* 확장형 for문
* String[] arr = {"a", "b", "c"};
* for(String s : arr)
*/
String animals = "dog,cat,bear";
String[] arr = animals.split(",");
for(String s : arr) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.join("-", arr)); //문자열과 문자열 사이에 "-"로 구분
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner("/","[","]");
//문자열을 add할때 - 문자열과 문자열사이 들어갈것(-), 문자열 시작에 들어갈 것([), 문자열 끝에 들어갈 것(])
for(String s : arr){
sj.add(s);
}
System.out.println(sj.toString());
}
}
* 결과
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
abc
abc
str1 == str2 : true
str1.equals(str2) : true
"abc"
"abc"
str3 == str4 : false
** 예제 MySample1130_7 **
package exec;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class MySample1130_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc"; //문자열 리터럴 "abc"의 주소가 str1에 저장
String str2 = "abc"; //문자열 리터럴 "abc"의 주소가 str2에 저장
//(결과는 str1과 str2는 문자열 "abc"를 같이 바라봄)
System.out.println("String str1 = \"abc\";");
System.out.println("String str2 = \"abc\";");
System.out.println(str1); //.toString()메소드 생략되어있음
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println("str1 == str2 : " + (str1 == str2)); //String객체는 == 연산자 할 때 객체가 가지고 있는 값을 비교함.
System.out.println("str1.equals(str2) : " + str1.equals(str2)); //String타입은 .equals로 비교하는 것이 좋음
System.out.println();
String str3 = new String("\"abc\""); //새로운 String인스턴스 생성
String str4 = new String("\"abc\""); //새로운 String인스턴스 생성
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
System.out.println("str3 == str4 : " + (str3 == str4));
System.out.println("str3.equals(str4) : " + str3.equals(str4));
System.out.println();
/*
* 확장형 for문
* String[] arr = {"a", "b", "c"};
* for(String s : arr)
*/
String animals = "dog,cat,bear";
String[] arr = animals.split(",");
for(String s : arr) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.join("-", arr)); //문자열과 문자열 사이에 "-"로 구분
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner("/","[","]");
//문자열을 add할때 - 문자열과 문자열사이 들어갈것(-), 문자열 시작에 들어갈 것([), 문자열 끝에 들어갈 것(])
for(String s : arr){
sj.add(s);
}
System.out.println(sj.toString());
}
}Calendar 클래스 : 추상 클래스이므로 객체를 직접생성할 수 없고, 메서드를 통해서 완전히 구현된 인스턴스를 얻어야 한다.
* Calendar클래스의 주요 상수(static final int) - 아래 표에는 final이 생략되어 있다.
cf) 상수 변수는 모두 대문자를 사용하고, 단어와 단어 사이에는 _(언더바)를 넣어준다.
| 상수 | 사용방법 | 설명 |
| static int YEAR | Calendar.YEAR | 현재 년도를 가져온다 |
| static intMONTH | Calendar.MONTH | 현재 월을 가져온다.(1월은 0) |
| static intDATE | Calendar.DATE | 현재 월의 날짜를 가져온다. |
| static intWEEK_OF_YEAR | Calendar.WEEK_OF_YEAR | 현재 년도의 몇째 주 |
| static intWEEK_OF_MONTH | Calendar.WEEK_OF_MONTH | 현재 월의 몇째 주 |
| static intDAY_OF_YEAR | Calendar.DAY_OF_ YEAR | 현재 년도의 날짜 |
| static intDAY_OF_MONTH | Calendar.DAY_OF_ MONTH | 현재 월의 날짜(DATE와 동일) |
| static intDAY_OF_WEEK | Calendar.DAY_OF_ WEEK | 현재 요일(일요일1, 토요일7) |
| static intHOUR | Calendar.HOUR | 현재시간 (12시간제) |
| static intHOUR_OF_DAY | Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY | 현재시간 (24시간제) |
| static intMINUTE | Calendar. MINUTE | 현재 분 |
| static intSECOND | Calendar. SECOND | 현재 초 |
cf) 추상클래스의 추상메소드를 쓰는 이유 -> 자식클래스가 반드시 그 메소드를 정의해야함을 부여
인터페이스
* Calendar클래스 메소드
Calendar cal = new Calendar(); //에러. 추장클래스는 인스턴스 생성불가
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); //이렇게 객체생성 해야함
** 예제 MySample1130_8 (캘린더) **
package exec;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class MySample1130_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 캘린더 클래스
Calendar today = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("년도 : " + today.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println("월, 1월(0) : " + today.get(Calendar.MONTH));
System.out.println("올해의 몇째 주 : " + today.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_YEAR));
System.out.println("이번달의 몇째 주 : " + today.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("이달의 며칠 : " + today.get(Calendar.DATE));
System.out.println("올해의 며칠 : " + today.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
System.out.println("요일1(일요일) : " + today.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));
System.out.println("이달의 몇째 요일 : " + today.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH));
System.out.println("오전/오후(0:오전, 1:오후) : " + today.get(Calendar.AM_PM));
System.out.println("시간(0~11) : " + today.get(Calendar.HOUR)); //12시기준
System.out.println("시간(0~23) : " + today.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)); //24시기준
System.out.println("분(0~59) : " + today.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("초(0~59) : " + today.get(Calendar.SECOND));
System.out.println("이달의 마지막날 : " + today.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DATE));
final String[] DAY_OF_WEEK = {"","일", "월", "화", "수", "목", "금", "토"};
Calendar date1 = Calendar.getInstance();
Calendar date2 = Calendar.getInstance();
date1.set(2001, 3, 8);
System.out.println("date2 : " + toString2(date2) + DAY_OF_WEEK[date2.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)] + "요일입니다.");
System.out.println("date1 : " + toString2(date1) + DAY_OF_WEEK[date1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)] + "요일입니다.");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=== 1일 후 ===");
date2.add(Calendar.DATE, 1);
System.out.println(toString2(date2));
System.out.println("=== 5달 전 ===");
date2.add(Calendar.MONTH, -5);
System.out.println(toString2(date2));
System.out.println("=== 31일 후 ===(roll)");
date2.roll(Calendar.DATE, 20); //roll -> 일만 바꿔준다.(월은 변경되지 않음)
System.out.println(toString2(date2));
System.out.println("=== 31일 후 ===(add)");
date2.add(Calendar.DATE, 20); //add -> 월과 일을 같이 바꿔준다.
System.out.println(toString2(date2));
}
public static String toString2(Calendar date) {
return date.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "년 " + (date.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1) + "월 " + date.get(Calendar.DATE)+ "일 ";
}
}** 예제 MySample1130_9 (캘린더) **
// 월과 년을 입력받았을 때 날짜를 알려주는 프로그램
package exec;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class MySample1130_9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 월과 년을 입력받았을 때 날짜를 알려주는 프로그램
System.out.println("args.length : " + args.length);
if(args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("args 오류 ... 년과 월을 입력하세요.>");
return; //밑에 있는거 실행하지 않고 나를 호출한 곳으로 돌아감 (여기서는 JVM이라서 프로그램종료)
}
System.out.println("성공 ...");
//* args배열에 값입 력하는 법
//Project Explorer의 현재 클래스 우클릭 -> run as -> run configurations... -> arguments -> program arguments에 스페이스 기준으로 입력
int year = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int month = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
Calendar sDay = Calendar.getInstance(); //시작일
Calendar eDay = Calendar.getInstance(); //끝일
sDay.set(year, month-1, 1);
//해당월의 마지막날 - 입력월의 마지막날 getActualMaximun 이용
eDay.set(year, month-1, sDay.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DATE));
//1일이 속한 주의 일요일로 날짜 선정
sDay.add(Calendar.DATE, -sDay.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) + 1);
//말일이 속한 주의 토요일 날짜 선정
eDay.add(Calendar.DATE, 7 - eDay.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));
System.out.println(" " + year + "년 " + month + "월");
System.out.println(" 일 월 화 수 목 금 토");
//시작일부터 마지막일까지 (sDay <= eDay) 1일씩 증가 시키면서
//일(Calendar.DATE)출력
int day;
for(int n = 1 ; sDay.before(eDay)||sDay.equals(eDay) ; sDay.add(Calendar.DATE, 1)) {
day = sDay.get(Calendar.DATE);
System.out.print((day < 10) ? (" " + day) : (" " + day));
if(n++ % 7 == 0) System.out.println();
}
}
}
| 12/04 수업 (23일차) _ Vector / Stack & Queue / LinkedList (1) | 2023.12.04 |
|---|---|
| 12/01 수업 (22일차) _ SimpleDateFormat / 컬렉션 프레임웍 (Collections Framework) / (2) | 2023.12.01 |
| 11/29 수업 (20회차) _ 예외 처리 (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
* 예외처리란?
- 프로그램 실행시 발생할 수 있는 예기치 못한 예외의 발생에 대비한 코드를 작성하는 것
- 목적 : 예외 발생시 실행중인 프로그램의 갑작스런 비정상 종료를 막고, 비정상 종료를 막아 정상적인 실행 상태를 유지할 수 있도록 하는 것
- 구조
try{
예외처리하길 원하는 실행코드;
}
// catch는 여러개 사용가능함
catch(Exception1 e1){
Exception1이 발생했을 경우, 처리하기위한 문장
}
catch(Exception2 e2){
Exception2이 발생했을 경우, 처리하기위한 문장
}
....
finally{
예외발생 여부와 상관없이 무조건 실행될 코드
}
프로그램이 실행 중 어떤 원인의 의해서 오작동을 하거나 비정상적으로 종료되는 경우를 프로그램 에러 또는 오류하고 함.
프로그램이 실행되는 도중 발생하는 예외를 처리하기 위해
try / catch / finally 문을 사용
| 컴파일 에러 | - 컴파일 시에 발생하는 에러 |
| 런타임 에러 | - 실행 시에 발생하는 에러 |
| 논리적 에러 | - 실행은 되지만, 의도와 다르게 동작하는 것 |
* 자바에서 실행 시 발생할 수 있는 프로그램 오류
- 에러(error) : 프로그램 코드에 의한 수습될 수 없는 심각한 오류
- 예외(exception) : 프로그램 코드에 의해서 수습될 수 있는 오류
예외가 발생하더라도 프로그래머가 이에대한 적절한 코드를 미리 작성해 놓아 프로그램이 비정상적으로 종료되는 것을 막는 것을 의미함.
- 예외 클래스 계층구조 : 모든 예외의 최고 조상은 Exception클래스
FileNotFoundException
ClassNotFoundException
DataFormatException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
** 예제 exec Pakage _ MySample1129 (예외처리) **
package exec;
public class MySample1129 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리
int[] a = {2, 0};
int b = 4;
//int c =a[2]; //먼저 실행 후 오류 확인
try {
int c = b / a[2]; //int c = a[2];
System.out.println("c " + c);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("배열 인덱스 오류 발생");
}
// catch(ArithmeticException e) {
// System.out.println("0으로 나눌수 없습니다. : " + e);
// }
//프로그램은 위에서 아래로 흐르기에 가장 최고조상인 Exception 은 가장 아래에 있어야 오류 안난다.
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("뭔지몰라 오류 발생 : " + e);
}
finally {
System.out.println("무조건 실행됨");
}
System.out.println("try~catch 끝.");
}
}** 예제 MySample1129 _ 2 (예외처리) **
package exec;
public class MySample1129_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리
//0으로 나누었을 떄 "0으로 나눌 수 없습니다." 메세지 출력 후 계속 진행
int number = 10;
int result = 0;
int i;
// try {
// for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
// result = number/(int)(Math.random( )* 10);
// System.out.println("result " + result);
// }
// }
// catch(ArithmeticException e) {
// System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.: " + e);
// }
//
//
// for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
// try {
// result = number/(int)(Math.random( )* 10); //0~9
// System.out.println("result " + result);
// }
// catch(ArithmeticException e) {
// System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.: " + e);
// }
//
// }
//실행순서
System.out.println("1");
try {
System.out.println("2");
int a = 5 / 0;
System.out.println("3");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("4");
}
finally {
System.out.println("4-2");
}
System.out.println("5");
}
}** 예제 MySample1129_3 (예외처리) **
package exec;
public class MySample1129_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리
System.out.println("1");
try {
System.out.println("2");
System.out.println(2 / 0);
System.out.println("3");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("4");
if(e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("true");
System.out.println("ArithmeticException");
e.printStackTrace(); //디버깅용
System.out.println("예외 메세지 : " + e.getMessage());
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("5");
System.out.println("예외 메세지 : " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("6");
}
}** 예제 MySample 1129_4 (예외발생시켜보기)**
package exec;
public class MySample1129_4 extends Exception{
MySample1129_4(String a){
super(a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//예외발생
try {
MySample1129_4 e = new MySample1129_4("일부러 오류 발생 시켰음.");
//Exception e = new Exception("일부러 오류 발생 시켰음.");
throw e; //예외를 발생시키는 throw
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("에러메세지 : " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 종료 되었음.");
}
}** 예제 MySample 1129_5 (메서드예외) **
package exec;
public class MyClass1129_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리 - 메서드 예외
// 예)void method() throws Exception1,Exception2,.....{ }
try {
method1();
System.out.println("555555555555555");
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("e.message : " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("main 끝.");
}
//메소드 예외처리 : throws Exception 있으면 모든 예외를 나를 호출한 곳에서 try/catch.
//throws Exception 메서드에 예외가 발생하면 더이상 실행하지 않고 나를 호출한 곳으로 돌아간다.
static void method1() throws Exception{
System.out.println("111111111111111");
method2();
System.out.println("222222222222222");
}
static void method2() throws Exception{
System.out.println("333333333333333");
int c = 5 / 0;
System.out.println("444444444444444");
}
}** 예제 MySample 1129_6 ( 예외처리 - finally블럭 ) **
package exec;
public class MySample1129_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리 - finally블럭
try {
startInstall();
copyFiles();
//deleteTempFiles();
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//deleteTempFiles();
}
finally {
deleteTempFiles(); //try/catch 둘다사용해야하는 경우는 보통 finally로 빼준다.
}
method1();
System.out.println("method1() 실행 끝나고 main으로 돌아옴.");
}
static void startInstall() {
System.out.println("프로그램 설치에 필요한 준비작업하는 영역..");
}
static void copyFiles() {
System.out.println("파일들을 복사하는 영역..");
}
static void deleteTempFiles() {
System.out.println("임시파일들 삭제하는 영역..");
}
static void method1() {
try {
System.out.println("method1() 실행시작");
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
System.out.println("method1() finally블럭실행");
}
}
}** 예제 MySample 1129_7 (클래스 예외처리 - 예외클래스 생성 후 다른클래스 메소드에서 예외처리) **
package exec;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySample1129_7 {
static Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in); //main메소드가 static이라서
public static int inputScore() throws ScoreException{ //예외 클래스 만든것을 메소드에서 예외처리함
int score = scn.nextInt();
if(score < 0 || score > 100){
ScoreException ex = new ScoreException("점수는 0~100점 사이 입력하세요.");
throw ex;
}
return score;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리(클래스)
try {
System.out.print("국어 점수 입력>");
int kor = inputScore();
System.out.println("국어 점수는 " + kor + "점 입니다.");
System.out.print("영어 점수 입력>");
int eng = inputScore();
System.out.println("영어 점수는 " + eng + "점 입니다.");
}
catch(ScoreException ex) {
System.out.println("오류메세지 : " + ex.getMessage());
}
finally {
System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
}
}
}
class ScoreException extends Exception{ //예외처리클래스
ScoreException(){
super("점수 입력 오류");
}
ScoreException(String nsg){
super(nsg);
}
}** 문제 MySample1129_8 (예외처리) **
// 예외처리 - 문제
/*
* 20번 반복해서 랜덤발생을 0~9까지 발생시킨후 랜덤값으로 나눈 결과를 화면에 출력하되 0으로 나누면 오류 발생함.
* ArithmeticException 에 대한 예외처리를 적용하고 예외에 대한 출력은 0으로 처리하고, 0으로 나눈 횟수 발생한
* 건수를 최종 출력하는 프로그램
* 출력예)
* 16
* 20
* 11
* 0 -> 랜덤발생이 0으로 되어 예외처리부분.
* 33
* 100
* ...
* 0 발생 건수 : 1건
* 단, number = 100; 으로 초기 설정 후 (int)(Math.random() * 10); 처리함
*/
package exec;
public class MySample1129_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예외처리 - 문제
/*
* 20번 반복해서 랜덤발생을 0~9까지 발생시킨후 랜덤값으로 나눈 결과를 화면에 출력하되 0으로 나누면 오류 발생함.
* ArithmeticException 에 대한 예외처리를 적용하고 예외에 대한 출력은 0으로 처리하고, 0으로 나눈 횟수 발생한
* 건수를 최종 출력하는 프로그램
* 출력예)
* 16
* 20
* 11
* 0 -> 랜덤발생이 0으로 되어 예외처리부분.
* 33
* 100
* ...
* 0 발생 건수 : 1건
* 단, number = 100; 으로 초기 설정 후 (int)(Math.random() * 10); 처리함
*/
int number = 100;
int result, cnt = 0;
int i;
// for (i = 0 ; i < 20 ; i++) {
// try {
// result = number / (int)(Math.random() * 10);
// System.out.println(result);
// }
// catch(ArithmeticException a) {
// result = 0;
// cnt++;
// System.out.println(result);
// }
// }
// System.out.println("0 발생 건수 : " + cnt);
// //다른방법 (깔끔함)
// for (i = 0 ; i < 20 ; i++) {
// try {
// result = number / (int)(Math.random() * 10);
// }
// catch(ArithmeticException a) {
// result = 0;
// cnt++;
// }
// finally {
// System.out.println(result);
// }
// }
// System.out.println("0 발생 건수 : " + cnt);
//결과는 위화 동일하며 try~catch문을 사용하지 않고 프로그램 구현.
for (i = 0 ; i < 20 ; i++) {
int tmp = (int)(Math.random() * 10);
if(tmp != 0) {
result = number / tmp;
}
else {
result = 0;
cnt++;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
System.out.println("0 발생 건수 : " + cnt);
}
}
| 12/01 수업 (22일차) _ SimpleDateFormat / 컬렉션 프레임웍 (Collections Framework) / (2) | 2023.12.01 |
|---|---|
| 11/30 수업 (21회차) _ java.lang패키지 / String 클래스 / Calendar클래스 (2) | 2023.11.30 |
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
| 11/22 수업 (17일차) _ 접근 제어자 / 다형성 (1) | 2023.11.22 |
자바에서 다중상속은 지원하지 않으므로, 인터페이스를 통해 다중상속 지원
다른 클래스를 작성할 때 기본이 되는 틀을 제공하면서, 다른 클래스 사이의 중간 매개 역할 까지 담당하는 추상 클래스를 의미함
추상 클래스 - 추상메소드, 생성자, 필드, 일반 메소드로 포함
인터페이스 - 오로지 추상 메소드( public abstract )와 상수( public static final )만을 포함
인터페이스클래스에 있는 메소드는 모두 추상메소드 → abstract 를 쓰지않아도 컴파일러자 자동으로 추상메소드로 읽어준다.
문법) 인터페이스이름 = 클래스이름
| 문법) 접근제어자 interface 인터페이스이름{ public static final 타입 상수이름 = 값; ... public abstract 리턴타입 메소드이름(매개변수목록); ... } //인터페이스를 상속 받을 때 문법 class 클래스이름 implements 인터페이스이름 {...} //인터페이스이름자리에 , 로 여러개의 인터페이스클래스 명 올 수 있다. |
| 모든 필드는 public static final 모든 메소드는 public abstract 제어자( public static final , public abstract )는 생략 가능하며 생략된 제어자는 컴파일시 자동 추가 |
** 예제 1128 **
package inter;
interface Animal{
public static final int A = 10; //public static final 생략 가능
public abstract void cry(); //public abstract 생략 가능
}
class Cat implements Animal{
public void cry() {
System.out.println("야옹야옹..");
}
}
class Dog implements Animal{
public void cry() {
System.out.println("멍멍..");
}
}
public class MySample1128 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인터페이스
Cat c = new Cat();
Dog d = new Dog();
c.cry();
d.cry();
}
}** 예제 1128_2 **
package inter;
interface Providable{
public abstract void leisureSports(); //레저스포즈
public abstract void sightSeeling(); //관광
public abstract void food(); //음식
}
class KoreaTour implements Providable{
public void leisureSports() {
System.out.println("한강에서 수상스키 투어");
}
public void sightSeeling() {
System.out.println("경복궁 관광 투어");
}
public void food() {
System.out.println("불고기");
}
}
class TourGuide{
private Providable tour = new KoreaTour();
public void leisureSports() {
tour.leisureSports();
}
public void sightSeeling() {
tour.sightSeeling();
}
public void food() {
tour.food();
}
}
public class MySample1128_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인터페이스 (캡슐, 상속, 다형성)
TourGuide guide = new TourGuide();
guide.leisureSports();
guide.sightSeeling();
guide.food();
}
}** 문제 1125_3 **
package inter;
/*
문제) 인터페이스 Animal2 와 Pet을 정의하며, Animal2 클래스는 울음소리(cry)를 Pet클래스는 움직임(play)를 정의함.
고양이2 클래스와 강아지2 클래스에서 울음소리와 움직임에 대한 재정의를 구현함.
단, 고양이는 울음소리는 "야오야용" 움직임은 "폴짝폴짝 뛰어다니기"로 출력하고
강아지는 울음소리는 "멍멍" 움식임은 "산책하기"로 출력함.
*/
interface Animal2{
public abstract String cry();
}
interface Pet{
public abstract void play();
}
class Cat2 implements Animal2, Pet{
public String cry() {
return "야옹야옹";
}
public void play() {
System.out.println("폴짝폴짝");
}
}
class Dog2 implements Animal2{
public String cry() {
return "몽몽";
}
public void play() {
System.out.println("산책하기");
}
}
public class MySample1128_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인터페이스를 통한 다중상속 (implements A, B)
Dog2 d = new Dog2();
Cat2 c = new Cat2();
System.out.println(c.cry());
c.play();
System.out.println();
System.out.println(d.cry());
d.play();
}
}** 예제 1128_4 **
package inter;
interface Gamer{
public static final int GAME_MAX_LEVEL = 100;
public abstract void doGame();
}
interface Singer{
int AUDITION_MAX_CHANCE = 10; //public static final 이 생략됨
int GAME_MAX_LEVEL = 99; //public static final 이 생략됨
void singSong(); //public abstract 생략됨
}
class Student implements Gamer, Singer{
String name;
int score;
Student(String name, int score){
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public void doGame() {
System.out.println(name + "은 게임을 합니다.");
}
public void singSong() { //메소드 오버라이딩하려면 접근지정자까지 일치해야해서 생략된 public써줘야한다.
System.out.println(name + "은 노래를 부릅니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1128_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인터페이스 다중상속
Student s = new Student("김둘리", 83);
System.out.println("게임의 최고 레벨(Gamer) : " + Gamer.GAME_MAX_LEVEL);
System.out.println("가수의 최고 레벨(Singer) : " + Singer.GAME_MAX_LEVEL);
s.doGame();
System.out.println(s.name + "의 점수 : " + s.score);
System.out.println("오디션 최대 기회 : " + Singer.AUDITION_MAX_CHANCE);
}
}** 문제 inter2 pakage (RemoteControl) **
package inter2;
public interface RemoteControl {
public static final int MAX_VOLUME = 10;
public static final int MIN_VOLUME = 0;
void turnOn();
public abstract void turnOff();
public abstract void setVolume(int volume);
}
/*
turnOn 은 "TV를 켭니다." 또는 "오디오를 켭니다." / turnOff는 "TV를 끕니다." 또는 "오디오를 끕니다."
setVolume은 max값과 min값에 대한 체크 후 tv는 "현재 TV볼륨은 : 5", 오디오는 "현재 오디오볼륨은 : 7"
출력예)1111111111
TV를 켭니다.
현재 TV볼륨 : 5
2222222222
오디오를 켭니다.
현재 오디오볼륨 : 5
오디오를 켭니다.
현재 오디오볼륨 : 5
3333333333
오디오를 겹니다.
현재 오디오 볼륨 : 5
4444444444
TV를 켭니다.
현재 TV볼륨은 : 5
*/package inter2;
public class Tv implements RemoteControl{
private int volume;
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("TV를 켭니다.");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("TV를 끕니다.");
}
public void setVolume(int volume) {
if (volume > MAX_VOLUME) {
this.volume = MAX_VOLUME;
}
else if(volume < MIN_VOLUME) {
this.volume = MIN_VOLUME;
}
else {
this.volume = volume;
}
System.out.println("현재 TV볼륨은 : " + getVolume());
}
public int getVolume() {
return this.volume;
}
}package inter2;
public class Audio implements RemoteControl{
private int volume; //인스터스변수의 접근자가 private이면 보통 set/get메소드 사용한다.
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("오디오를 켭니다.");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("오디오를 끕니다.");
}
public void setVolume(int volume) {
if (volume > MAX_VOLUME) {
this.volume = MAX_VOLUME;
}
else if (volume < MIN_VOLUME) {
this.volume = MIN_VOLUME;
}
else {
this.volume = volume;
}
System.out.println("현재 TV볼륨은 : " + getVolume());
}
public int getVolume() {
return this.volume;
}
}package inter2;
public class MyClass {
RemoteControl rc = new Tv();
MyClass(){
}
MyClass(RemoteControl rc){
this.rc = rc;
rc.turnOn(); //this.rc.turnOn(); -> 둘다 같은의미 (this.rc 에 매개변수 rc를 대입했기때문)
rc.setVolume(5);
this.rc.turnOn();
this.rc.setVolume(5);
}
void methodA() {
RemoteControl rc = new Audio();
rc.turnOn();
rc.setVolume(5);
}
void methodA(RemoteControl rc) { //메소드 오버로딩
rc.turnOn();
rc.setVolume(5);
}
}package inter2;
public class MyClassMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인터페이스
/*출력예)1111111111
TV를 켭니다.
현재 TV볼륨 : 5
2222222222
오디오를 켭니다.
현재 오디오볼륨 : 5
오디오를 켭니다.
현재 오디오볼륨 : 5
3333333333
오디오를 겹니다.
현재 오디오 볼륨 : 5
4444444444
TV를 켭니다.
현재 TV볼륨은 : 5
*/
System.out.println("1111111111");
MyClass myClass1 = new MyClass();
myClass1.rc.turnOn();
myClass1.rc.setVolume(5);
System.out.println("2222222222"); //MyClass에서 생성자를 통해
Audio a = new Audio();
MyClass myClass2 = new MyClass(a); //new MyClass(new Audio()); 사용해도된다 (후에 a 사용없을시)
System.out.println("3333333333"); //MyClass의 매개변수 없는 메소드를 통해
MyClass myClass3 = new MyClass();
myClass3.methodA();
System.out.println("4444444444"); //MyClass의 매개변수 있는 메소드를 통해
MyClass myClass4 = new MyClass();
myClass4.methodA(new Tv());
}
}** 예제 inter3 pakage (그래픽카드) **
package inter3;
public interface GraphicsCard {
//제조사
public abstract String company();
//모델
public String model();
//메모리
public int memory();
//출력
public void write(PointColor pointcolor);
}package inter3;
public class Rgb {
private int red;
private int green;
private int blue;
public Rgb() {
this(0,0,0);
}
public Rgb(int red, int green, int blue) {
this.red = red;
this.green = green;
this.blue = blue;
}
public int getRed() {
return this.red;
}
public void setRed(int red) {
this.red = red;
}
public int getGreen() {
return this.green;
}
public void setGreen(int green) {
this.green = green;
}
public int getBlue() {
return this.blue;
}
public void setBlue(int blue) {
this.blue = blue;
}
}package inter3;
public class PointColor {
//x좌표값
private int x;
//y좌표값
private int y;
//RGB색상표
private Rgb rgb;
public PointColor() {
this(0,0,new Rgb());
}
public PointColor(int x, int y, Rgb rgb) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.rgb = rgb;
}
public Rgb getRgb() {
return this.rgb;
}
public void setRgb(Rgb rgb) {
this.rgb = rgb;
}
public int getX() {
return this.x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return this.y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}package inter3;
public class NvidiaGeForce implements GraphicsCard{
private String company;
private String model;
private int memory;
NvidiaGeForce(String model, int memory){
company = "NVIDIA";
this.model = model;
this.memory = memory;
}
//제조사
public String company() {
return this.company;
}
//모델
public String model() {
return this.model;
}
//메모리
public int memory() {
return this.memory;
}
//출력
public void write(PointColor pointColor) {
if(pointColor != null) {
Rgb rgb = pointColor.getRgb();
System.out.println("---" + company + "GraphicsCard 출력");
System.out.println("1.좌표를 구한다.");
System.out.println("x : " + pointColor.getX());
System.out.println("y : " + pointColor.getY());
System.out.println("2.color 구성.");
// if(rgb != null) {
// System.out.println("Rgb : " + rgb.getRed());
// System.out.println("Green : " + rgb.getGreen());
// System.out.println("Blue : " + rgb.getBlue());
// }
//바로 위 주석을 아래와 같이 변경 가능.
if(pointColor.getRgb() != null) {
System.out.println("Rgb : " + pointColor.getRgb().getRed());
System.out.println("Green : " + pointColor.getRgb().getGreen());
System.out.println("Blue : " + pointColor.getRgb().getBlue());
}
System.out.println("3.모니터 좌표에 색상출력.");
}
}
}package inter3;
public class AmdRadeon implements GraphicsCard{
private String company;
private String model;
private int memory;
public AmdRadeon(String model, int memory) {
this.company = "AMD";
this.model = model;
this.memory = memory;
}
//제조사
public String company() {
return this.company;
}
//모델
public String model() {
return this.model;
}
//메모리
public int memory() {
return this.memory;
}
//출력
public void write(PointColor pointColor) {
if(pointColor != null) {
Rgb rgb = pointColor.getRgb();
System.out.println("---" + company + "GraphicsCard 출력");
System.out.println("1.color를 구성한다.");
if(rgb != null) {
System.out.println("Blue : " + rgb.getBlue()); //pointColor.getRgb().getBlue()
System.out.println("Red : " + rgb.getRed()); //pointColor.getRgb().getBlue()
System.out.println("Green : " + rgb.getBlue()); //pointColor.getRgb().getBlue()
}
System.out.println("2.좌표를 구한다.");
System.out.println("x : " + pointColor.getX());
System.out.println("y : " + pointColor.getY());
System.out.println("3.여기서 모니터 좌표에 색상 출력");
}
}
//제너레이트 사용법 : Source -> Generate Getters and Setters -> selectAll
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public int getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public void setMemory(int memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
}package inter3;
public class GraphicsCardMain {
//.java 에있는 인스턴스변수(private)는 set/get메서드로 접근한다.
//운영체제에서 그래픽 출력
public void operatingSystemWrite(GraphicsCard graphicsCard, PointColor pointColor) {
if (graphicsCard != null) {
System.out.println("그래픽 카드 출력");
System.out.println("회사명 : " + graphicsCard.company());
System.out.println("모델명 : " + graphicsCard.model());
System.out.println("메모리 : " + graphicsCard.memory());
graphicsCard.write(pointColor);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//인터페이스 예제
//라데온 그래픽 카드 생성
GraphicsCard amdRadeon = new AmdRadeon("Rx 5000", 4096);
//엔비디아 그래픽 카드 생성
NvidiaGeForce nvidiaGeForce = new NvidiaGeForce("Gefpre GT 710", 2048);
//포인트 컬러 생성
PointColor pointColor = new PointColor();
pointColor.setX(100);
pointColor.setY(200);
pointColor.setRgb(new Rgb(255,128,100));
// PointColor pointColor = new PointColor(100,200,new Rgb(255,128,100));
GraphicsCardMain gCardMain = new GraphicsCardMain();
gCardMain.operatingSystemWrite(amdRadeon, pointColor);
System.out.println();
gCardMain.operatingSystemWrite(nvidiaGeForce, pointColor);
}
}
| 11/30 수업 (21회차) _ java.lang패키지 / String 클래스 / Calendar클래스 (2) | 2023.11.30 |
|---|---|
| 11/29 수업 (20회차) _ 예외 처리 (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
| 11/22 수업 (17일차) _ 접근 제어자 / 다형성 (1) | 2023.11.22 |
| 11/21 수업 (16일차) _ 오버라이딩 / 접근 제어자 (3) | 2023.11.21 |
** 예제 1123 (다형성) **
class Parent4{
int x = 100;
void method() {
System.out.println("Parent4 method()...");
}
}
class Child4 extends Parent4{
int x = 200;
void method() {
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("super.x = " + super.x);
System.out.println("this.x = " + this.x);
}
}
public class MySample1123 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형선 - 참조형변수와 인스턴스 연결
// 다형성 _ 부모타입의 참조변수로 자식의 객체를 만든다.
Parent4 p = new Child4();
Child4 c = new Child4();
System.out.println("p.x = "+ p.x); //인스턴스 변수는 참조(잠조형변수=부모의 인스턴스변수)하는 값이 찍힌다. p.x = 200
p.method();
System.out.println("c.x = " + c.x);
c.method();
//Parent p = new Child();
//인스턴스 변수
//부모에게 있고 자식에도 있으면 -> 부모꺼 실행
//부모에게 있고 자식에게 없으면 -> 부모꺼 실행
//부모에는 없고 자식에게 있으면 -> 오류2
//메소드
//부모에게 있고 자식에도 있으면 -> 자식꺼 실행 (메소드 오버라이딩)
//부모에게 있고 자식에게 없으면 -> 부모꺼 실행
//부모에는 없고 자식에게 있으면 -> 오류2
}
}** 예제 1123_2 (다형성) **
class Product2{
int price; //제품가격
int bonusPoint; //제품구매시 제공 보너스 점수
Product2(int price){
this.price = price;
bonusPoint = (int)(price / 10.0); //제품가격의 10퍼센트 적용
}
}
class Tv3 extends Product2{
Tv3(){
super(900);
}
public String toString() {
return "Tv";
}
}
class Computer2 extends Product2{
Computer2(){
super(500);
}
public String toString() {
return "Computer";
}
}
class Buyer{
int money = 10000; //보유금액
int bonusPoint = 0; //보유보너스
void buy(Product2 p) { //매개변수의 다형성
if (money < p.price) { //보유금액보다 사려는 가격비 비싼경우 못사게 처리
System.out.println("잔액 부족으로 물건을 살 수 없습니다.");
return; //프로그램 끝
}
money -= p.price; //this.money = this.money - p.price;
bonusPoint += p.bonusPoint; //this.bonusPoint = this.bonusPoint + p.bonusPoint
System.out.println(p + "을(를) 구매하셨습니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1123_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 - 매개변수의 다형성
Buyer b = new Buyer();
System.out.println("현재 보유중인 현금은 " + b.money + "만원 입니다.");
Product2 p = new Tv3(); //Tv3 p = new Tv3(); 으로 해도 결과는 같음 (Buyer 클래스 buy메서드에 매개변수가 매개변수가 다형성)
b.buy(p); //b.buy(new Tv3()); -> main()메서드에서 구매제품에 대한 정보를 알 수 없음.
System.out.println("현재 구매한 가격은 " + p.price + "입니다.");
System.out.println("현재 남은 돈은 " + b.money + "만원 입니다.");
System.out.println("현재 보유중인 보너스 점수는 " + b.bonusPoint + "점 입니다.");
System.out.println("\n");
Product2 p2 = new Computer2();
b.buy(p2);
System.out.println("현재 구매한 가격은 " + p2.price + "입니다.");
System.out.println("현재 남은 돈은 " + b.money + "만원 입니다.");
System.out.println("현재 보유중인 보너스 점수는 " + b.bonusPoint + "점 입니다.");
}
}** 예제 1123_3 (다형성 - 객체를 배열로) **
class Product3{
int price;
int bonusPoint;
Product3(int price){
this.price = price;
this.bonusPoint = (int)(price*0.1);
}
}
class Tv4 extends Product3{
Tv4(){
super(100);
}
public String toString() {
return "Tv";
}
}
class Computer3 extends Product3{
Computer3(){
super(300);
}
public String toString() {
return "컴퓨터";
}
}
class Audio extends Product3{
Audio(){
super(50);
}
public String toString() {
return "오디오";
}
}
class Buyer2{
int money = 1000;
int bonusPoint = 0;
Product3[] item = new Product3[10];
int cnt = 0; //배열에 사용될 카운트
void buy(Product3 p) {
if(money < p.price) {
System.out.println("잔액 부족으로 물건을 살 수 없습니다.");
return;
}
money -= p.price;
bonusPoint += p.bonusPoint;
item[cnt++] = p; //p - 객체의 시작 주소값
System.out.println(p + "을(를) 구매하셨습니다."); //각 클래스에 toString 오버라이딩 메서드 호출
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < item.length ; i++) {
System.out.println("item[" + i + "] : " + item[i]);
}
}
void summary() {
int sum = 0; //구입물품 가격 합계
String itemList = ""; //구입물품 목록
int i;
//구입한 물품 총 가격과 목록
for(i = 0 ; i < item.length ; i++) {
if(item[i] == null)
break;
sum += item[i].price;
itemList += item[i].toString() + ", ";
}
System.out.println("구입하신 물품의 총 금액은 " + sum + "만원 입니다.");
System.out.println("구입하신 제품은 "+ itemList + "입니다.");
System.out.println("구입하신 제품의 총 보너스 점수는 " + bonusPoint + "점 입니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1123_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 - 객체를 배열로
Buyer2 b = new Buyer2();
b.buy(new Tv4());
b.buy(new Computer3());
b.buy(new Audio());
b.summary();
}
}
- 자바의 배열은 고정 길이를 사용함. 즉, 배열이 한번 생성되면 배열의 길이를 증가하거나 감소 할 수 없다는 단점이 있음. (배열복사 말고)
- Vector클래스는 가변길이의 배열이라고 할 수 있음. (내부적으로 배열복사)
- 즉 Vector클래스는 객체에 대한 참조값을 저장하는 배열이므로 다양한 객체들이 하나의 Vectoer에 저장될 수 있고 길이도 필요에 따라 증감할 수 있다는 점이 배열과 다른 점이다.
.Vector 클래스의 생성자
| Vector 클래스의 생성자 | 설 명 |
| Vector() | 10개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다. 저장공간이 부족한 경우 10개씩 증가한다. |
| Vector(int size) | size 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다. 저장공간이 부족할 경우 size개씩 증가한다. |
| Vector(int size, int incr) | size 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다. 저장공간이 부족한 경우 incr개씩 증가한다. |
. Vetor 클래스의 주요 메서드
| 메서드 / 생성자 | 설 명 |
| Vector() | 10개의 객체를 저장할 수 있는 Vector인스턴스를 생성한다. 10개이상의 인스턴스가 저장되면, 자동적으로 크기가 증가된다. |
| boolean add(Object o) | Vector에 객체를 추가한다. 추가에 성공하면 결과값으로 true, 실패하면 false를 반환한다. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Vector에 객체를 제거한다. 제거에 성공하면 결과값으로 true, 실패하면 false를 반환한다. |
| boolean isEmpty(Object o) | Vector가 비어있는지 검사한다. 비어있으면 결과값으로 true, 비어있지 않으면 false를 반환한다. |
| boolean get(int index) | 저장된 위지(index)의 객체를 반환한다. 반환타입이 Object타입이므로 적절한 타입으로의 형변환이 필요하다. |
| int size() | Vetor에 저장된 객체의 개수를 반환한다. |
** 예제 1123_4 **
import java.util.Vector;
class Buyer3{
int money = 1000;
int bonusPoint = 0;
Vector item = new Vector();
void buy(Product3 p) {
System.out.println("vector size() : " + item.size());
if(money < p.price) {
System.out.println("잔액이 부족하여 물건을 살 수 없습니다.");
return;
}
money -= p.price;
bonusPoint += p.bonusPoint;
item.add(p);
System.out.println(p + "을(를) 구매하셨습니다.");
}
void summary() {
int sum = 0;
String itemList = "";
int i;
Product3 p = null;
if(item.isEmpty() == true) { //if(item.size()==0)
System.out.println("구입한 물건이 없습니다.");
return;
}
for(i = 0 ; i < item.size() ; i++) {
// p = (Product3)item.get(i); //p == item.get(i) ???
sum += p.price;
itemList += (i == 0) ? p : ("," + p) ; //p + ", ";
}
System.out.println("구입한 총 금액 " + sum + "만원 입니다.");
System.out.println("구입한 물품은 " + itemList + "입니다.");
}
//환불
void refund(Product3 p) {
if(item.remove(p)) {
money += p.price;
bonusPoint -= p.bonusPoint;
System.out.println(p + "을(를) 반풍하셨습니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("해당제품이 없습니다.");
}
}
}
public class MySample1123_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Vector() 클래스
Buyer3 b = new Buyer3();
Tv4 t = new Tv4();
Computer3 com = new Computer3();
Audio audio = new Audio();
b.buy(t);
b.buy(com);
b.buy(audio);
b.summary();
System.out.println("\n");
//환불
b.refund(com);
b.summary();
b.refund(com); //이미 삭제된 상품이므로 vector에 없음. 오류발생
}
}- 하나 이상의 추상 메소드를 포함하는 클래스를 의미함
- 추상메소드 : 자식클래스에서 반드시 오버라이딩 해야만 사용할 수 있는 메소드
- 반드시 사용되어야 하는 메소드를 추상클레스에 추상메소드로 선언을 하면, 이 클래스를 상속받는 모든 클래스에서 이 추상 메소드를 반드시 재정의 해야함
abstract class 클래스 이름 {
...
abstract 반환타입 메소드이름();
...
}
- 추상클래스는 추상메소드를 포함하고 있다는 점 이외에는 일반 클래스와 모든점이 같다. 즉 생성자와 변수, 일반 메소드도 포함 할 수 있음.
** 예제 abs패키지 _ 1123_5 **
package abs;
abstract class Animal{
int num;
void numChk() {
System.out.println("num : " + num);
}
abstract void cry(); //추상클래스에는 추상메서드가 있어야한다.
}
class Cat extends Animal{
void cry() { //추상클래스에 있는 추상메소드 오버라이딩 한 것. but 상속받는 클래스에서 오버라이딩 할 때는 abstarct 쓰지 않는다.
System.out.println("야오야옹");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void cry() {
System.out.println("멍멍....");
}
}
public class MySample11223_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 추상클래스
//Animal a = new Animal(); //추상클래스는 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없음.(객체생성 불가)
Cat c = new Cat(); //Animal c = new Cat(); 가능
Dog d = new Dog(); //Animal d = new Dog(); 가능
c.cry();
d.cry();
}
}** 예제 abs패키지 _ 1123_6 (포켓몬) **
package abs;
abstract class Pokemon
{
private String name;
// Pokemon(){
//
// }
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
abstract void attack(); //공격
abstract void sound(); //소리
}
class Pikachu extends Pokemon{
Pikachu(){
super.setName("피카츄");
}
void attack() {
System.out.println("전기공격");
}
void sound() {
System.out.println("피카피카");
}
}
class Spuirtle extends Pokemon{
Spuirtle(){
setName("꼬부기");
}
void attack() {
System.out.println("물뿌리기 공격");
}
void sound() {
System.out.println("꼬북꼬북");
}
}
public class MySample1123_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//추상클래스
Pikachu p1 = new Pikachu();
System.out.println("포켓몬 이름은 " + p1.getName());
p1.attack();
p1.sound();
Spuirtle s1 = new Spuirtle();
System.out.println("포켓몬 이름은 " + s1.getName());
s1.attack();
s1.sound();
}
}
** abs2 패키지 _ 추상클래스 상속 _ Animal 클래스 / Bird 클래스 / Cat 클래스 / Dog 클래스 **
package abs2;
public abstract class Animal {
//동물이름
protected String name; //private String name;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//어떻게 우는지
public abstract String getCry();
//어떻게 움직이는지
public abstract String getMove();
//무엇을 먹는지
public abstract String getFood();
//출력
public abstract void print();
}* class Bird *
package abs2;
public class Bird extends Animal{
//생성자는 이름(name)을 매개변수로 하는 것과 매개변수가 4개로 생성자를 각각 정의함.
//이름 : name, 울음 : 짹짹, 움직임 : 날아다닌다, 음식 : 벌레
private String cry;
private String move;
private String food;
Bird(String name){
this(name, "짹짹", "날아다닌다", "애벌레");
}
Bird(String name, String cry, String move, String food){
//super(); //생략되어있다.
setName(name); //super. 생략
setCry(cry);
setMove(cry);
setFood(food);
}
public String getCry() {
return this.cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry) {
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove() {
return this.move;
}
public void setMove(String move) {
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood() {
return this.food;
}
public void setFood(String food) {
this.food = food;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Bird [name : "+ getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + "]");
}
}* class Cat *
package abs2;
public class Cat extends Animal{
private String cry;
private String move;
private String food;
Cat(String name){
this(name, "야옹", "걸어댜녀요", "생선");
}
Cat(String name, String cry, String move, String food){
setName(name);
setCry(cry);
setMove(move);
setFood(food);
}
public String getCry() {
return this.cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry) {
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove() {
return this.move;
}
public void setMove(String move) {
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood() {
return this.food;
}
public void setFood(String food) {
this.food = food;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Cat [name : " + getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + "]");
}
}* class Dog *
package abs2;
public class Dog extends Animal {
//멍멍, 촐랑촐랑 뛴다. 사료
private String cry;
private String move;
private String food;
Dog(String name){
this(name, "멍멍", "촐랑촐랑 뛴다", "사료");
}
Dog(String name, String cry, String move, String food){
setName(name); //super.name = name;
setCry(cry);
setMove(move);
setFood(food);
}
public String getCry() {
return this.cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry) {
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove() {
return this.move;
}
public void setMove(String move) {
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood() {
return this.food;
}
public void setFood(String food) {
this.food = food;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Dog [name : " + getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + "]");
}
}package abs2;
public class AnimalMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 추상클래스 메인
Dog dog = new Dog("재롱이");
Cat cat = new Cat("나비");
Bird bird = new Bird("짹짹이");
cat.print();
System.out.println();
dog.print();
System.out.println();
bird.print();
System.out.println();
cat.setCry("어흥");
cat.print();
System.out.println();
bird.setMove("펄럭펄럭");
bird.print();
System.out.println();
dog.setFood("건조 닭고기");
dog.print();
}
}** 실습 abs1 패키지 **
/*
*추상클래스
*문제)Animal클래스를 추상클래스로 정의하고 이름(name), 나이(age) 변수를 정의하고 생성자(매개변수2개)를 통해 값 저장
* 이동하는 메서드(move)로 먹는 메서드(eat)로 정의하여 이동은 "이동한다", 먹는것은 "먹는다"로 출력함.
* 자식 클래스(Dog, Cat)에서 반드시 재정의 하도록 bark() 메서드로 짖는걸 구현함.
*출력예)이동한다.
* 멍멍
* 먹는다.
*
* 이동한다.
* 야옹
* 먹는다.
*/
| 11/29 수업 (20회차) _ 예외 처리 (0) | 2023.11.29 |
|---|---|
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 11/22 수업 (17일차) _ 접근 제어자 / 다형성 (1) | 2023.11.22 |
| 11/21 수업 (16일차) _ 오버라이딩 / 접근 제어자 (3) | 2023.11.21 |
| 11/17 수업 (15회차) _ 상속 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
** 문법 **
trim() : 문자열의 맨앞과 맨 뒤 공백만 제거
replace(" ","") : 문자열에서 첫번째 인수를 찾아 두번쨰 인수로 변경
replaceAll(" ", "") : 문자열에서 첫번째인수를 찾아 두번째 인수로 변경
public class MyProject1121_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//접근제어자
//******************************************************************************
/* 문법
trim() : 문자열의 맨앞과 맨 뒤 공백만 제거
replace(" ","") : 문자열에서 첫번째 인수를 찾아 두번쨰 인수로 변경
replaceAll(" ", "") : 문자열에서 첫번째인수를 찾아 두번째 인수로 변경
*/
String tmp = " 홍 길동 ";
System.out.println("trim() : [" + tmp.trim() + "]");
System.out.println("replace() : [" + tmp.replace(" ", "") + "]");
System.out.println("replace() : [" + tmp.replaceAll(" ", "홍") + "]");
//******************************************************************************
}
}** 실습 1122 (접근제어자 + 오버라이딩)**
/* 접근제어자, 오버라이딩
*출력예)좋은 아침입니다. 오전에는 맑음 입니다.
* 즐거운 점심입니다. 점심에는 흐림입니다.
* 행복한 오후되세요. 오후에는 비가 내리겠습니다.
*단, greeting메서드를 이용함
*/
class Today{ //extends Object 생략
private String weather;
public String getWeather() {
return this.weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
void greeting() {
System.out.println("즐거운 하루 되세요.");
}
// //자식클래스 생성자에 super(weather); 사용할 경우
// Today(String weather){
// setWeather(weather);
// }
}
class Morning extends Today{
Morning(String weather){
//super(); //생략되어있다.
setWeather(weather); //super. 생략됨 (Morning 클래스에 setWeather 메서드가 없기때문)
// //super(weather);
}
void greeting() {
System.out.println("좋은 아침입니다. 오전에는 " + super.getWeather() + "입니다.");
//super. 생략가능 (Morning 클래스에 setWeather 메서드가 없기때문)
}
}
class Lunch extends Today{
Lunch(String weather){
setWeather(weather);
}
void greeting() {
System.out.println("즐거운 점심 입니다. 점심에는 " + getWeather() + "입니다.");
}
}
class Dinner extends Today{
Dinner(String weather){
super.setWeather(weather);
}
void greeting() {
System.out.println("행복한 오후되세요. 오후에는 " + getWeather() + "가 내리겠습니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1122 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속 + 오버라이딩
Morning m = new Morning("맑음");
Lunch l = new Lunch("흐림");
Dinner d = new Dinner("비");
m.greeting();
l.greeting();
d.greeting();
}
}** 실습 1122_2 (오버라이딩 + 접근제어자) **
class Car3{
private int door;
private String gearType;
private String color;
Car3(String color){
//setColor(color);
//setGearType("auto");
//setDoor(4);
this(color, "auto", 4); //this. 같은 클래스 내에있는 타입갯수와 종류에 맞는 생성자 불러옴
}
Car3(String color, String gearType){
//setColor(color);
//setGearType(gearType);
//setDoor(4);
this(color, gearType, 4);
}
Car3(String color, String gearType, int door){
setColor(color);
setGearType(gearType);
setDoor(door);
}
public int getDoor() {
return this.door;
}
public void setDoor(int door) {
this.door = door;
}
public String getGearType() {
return this.gearType;
}
public void setGearType(String gearType) {
this.gearType = gearType;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
class SportsCar extends Car3{
int speedLimit; //제한속도
SportsCar(String color){
super(color);
//setColor(color); //super(); 생략되어있어서 오류남
this.speedLimit = 200;
}
SportsCar(String color, int speedLimit){
super(color);
this.speedLimit = speedLimit;
}
SportsCar(String color, String gearType){
super(color, gearType);
this.speedLimit = 200;
}
SportsCar(String color, String gearType, int speedLimit){
super(color, gearType);
this.speedLimit = speedLimit;
}
SportsCar(String color, String gearType, int door, int speedLimit){
super(color, gearType, door);
this.speedLimit = speedLimit;
}
public String toString() {
return "차량의 색은 "+ getColor() +"이고, " + getGearType() + "이며, 문의 개수는 " + getDoor() + "개이며," + " 제한 속도는 " + speedLimit + " 입니다.";
}
}
public class MySample1122_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
실행결과)차량의 색은 red이고, auto이며, 문의 개수는 4개이며,
제한 속도는 330 입니다.
(단, 차량 색은 반드시 입력받고, 제한속도가 없을 경우 200, 기어타입이 없을 경우 auto로 정의함)
문 개수가 없을 경우 기본 4개로 정의함.
클래스와 변수는 세팅되있는것만 사용한다.
단 정수가 하나만들어온 경우 speedLimit으로 여긴다.
*/
SportsCar cs = new SportsCar("red", 330);
System.out.println(cs.toString()); //.toString 생략되어있음
}
}하나의 객체가 여러가지 타입을 가질 수 있는 것을 의미.
부모 클래스 타입의 참조 변수로 자식클래스 타입의 인스턴스를 참조 할 수 있도록 구현.
참조 변수의 다형성
class Parent{...}
class Chlid extends Parent{...}
...
Parent pa = new Parent(); // 허용
chlid ch = new Child(); // 허용
Parent pc = new Chlid(); // 허용
Child cp = new Parent(); // 오류 발생
//상속을 통해 확장된 수 있으나 축소될수는 없음. 자식클래스에서 사용할 수 있는 멤버(인스턴스변수, 인스턴스 메소드...)의 개수가 언제나 부모 클래스와 같거나 많게됨
instanceof : 연산자 / 참조변수가 참조하고 있는 인스턴스 실제 타입 확인
문법)참조변수 instanceof 클래스이름 -> true, false 리턴
| 다형성에서 어떠한 변수와 메소드를 사용할 것인가? * 인스턴스 변수 // 부모에게 있고 자식에도 있으면 -> 부모꺼 실행 // 부모에게 있고 자식에게 없으면 -> 부모꺼 실행 // 부모에는 없고 자식에게 있으면 -> 오류2 * 메소드 // 부모에게 있고 자식에도 있으면 -> 자식꺼 실행 (메소드 오버라이딩) // 부모에게 있고 자식에게 없으면 -> 부모꺼 실행 // 부모에는 없고 자식에게 있으면 -> 오류2 |
** 1122_3 예제 (다형성) **
class A{
void methodA() {
System.out.println("methodA()...");
}
}
class B extends A{
void methodB() {
System.out.println("methodB()...");
}
}
public class MySample1122_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A obj = new B();
obj.methodA(); //가능
// obj.methodB(); //불가능
B obj2 = new B();
obj.methodA(); //가능
obj2.methodB(); //가능
}
}** 예제 1122_4 (다형성) **
class Car4{
String color;
int door;
void drive() {
System.out.println("drive()...Car4");
}
void stop() {
System.out.println("stop()...Car4");
}
}
class FireEngine extends Car4{
void water() {
System.out.println("water()...FireEngine");
}
}
public class MySample1122_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성
// Car4 c = null;
// FireEngine f = new FireEngine();
// FireEngine f2 = null;
//
// f.water();
// c = f; //다형성 => Car4 c = new FireEngine(); 과 같다.
// //내부적으로 형변환이 발생했음.(up-casting)
//
// //c.water(); //불가능(부모형 참조변수로 자식객체를 바라볼수 있으나 자식객체에 메서드는 사용할 수 없음)
//
// f2 = (FireEngine)c; //안되지만 (FireEngine)으로 강제 형변환해서 사용가능
// //down-casting이므로 강제 형변환 꼭해야함.
// f2.water();
//불가능한예제
Car4 c = new Car4(); //= new FireEngine();로 변경하면 1.싫애시에도오류안남
// Car4 c = new FireEngine();
Car4 c2 = null;
FireEngine f = null;
Car4 c3 = new FireEngine();
c.drive();
//f = (FireEngine)c; //f = c; 는 불가능 하나 형변환을 통해서 가능
//컴파일은 가능하나 시행시 오류 발생
f.drive(); // 실행시오류
c2 = f; //up-casting
//c2.water(); //불가능 : c2 참조변수는 클래스 타입이 Sard4이고 water()a메서드는
c2.drive();
c2.stop(); // FireEngine클래스의 메서드이기 떄문에 호출불가
}
}** 예제 1122_6 (다형성) **
class Animal3{
void breath() {
System.out.println("숨쉬기");
}
public String toString() {
return "몰라";
}
}
class Lion3 extends Animal3{
public String toString() {
return "사자";
}
}
class Rabbit extends Animal3{
public String toString() {
return "토끼";
}
}
class Monkey extends Animal3{
public String toString() {
return "원숭이";
}
public void printA() {
System.out.println("printA()...");
}
}
class ZooKeeper{
// void feed(Lion3 lion) {
// System.out.println(lion + "에게 먹이주기...");
// }
//
// void feed(Rabbit rabbit) {
// System.out.println(rabbit + "에게 먹이주기...");
// }
//
// void feed(Monkey monkey) {
// System.out.println(monkey + "에게 먹이주기...");
// }
void feed(Animal3 animal) {
System.out.println(animal + "에게 먹이주기...");
}
}
public class MySample1122_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성
ZooKeeper j = new ZooKeeper();
//
// Lion3 lion1 = new Lion3();
// j.feed(lion1);
//
// Rabbit rabbit = new Rabbit();
// j.feed(rabbit);
//
// Monkey monkey = new Monkey();
// j.feed(monkey);
Animal3 lion1 = new Lion3(); //객체생성은 Lion3, 바라보는관점은 Animal3 -> Animal3에 있는 것들을 사용할 수 있음
j.feed(lion1);
Animal3 rabbit = new Rabbit();
j.feed(rabbit);
Animal3 monkey = new Monkey();
j.feed(monkey);
j.feed(new Animal3()); // Animal3 animal = new Monkey(); //다시보기!!!!
monkey.printA(); // 오류 : monkey참조변수는 Animal3클래스의 참조변수이므로
// Monkey() 클래스에 있는 printA()메서드 접근 불가능
}
}** 예제 1122_6 (다형성_ 연산자 instanceof) **
class Parent3{
}
class Child3 extends Parent3{
}
class Brother extends Parent3{
}
public class MySample1122_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다형성 (instanceof 연산자)
Parent3 p = new Parent3();
System.out.println(p instanceof Object); // true
System.out.println(p instanceof Parent3); // true
System.out.println(p instanceof Child3); // false
Parent3 p2 = new Child3();
System.out.println(p2 instanceof Object); // true
System.out.println(p2 instanceof Parent3); // true
System.out.println(p2 instanceof Child3); // true
//부모에게 있고 자식에도 있으면 -> 자식꺼 실행
//부모에게 있고 자식에게 없으면 -> 부모꺼 실행
//부모에는 없고 자식에게 있으면 -> 오류
}
}
| 11/28 수업 (19회차) _ 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
|---|---|
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
| 11/21 수업 (16일차) _ 오버라이딩 / 접근 제어자 (3) | 2023.11.21 |
| 11/17 수업 (15회차) _ 상속 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| 11/16 수업 (14회차) _ 메소드 오버로딩 / 생성자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
** 실습 1121 (상속) **
/* 1
문제)친구정보를 기록할 MyFriendInfo 클래스를 상세정보를 기록할 MyFriendDetailInfo클레스에 상속하고
이름, 나이는 MyFriendInfo 클래스에서 주소와 전화번호는 MyFriendDetailInfo 클래스에서 입력할 수 있도록 구성함.
출력예)이름 : 이순신
나이 : 100
주소 : 성균관
전화 : 010-1111-2222
단, 각 클래스에서 출력하는 메서드가 존재하며, main 메서드에서는 생성자와 출력메서드 한번만 호출(자식클래스)하여 적용함.(메인에는 두줄)
입력값은 생성자를통해서 하드코딩하여 저장함. new 클래스( "이순신", 100, "성균관 ', "010-1111-2222")
*/
class MyFriendInfo{
String name;
int age;
MyFriendInfo(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age= age;
}
void printMyFriendInfo(){
System.out.println("이름 : " + name);
System.out.println("나이 : " + age);
}
}
class MyFriendDetailInfo extends MyFriendInfo{
String add;
String num;
MyFriendDetailInfo(String name, int age, String add, String num){
super(name, age);
// super.name = name; //이렇게 쓰지 않는 이유 : 나중에 배울 오버라이딩 배우면 앎
// super.age = age; //이렇게 쓰려면 위의 MyFriendInfo 메서드 없어야 함.
this.add = add;
this.num = num;
}
void printMyFriendDetailInfo() {
super.printMyFriendInfo(); //여기서는 super. 생략되도 됨 (이유 : 같은 메소드명이 자식에 없기때문임)
System.out.println("주소 : " + add);
System.out.println("전화 : " + num);
}
}
public class MySample1121 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속
MyFriendDetailInfo mfdi = new MyFriendDetailInfo("이순신", 100, "성균관 ", "010-1111-2222");
mfdi.printMyFriendDetailInfo();
}
}class MyFriendInfo
{
MyFriendInof(){
}
}
class MyFriednDetailInfo extends MyFriendInfo
{
MyFriednDetailInfo(){
super();
}
}
//class MyFriendInfo 와 class MyFriednDetailInfo가 생성자 없이 만들어지면
//JVM이 매개변수없는 생성자를 하나씩 만들어준다. (코드에 보이지 않아도 존재한다)
//-> but 생성자를 만들어 놓으면 JVM이 매개변수없는 생성자를 생성해주지 않는다.
//상속 받는 자식클래스의 매개변수 없는 생성자에는 super();이 생략되어있다.
생성자 or 매서드 에서 변수의 순위
지역변수 -> 인스턴스변수 -> 부모변수
생성자 or 메서드에서 변수 쓰임
지역변수 : 변수명만 쓴다.
인스턴스변수 : this.변수명
부모변수 : super.변수명
// 모든 클래스는 object.class를 상속받게 되어있다.(object 는 상속받는 클래스의 최상위 클래스라고 생각하면 된다.)
// JDK가 object.class 를 상속받게 해둔다.
** 예제 1121_2 (상속) **
// 상속
/*
실행결과)kind : SPACE, number : 1
kind : HEART, number : 7 (실행시 마다 변경)
*/
import java.util.Random;
class Card2{
static final int KIND_MAX = 4; //카드무늬수 (클래스 상수로 정의)
static final int NUM_MAX =13; //무니별 카드수
static final int SPADE = 4;
static final int DIAMOND = 3;
static final int HEART = 2;
static final int CLOVER = 1;
int kind;
int number;
Card2(){
this(SPADE, 1);
}
Card2(int kind, int number){
this.kind = kind;
this.number = number;
}
public String toString() {
String[] kinds = {"", "CLOVER", "HEART", "DIAMOND", "SPADE"};
String numbers = "0123456789XJQK"; //숫자 10은 X로 사용
return "kind : " + kinds[this.kind] + ", number : " + numbers.charAt(this.number); //charAt this.number 의 위치값만 뽑아옴
}
}
class Deck{
final int CARD_NUM = 52; //카드개수
Card2[] cardArr = new Card2[CARD_NUM];
Deck() {
int i = 0, k, n;
for(k = Card2.KIND_MAX ; k > 0 ; k--) { //4
//KIND_MAX 4부터 시작(4~1)
for(n = 0 ; n < Card2.NUM_MAX ; n++) { //13
//NUM_MAX = 13 (1~12)
System.out.println("Deck()생성자 : i = " + i + ", k = " + k + ", n = " + n);
cardArr[i++] = new Card2(k, n+1);
}
}
}
//지정된 위치(index)에 있는 카드 하나를 꺼내 반환함.
Card2 pick(int index) { //리턴타입 Card 객체
return cardArr[index];
}
Card2 pick() { //메소드 오버로딩
int index = (int)Math.random() * 52; //0~51사이값, 오류뜨면 Math앞에 java.lang. 써준다.
return pick(index);
}
//카드 순서 섞기
void shuffle() {
int i, r;
Card2 tmp;
for(i = 0 ; i < cardArr.length ; i++) {
r = (int)(java.lang.Math.random() * CARD_NUM); //0~51사이
tmp = cardArr[i];
cardArr[i] = cardArr[r];
cardArr[r] = tmp;
}
}
void printArr() {
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < cardArr.length ; i++)
{
System.out.println("cardArr[" + i + "] : " + cardArr[i]);
}
}
}
public class MySample1121_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 상속
/*
실행결과)kind : SPACE, number : 1
kind : HEART, number : 7 (실행시 마다 변경)
*/
Deck d = new Deck();
Card2 c = d.pick(0); //카드를 섞기 전에 제일 위 카드 뽑기
System.out.println("before : " + c.toString());
System.out.println("before : " + c); //윗줄과 결과 같다.
System.out.println("\n");
d.printArr();
d.shuffle(); //카드 섞기
c = d.pick(0); //카드 섞고나서 제일 위 카드 뽑기
System.out.println("after : " + c.toString());
System.out.println("\n");
d.printArr();
}
}상속관계에서 부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 메서드의 내용(구현부)을 자식클래스에서 변경하는 것
자손 클래스에서 오버라이딩하는 메서드는 조상 클래스의 메서드와 선언부가 같아야한다.
-.이름(메소드명)이 같아야한다.
-.매개변수가 같아야 한다.
-.반환타입이 같아야한다.
** 예제 1121_3 (오버라이딩) **
class Point2{
int x;
int y;
String getLocation() {
return "x : " + x + "y : " + y;
}
}
class Point3D extends Point2{
int z;
String getLocation() {
//return "x : " + x + ", y : " + y + ", z : " +z;
//부모클래스의 getLocation()메서드 호출방법
return super.getLocation() +", z : " + z;
}
}
public class MySample1121_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오버라이딩
Point3D p3 = new Point3D();
p3.x = 10;
p3.y = 20;
p3.z = 30;
System.out.println(p3.getLocation());
}
}
** 예제 1121_4 (오버라이딩) **
class Parent{
int x = 10;
}
class Child extends Parent{
int x = 20;
void methodA() {
int x = 30;
System.out.println("x : " + x); //지역변수
System.out.println("this.x : " + this.x); //인스턴스 변수
System.out.println("super.x : " + super.x); //부모에 정의된 인스턴스 변수
}
}
public class MySample1121_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.methodA();
}
}** 예제1121_5 (오버라이딩) **
class Point3{
int x, y;
Point3(){
this(0,0);
}
Point3(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x : " + x + ", y : " + y;
}
}
class Point3D2 extends Point3{
int z;
Point3D2(){
this(0, 0, 0);
}
Point3D2(int x, int y, int z){
super(x, y);
//super.x = x;
//super.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
String getLocation() {
//return "x : " + x + ", y : " + y + ", z : " + z;
return super.getLocation();
}
}
public class MySample1121_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오버라이딩
Point3D2 p3 = new Point3D2(1, 2 , 3);
System.out.println(p3.getLocation());
//getLocation()메서드를 Point3클래스 메서드를 호출하는 방법 2가지
//첫번째
Point3 p = new Point3(1, 2);
System.out.println(p.getLocation());
//두번째
System.out.println(p3.getLocation()); //Point3D2의 getLocation()메서드를 return super.getLocation();로 바꾼다.
}
}class Clothes{
void cutHeight() {
System.out.println("높이 수선하였습니다.");
}
void cutWidth() {
System.out.println("넓이를 수선하였습니다.");
}
void showPrice() {
System.out.println("수선비용은 : 5000원");
}
}
class Reform extends Clothes{
void cutHeight() {
System.out.println("높이를 다시 맞춰 수선하였습니다.");
}
void cutWidth() {
System.out.println("넚이를 다시 맞춰 수선하였습니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1121_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오버라이딩
Clothes ct = new Clothes();
Reform re = new Reform();
ct.cutHeight();
ct.cutWidth();
ct.showPrice();
re.cutHeight();
re.cutWidth();
re.showPrice(); //자식메소드를 통해 부모메소드를 불러옴
}
}- 멤버 또는 클래스에 사용되어 해당하는 멤버 또는 클래스 외부에서 접근하지 못하도록 제한하는 역할
* 접근제어자의 종류
| 접근제어자 | 사용 가능 범위 |
| private | 같은 클래스 내에서만 접근 가능 / 접근제어자 가장 강함 |
| default | 같은 패키지 내에서만 접근 가능 (아무것도 쓰지 않으면 default) |
| protected | 같은 패키지 내에서와 다른 패키지의 자손클래스에서 접근 가능 |
| public | 접근 제한 없음 / 접근제어자 가장 약함 |
- 위로 갈 수 록 접근제어가 강해진다.
cf) 패키지란? + 패키지 생성
- src 아래 (default package) 가 package이다.
- src 클릭후 new -> package 생성 또는 src 클릭후 new -> class 생성 (생성할 때 package명에 사용할 package명 입력하고 생성)
* 대상에 따라 사용할 수 있는 접근 제어자
| 대상 | 사용가능한 접근 제어자 |
| 클래스 | public, (default) |
| 메서드 멤버변수 |
public, protected, (default), private |
| 지역변수 | 없음(메서드 안에 있기에 메서드 끝나면 끝남) |
* 접근제어자 사용 이유
- 외부로부터 데이터 보호
- 내부적으로 사용되는 부분을 감추기 위해
** 예제 1121_6 (접근제어자) **
class Time{
private int hour, minute, second;
Time(int hour, int minute, int second){
setHour(hour); //this.hour = hour;
setMinute(minute); //this.minute = minute;
setSecond(second); //this.second = second;
}
public void errorPrint(String msg) {
System.out.println("현재 오류는 " + msg + "입니다.");
}
public int getHour() {
return this.hour;
}
public void setHour(int hour) {
//시간 0 ~ 23시 사이 값만 허용
if(hour < 0 || hour >23) {
errorPrint("시간(0~23시 사이) 오류");
return; //이 아래로 실행하지 않고 중간에 나를 호출한 곳으로 다시 돌아가겠다는 의미
}
this.hour = hour;
}
public int getMinute() {
return this.minute;
}
public void setMinute(int minute) {
//분은 0~59분 사이 값만 허용.
if(minute < 0 || minute > 59) {
errorPrint("분(0~59분 사이) 오류");
return;
}
this.minute = minute;
}
public int getSecond() {
return this.second;
}
public void setSecond(int second) {
//초는 0~59분 사이 값만 허용.
if(second < 0 || second > 59) {
errorPrint("초(0~59분 사이) 오류");
return;
}
this.second = second;
}
public String toString() {
return getHour() + ":" + getMinute() + ":" + getSecond();
}
}
public class MySample1121_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//접근제어자(private, (default), protected, public)
Time t = new Time(16, 40, 31);
System.out.println(t);
t.setHour(t.getHour() + 1); //t.hour = 17;
System.out.println(t); //t대신 t.toString 사용해도 같은의미다.
}
}** 실습 1121_7 (접근제어자) **
/*
문제)이름, 나이, 직업을 입력받아 입력받은 값을 화면에 출력하며, 이름에 "끝:이 입력되면 종료되는 프로그램 작성.
단, 이름/나이/직업과 관련된 정보는 메서드를 사용하여 작성.(private)
문자열비교 : 변수명.equals("끝")
이름.나이.직업을 관리하는 클래스는 Person3 으로 하며, 예외처리 : 프로그램 종료여부와 정보출력(출력예) 메서드는 msgPrint()
입력예)이름은 > 홍길동
나이는 > 23
직업은 > 프로그래머
출력예)홍길동님의 나이는 23살이며, 직업은 프로그래머 입니다.
입력예)이름은 > 끝
나이는 > 22
직업은 > 백수
출력예)프로그램을 종료합니다.
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
/* 1
문제)이름, 나이, 직업을 입력받아 입력받은 값을 화면에 출력하며, 이름에 "끝:이 입력되면 종료되는 프로그램 작성.
단, 이름/나이/직업과 관련된 정보는 메서드를 사용하여 작성.(private)
문자열비교 : 변수명.equals("끝") //String 타입 비교 (문자열)
이름.나이.직업을 관리하는 클래스는 Person3 으로 하며, 예외처리 : 프로그램 종료여부와 정보출력(출력예) 메서드는 msgPrint()
입력예)이름은 > 홍길동
나이는 > 23
직업은 > 프로그래머
출력예)홍길동님의 나이는 23살이며, 직업은 프로그래머 입니다.
입력예)이름은 > 끝
나이는 > 22
직업은 > 백수
출력예)프로그램을 종료합니다.
*/
class Person3{
private String name, job;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getJob(){
return this.job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
//프로그램 종료여부와 출력
public boolean msgPrint() {
if(getName().equals("끝")) {
System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println(getName() + "님의 나이는 " + getAge() + "살이며, 직업은 " + getJob()+ "입니다.");
return false;
}
}
// //위 boolean을 int로 사용할 경우 while(msgPrint()==1)로 쓴다.
// public int msgPrint() {
// if(getName().equals("끝")) {
// System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
// return 1;
// }
// else {
// System.out.println(getName() + "님의 나이는 " + getAge() + "살이며, 직업은 " + getJob()+ "입니다.");
// return 0;
// }
// }
}
public class MyProject1121_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
//접근제어자
Person3 p3 = new Person3();
//Person3 p3 = null; //다른방법1
while(true) {
//p3 = new Person3(); //다른방법1
System.out.print("이름은 > ");
p3.setName(scn.next()); //nextLine은 엔터키를 가지고 있기에 next()적용
System.out.print("나이는 > ");
p3.setAge(scn.nextInt());
System.out.print("직업은 > ");
p3.setJob(scn.next());
if(p3.msgPrint()) {
break;
}
// nextInt 와 next 는 공백도 자른다. nextLine은 엔터키를 가지고 있다.
}
}
}
| 11/23 수업 (18회차) _ 다형성 예제 / Vector 클래스 / 추상 클래스 (1) | 2023.11.23 |
|---|---|
| 11/22 수업 (17일차) _ 접근 제어자 / 다형성 (1) | 2023.11.22 |
| 11/17 수업 (15회차) _ 상속 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| 11/16 수업 (14회차) _ 메소드 오버로딩 / 생성자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| 11/15 수업(13회차) _ 매개 변수 예제/ 반환 타입 예제 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
- 컴퓨터에서 일을 수행하는 프로그램을 작성하기 위해 고안된 언어이다.
- 컴퓨터는 0과 1로 구성된 데이터만 읽고 처리할 수 있는데,
이렇게 0과 1의 조함으로 구성된코드를 바이너리(binary) 코드, 즉 기계어라고 한다.
- 사람이 작성한 소스코드를 컴퓨터가 이해하려면 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있는 언어인 기계어로 변환해야 한다.
· 저급 언어 : 하드웨어 지향의 기계 중심언어 ex) 기계어, 어셈블리어
· 고급 언어 : 사람이 이해하고 작성하기 쉬운 사람 중심 언어 ex) JAVA , C, C++, FORTRAN, COBOL..
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍 언어
- 개발도구(JDK) + 실행환경(JRE) + 라이브러리(API) 를 제공.
- 객체지향언어 (상속, 캡슐화, 다형성)
- 운영체제(윈도우,리눅스,유닉스,,,)에 독립적이다. (= 이식성이 높다)
→ JAVA는 JVM(java virtual machine) 위에서 돌아가기 때문 (다른언어는 운영체제에서 돌아감)
- C++에서 연산자.기본구분 + 스몰톡에서 객체지향언어관련 구문 가져옴
- Garbage Collection(GC.자동 메모리 관리) → 자동적으로 메모리 관리를 해줌 : 프로그래머가 따로 관리 불필요
- 멀티쓰레드 지원 (하나의 프로그램에서 동시에 여러 작업 가능)
- 네트워크와 분산처리지원
* Java SE (Standard Addition)
- JDK(java development Kit) : 자바 개발 키트
- JRE(Java Runtime Environment) : 자바 실행 환경
- JVM(Java Virtual Machine) -> 자바를 실행하기 위한 가상 머신 (JDK를 설치하면 포함되어 있다.)
· Java는 OS가 달라도 각 OS의 환경에 맞게 번역해주는 JVM만 있으면 동일하게 번역된 결과 출력 가능
· 자바로 작성된 애플리케이션은 모두 이 가상컴퓨터(JVM)에서만 실행되기 때문에 자바 애플리케이션이 실행되기 위해서는 반드시 JVM 필요하다.
** Hello.java 작성 ----(javac.exe)(컴파일)----> Hello.class 생성 ----(java.exe)(실행)----> "Hello World" 출력
· 클래스 이름과 파일 이름은 반드시 동일해야 한다.
· 테스트 목적이 아닌 이상 하나의 파일에 하나의 클래스만 작성한다.
· 클래스 이름 : 대문자로 시작하고 새로운 단어가 결합될 때 첫글자를 대문자로 처리한다.(카멜 표기법 camel case)
· 시작블록 : { 종료블록 : } 을 이용하여 클래스의 시작과 끝 알린다.
· public static void main(String[] args) 메소드가 있는 클래스만 실행할 수 있다.
(실행할 모든 코드는 main() 메소드 블록 안에 위치해야 한다.)
** 메세지 출력
System.out.print("메세지"); //메세지를 출력하고 개행(Enter)처리를 하지 않는다.
System.out.println("메세지"); //메세지를 출력하고 개행(Enter)처리를 한다.
· 세미콜론(;) - 명령종료
· 빨간색 x - 문법 오류 (x에 마우스 포인트를 올리면 어떤 오류인지 자세히 알려준다.)
· 전구모양 빨간색 x - 단순한 오타
· 들여쓰기 단축키 : <Ctrl> + <Shift> + <F> (자바뿐만 아니라 이클립스로 작성한 모든파일 가능 HTML, XML, JSP...)
▶주석문(comment) - 프로그램 설명을 기입하는 것으로 컴파일과 실행을 하지 않음.
// : 한줄주석(뒤부터 한줄만 주석)
/* */ : 범위주석, 한줄 혹은 여러줄 주석(/*로 시작해서 */끝날때까지 주석)
ex) /************************************
주석 처리할 문장
************************************/
주석 단축키 → // : <Ctrl> + /
/* */ : <Ctrl> + <Shift> + /
- bit : 1 자리 (0 또는 1)
- byte = bit 8개 (JAVA는 byte로 컴파일됨)
ex) 1byte → 00101000
- 대문자로시작 (.java) → 클래스
- 소문자로시작 → 메소드 ( ex>main )
** 예제 1117 (생성자) **
class Document{
static int count = 0;
String name;
Document(){
this("제목없음" + (++count));
}
Document(String name){
this.name = name;
System.out.println("문서 " + name + "이 생성되었습니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1117 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//생성자
Document d1 = new Document();
Document d2 = new Document("자바.txt");
Document d3 = new Document();
Document d4 = new Document();
}
}
* 결과
문서 제목없음1이 생성되었습니다.
문서 자바.txt이 생성되었습니다.
문서 제목없음2이 생성되었습니다.
문서 제목없음3이 생성되었습니다.
- 기존의 클래스를 재사용하여 새로운 클래스를 작성하는 것
- 상속을 통해 부모의 클래스가 가지고 있는 모든 것을 (생성자 제외) 자식클래스가 물려받아 같이 공유하고 확장하는 기념
// new 객체가 만들어진 순간에는 호출되지만, 생성자를 물려받아 공유할 수는 없다.
- 예) class Child extends Parent {
}
// extends 다음에 부모클래스는 한개만 쓸수 있다.
조상클래스 : 부모(Parent)클래스, 상위(super)클래스, 기반(base)클래스
자손클래스 : 자식(chlid)클래스, 하위(sub)클래스, 파생된(derived)클래스
- 예) class Parent(
int age;
}
class Child extends Parent {
}
** 예제 1117_2 (상속) **
class Tv2{
boolean power; //전원상태(on/off)
int channel;
Tv2(){
channel = 11;
System.out.println("Tv2() 생성자...");
}
void power() {
power = !power;
}
void channelUp() { //부모변수가 증가함.
++channel;
}
void channelDown() {
--channel;
}
}
class CaptionTv extends Tv2{
boolean caption; //자막상태
int channel;
CaptionTv(){ //생성자에서 부모가 호출된다.
// super(); //생략되어있음. 무조건 첫번째줄에 와야함. super를 부르기때문에 부모 먼저 호출됨
channel = 20;
System.out.println("CaptionTv() 생성자...");
}
void displayCaption(String text) {
int channel = 30;
if(caption) { //this.caption 에 this가 생략됨(지역변수 cation이 없기 때문)
System.out.println("자막내용 : " + text);
}
System.out.println("부모 channel : " + super.channel); //상속관계에서 부모인스턴스 지칭하는것 : super
System.out.println("인스턴스 : " + this.channel); //내 클래스의 인스턴스 지칭 : this
System.out.println("channel : " + channel);
//지역변수 인스턴스변수 부모변수 불러보기
}
int getChannel() { //
return super.channel; //인스턴스변수(지역변수가 있을 시) : this.channel | 부모변수 : super.channel
}
}
//변수값 찾을 때 지역변수 -> 자식인스턴스변수 -> 부모변수 순서로 찾는다. (cf : 메인메소드에서 channel찍으면 인스턴스 자식도있고 부모도있으)
public class MySample1117_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속
CaptionTv ctv = new CaptionTv(); //자식클래스 인스턴스ctv에 CaptionTv 객체 생성
System.out.println("channel : " + ctv.channel);
ctv.channel = 10; //인스턴스변수에 10 대입.
ctv.channelUp();
System.out.println("channel : " + ctv.channel);
ctv.displayCaption("Hello JAVA..."); //caption 디폴트값이 false라 출력 안됨.
ctv.caption = true;
ctv.displayCaption("Hello JAVA");
ctv.power(); //없으면 아래 ctv.power가 false로 출력됨
System.out.println("ctv.power : " + ctv.power);
System.out.println("ctv.getChannel : " + ctv.getChannel());
}
}
* 출력
Tv2() 생성자...
CaptionTv() 생성자...
channel : 20
channel : 10
부모 channel : 12
인스턴스 : 10
channel : 30
자막내용 : Hello JAVA
부모 channel : 12
인스턴스 : 10
channel : 30
ctv.power : false
ctv.getChannel : 12
// staic int channel이 아니지만 12 가 출력되는 이유
- ctv.channelUp();을 실행한후 값 유지 (이유 - ctv라는 동일한 인스턴스 객체이기때문 )
** 예제 1117_3 (상속) **
class Person{
void breath() {
System.out.println("숨쉬기");
}
void eat() {
System.out.println("밥먹기");
}
void say() {
System.out.println("말하기");
}
}
class Student extends Person{
void learn() {
System.out.println("공부하기...");
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{
void teach() {
System.out.println("설명하기...");
}
}
public class MySample1117_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속_2번 받는 경우
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.breath();
s1.learn();
Teacher t1 = new Teacher();
t1.eat();
t1.breath();
t1.teach();
}
}** 예제 1117_4 (상속) **
class Point{ //x, y좌표값만
int x;
int y;
Point(){
this(0, 0);
}
Point(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
String getXY() {
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ")"; //문자열 형태로 보내주기 위해 만듬
}
}
class Shape{ //색가지고 그리기만
String color = "black";
void draw() {
System.out.printf("[color = %s] \n", color);
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
Point center; //??
int r;
Circle(){
//Point p = new Point(0, 0);
//this(p, 100); //this() 는 항상 첫번째 라인에서 호출되어야 함.
this(new Point(0, 0), 100); //new Point(0, 0) -> new 객체생성한 주소값 반환
}
Circle(Point center, int r){
this.center = center;
this.r = r;
}
void draw() {
System.out.printf("[center=(%d, %d), r=%d, color=%s]\n", center.x, center.y, r, color);
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
Point[] p = new Point[3]; // 좌표를 배열로 3개 생성함
// Triangle() {
//
// } //메인에서 new Triangle 객체생성할 때 오류안나기 위해 만들어준다.
// 컬파일러 jdk가 생성자 만들어줌 - > 모든 클래스는 생성자가 하나 존재한다.
// jdk는 생성자가 하나라도 존재하면 빈생성자 만들어주기 않기때문에 -> 빈생성자 하나 만들어 줘야한다.
Triangle(Point[] p) { //Point[] 클래스 배열타입을 받겠다는 의미.
System.out.println("before : " + this.p.length);
this.p = p;
System.out.println("after : " + this.p.length);
}
void draw() {
System.out.printf("[p1=%s, p2=%s, p3=%s, color=%s] \n", p[0].getXY(), p[1].getXY(), p[2].getXY(), color);
}
}
public class MySample1117_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속_도형그리기
Point[] p = {
new Point(100, 100), //시작 주소값 넘겨줌
new Point(140, 50),
new Point(200, 100)
};
Triangle t = new Triangle(p);
Circle c = new Circle(new Point(150, 150), 50);
//바로 위 선을 분리하여 적용시 (더 직관적이지만 p2메모리가 더 할당되야한다.)
//Point p2 = new Point(150, 150);
//Circle c = new Circle(p2, 50);
t.draw(); //삼각형 그리기
c.draw(); //원그리기
}
}** 예제 1117_5 **
class Person2{
String name;
String job;
int age;
Person2(String name, String job, int age){
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Student2 extends Person2{ //생성자 때문에 오류남
int score;
Student2(String name, String job, int score, int age){
// super.name = name;
// super.job = job;
// super.age = age;
super(name, job, age);
this.score = score;
}
void print() {
// System.out.println("이름 : " + super.name + ", 직업 : " + super.job + ", 나이" + super.age + ", 점수" + this.score);
System.out.println("이름 : " + name + ", 직업 : " + job + ", 나이 : " + age + ", 점수 : " + score);
}
}
class Teacher2 extends Person2{
int pay;
Teacher2(String name, String job, int age, int pay){
// super.name = name;
// super.job = job;
// super.age = age;
super(name, job, age); //자식클래스에서 부모클래스의 변수에 값을 넣을때는 부모클래스의 생성자 이용하는 것이 좋다.
this.pay = pay;
}
void print() {
// System.out.println("이름 : " + super.name + ", 직업" + super.job + ", 나이" + super.age + ", 급여" + this.pay); //올바른 문법
System.out.println("이름 : " + name + ", 직업 : " + job + ", 나이 : " + age + ", 급여 : " + pay);
}
}
public class Sample1117_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 상속
Student2 s1 = new Student2("홍길동", "학생회장", 100, 19);
s1.print();
Teacher2 t1 = new Teacher2("펭수", "본부장", 40, 1000);
t1.print();
}
}
// s1이 바라보는 Person2와 t1이 바라보는 Person2는 다르다.
// super() -> 부모 생성자
// super.~~ -> 부모 인스턴스
** 실습 1117_6 **
/* 1
부모클래스틑 Animal 클래의 멤버변수는 이름, 이동수단, 울음소리, 다리수로 정의
각 멤버변수를 제어하는 메서드도 포함(get, set메서드를 활용하여 변수값 활용)
단, get으로 시작하는 메서드는 해당 클래스에 인스턴스변수 값을 보내주는 것이며,
set으로 시작하는 메서드는 해당 클래스에 인스턴스 변수에 값으르 저장하는 것임
Animal 클래스를 상속받은 자식 클래스를 만들어서 각각의 이름, 이동수단, 울음소리, 다리수를 출력하는 프로그램.
클래스는 Dog(강아지), Eagle(독수리), Lion(사자), Cat(고양이)
출력은 name(이름), move(이동수단), cry(울음소리), leg(다리수)
출력예)강아지 이름은 해피이고, 이동방법은 껑충껑충, 울음소리는 멍멍, 다리수는 4입니다.
독수리 이름은 이글이고, 이동방법은 펄럭펄럭, 울음소리는 구구, 다린수는 2입니다.
사자 이름은 어흥이고, 이동방법은 휙휙휙, 울음소리는 어흥어흥, 다리수는 4 입니다.
고양이 이름은 나비이고, 이동방범은 껑충껑충, 울음소리는 야옹야옹, 다리수는 4입니다.
단, 출력은 메인메서드에서 실행
*/
class Animal{
String name;
String move;
String cry;
int leg;
Animal(){
}
Animal(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
this.name = name;
this.move = move;
this.cry = cry;
this.leg = leg;
}
void setName(String name){ //set과 get은 세트로 잘 다닌다. set에서 값을 세팅하고 get에서 return반환값을 보낸다.
this.name = name;
}
String getName(){
return this.name;
}
void setMove(String move){
this.move = move;
}
String getMove(){
return this.move;
}
void setCry(String cry) {
this.cry = cry;
}
String getCry() {
return cry;
}
void setLeg(int leg) {
this.leg = leg;
}
int getLeg() {
return leg;
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
Dog(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal{
Eagle(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Lion extends Animal{
Lion(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
Cat(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
public class MySample1117_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속
Animal a = new Animal();
Dog d = new Dog("해피", "껑충껑충", "멍멍", 4);
Eagle e = new Eagle("이글", "펄럭펄럭", "구구", 2);
Lion l = new Lion("어흥", "휙휙휙", "어흥어흥", 4);
Cat c = new Cat("나비", "껑충껑충", "야옹야옹", 4);
System.out.println("강아지 이름은 " + d.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + d.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + d.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + d.getLeg() + "입니다.");
System.out.println("독수리 이름은 " + e.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + e.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + e.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + e.getLeg() + "입니다.");
System.out.println("사자 이름은 " + l.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + l.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + l.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + l.getLeg() + "입니다.");
System.out.println("고양이 이름은 " + c.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + c.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + c.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + c.getLeg() + "입니다.");
}
}
** 선생님 풀이 1117_6 (상속) **
// MySample1117_6의 문제를 선생님 방법
class Animal2{
String name; //이름
String move; //이동수단
String cry; //울음소리
int leg; //다리수
Animal2(){
this("","","",0);
}
Animal2(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
// this.name = name; //이름
// this.move = move; //이동수단
// this.cry = cry; //울음소리
// this.leg = leg;
//위 주석과 동일한 의미
setName(name);
setMove(move);
setCry(cry);
setLeg(leg);
}
String getName() {
return this.name;
}
void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
String getMove() {
return this.move;
}
void setMove(String move) {
this.move = move;
}
String getCry() {
return this.cry;
}
void setCry(String cry) {
this.cry = cry;
}
int getLeg() {
return this.leg;
}
void setLeg(int leg) {
this.leg = leg;
}
}
//-Animal 과 Animal을 상속받는 클래스들에 아무것도 없을때 오류가 안나는 이유 - 생성자 하나도 없으면 jdk에서 빈 생성자를 각각 하나씩 만들어주기 때문에
class Dog2 extends Animal{
Dog2(){
this("","","",0); //현단계에서 super(); 호출 하지 않게 하는 방법중 하나.
}
Dog2(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Eagle2 extends Animal{
Eagle2(){
}
Eagle2(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Lion2 extends Animal{
Lion2(){
}
Lion2(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
class Cat2 extends Animal{
Cat2(){
}
Cat2(String name, String move, String cry, int leg){
super(name, move, cry, leg);
}
}
public class MySample1117_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속
//강아지 이름은 해피이고, 이동방법은 껑충껑충, 울음소리는 멍멍, 다리수는 4입니다.
Dog2 d = new Dog2("해피","껑충껑충","멍멍",4);
System.out.println("강아지 이름은 " + d.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + d.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + d.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + d.getLeg() + "입니다.");
Eagle2 e = new Eagle2("이글", "펄럭펄럭", "구구", 2);
System.out.println("독수리 이름은 " + e.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + e.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + e.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + e.getLeg() + "입니다.");
Lion2 l = new Lion2("어흥이", "휙휙", "어흥어흥", 4);
System.out.println("사자 이름은 " + l.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + l.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + l.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + l.getLeg() + "입니다.");
Cat2 c = new Cat2("나비", "껑충꺼충", "야옹야옹", 4);
System.out.println("고양이 이름은 " + c.getName() + "이고, 이동방법은 " + c.getMove() + ", 울음소리는 " + c.getCry() + ", 다리수는 " + c.getLeg() + "입니다.");
}
}
// Generate 실행 예
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
| 11/22 수업 (17일차) _ 접근 제어자 / 다형성 (1) | 2023.11.22 |
|---|---|
| 11/21 수업 (16일차) _ 오버라이딩 / 접근 제어자 (3) | 2023.11.21 |
| 11/16 수업 (14회차) _ 메소드 오버로딩 / 생성자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| 11/15 수업(13회차) _ 매개 변수 예제/ 반환 타입 예제 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
| 11/14 수업 (12일차) (1) | 2023.11.14 |
** 메소드 오버로딩1115 **
//메서드 오버로딩
/* 1
출력예)1
13 (5, 8)
2
12 (5, 7.1)
3
12 (7.1, 5)
4
12.3 (7.1, 5.2)
5
210 (배열)
*/
class MyMath2{
int j;
int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(++j); // ++j 전치연산증감자 (초기값이 0이기때문)
return a + b;
}
int add(int a, double b) {
j++;
System.out.println(j);
return (int)(a + b); //둘다 int로 해도되고 b에만 int 형변환해도된다.
}
int add(double a, int b) {
System.out.println(++j);
return (int)a + b;
}
double add(double a, double b){
System.out.println(++j);
return a + b;
}
int add(int[] a) { //main의 배열 a와 같은 배열아니다.(a(임의로 사용_다른것도 가능)라는 배열을 매개 변수로 받겠다는 의미)
System.out.println(++j);
int i, sum = 0;
for(i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++) {
sum += a[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
public class MySample1116 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 오버로딩
/*
출력예)1
13 (5, 8)
2
12 (5, 7.1)
3
12 (7.1, 5)
4
12.3 (7.1, 5.2)
5
210 (배열)
*/
int[] a = new int[] {10,20,30,40,50,60};
MyMath2 m = new MyMath2();
MyMath2 m2= new MyMath2();
System.out.println(m.add(5,8));
System.out.println(m.add(5,7.1));
System.out.println(m.add(7.1,5));
System.out.println(m.add(7.1,5.2));
System.out.println(m.add(a));
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println(m2.add(5,3));
System.out.println(m2.add(5,7.1));
System.out.println(m2.add(7.1,5));
System.out.println(m2.add(7.1,5.2));
System.out.println(m2.add(a));** 메소드 오버로딩1115_2 **
//메서드 오버로딩
/*
실행결과)컴퓨터 가격은 : 10000원 입니다.
제품은 : 컴퓨터 입니다.
구매한 제품은 : 컴퓨터 이며, 10000원 입니다.
*/
class Computer{
void show(int a){
System.out.printf("컴퓨터 가격은 : %d원 입니다. \n", a);
}
void show(String a) {
System.out.printf("제품은 : %s 입니다. \n", a);
}
void show(String a, int b) {
System.out.printf("구매한 제품은 : %s 이며, %d원 입니다.", a, b);
}
}
public class MySample1116_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 오버로딩
/*
실행결과)컴퓨터 가격은 : 10000원 입니다.
제품은 : 컴퓨터 입니다.
구매한 제품은 : 컴퓨터 이며, 10000원 입니다.
*/
Computer c = new Computer();
c.show(10000);
c.show("컴퓨터");
c.show("컴퓨터", 10000);
}
}* 클래스 변수와 메서드, 인스턴스 변수와 메서드
//클래스 변수와 메서드, 인스턴스 변수와 메서드
class Member{
int iv = 10; //인스턴스 변수
static int cv = 20; //클래스 변수
int iv2 = iv; //가능(인스턴스 변수이기 때문에 가능)
// static int cv2 = iv; //불가능(iv는 인스턴스 변수이기 때문에)
//
// Member k = new Member();
// static int cv2 = k.iv; //불가능 (객체생성은 클래스영역말고 메서드에서 해야한다.) (Member객체 생성시기와 static변수 생성시기가 다르기 때문)
//
static int cv2 = new Member().iv; //가능은 하나 사용하지 않은것을 권장
static void staticMethod1() { //클래스 메서드
System.out.println(cv);
System.out.println(iv); //클래스 메소드에서 인스턴스 변수는 사용 불가능
Member k = new Member(); //클래스 메소드에서 인스턴스 변수사용하려면 이렇게 해야한다.
System.out.println(k.iv);
}
void instanceMethod1() { //인스턴스 메서드
System.out.println(cv);
System.out.println(iv);
}
static void staticMethod2() {
staticMethod1();
instanceMethod1(); //클래스 메서드에서 인스턴스 메소드 호출하려면 아래와같이 객체생성 후 가능
Member c = new Member();
c.instanceMethod1();
}
void instanceMethod2() {
staticMethod1();
instanceMethod1();
}
** 생성자 (Constructor) **
- 인스턴스가 생성될 때(new) 호출되는 인스턴스 초기화 메서드
인스턴스 변수의 초기화 작업에 주로 사용
메서드처럼 클래스 내에 선언되며, 리턴값이 없음(void 사용 안함)
- 생성자의 이름은 클래스의 이름과 같아야 함
- 생성자는 리턴 값이 없음
- 생성자에 메소드 오버로딩도 적용 가능하다.
예)
class Card{
Card(){ //매개변수 없는 생성자
...
}
Card(String k, int num){ //매개변수 있는 생성자
...
}** 예제 **
class Car{
String color;
String gearType;
int door;
Car(){
}
Car(String c, String g, int d){
color = c;
gearType = g;
door = d;
}
}
public class MySample1116_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c1 = new Car();
c1.color = "white";
c1.gearType = "auto";
c1.door = 4;
Car c2 = new Car("blue", "auto", 2); //c2.color...에 대입안하고 생성자에 대입함
System.out.println("c1의 color = " + c1.color + ", gearType = " + c1.gearType + ", door = " + c1.door);
System.out.println("c1의 color = " + c2.color + ", gearType = " + c2.gearType + ", door = " + c2.door);
}
}** 예제 **
public class MySample1116_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//생성자
Data2 d = new Data2();
Data2 d2 = new Data2(10);
System.out.println("d.value : " + d.value);
System.out.println("d2.value : " + d2.value);
}
}
class Data2{
int value;
Data2(){
System.out.println("생성자 Data2() 호풀");
}
Data2(int x){
System.out.println("생성자 Data2(int x) 호풀");
value = x;
}
}** 실습 1116_3 **
* 두번째
class Car{
String color;
String gearType;
int door;
//두번째
Car(String a){
color = a;
gearType = "Auto";
door = 4;
}
// // 위의 Car(String a)생성자의 매개변수명은 보통 a를 알아보기 쉽게 color로 할 경우
// Car(String color){
// this.color = color; //this.color로하면 그 클래스에 있는 인스턴스변수를 받는다. (변수명이 같을경우 사용하는 this)
// // = 뒤의 color는 매개변수 color를 받는다.
}
Car(){
color = "white";
gearType = "Auto";
door = 4;
}
}
public class MySample1116_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//두번째
//매개변수 1개는 color에 적용. 매개변수 없을 때는 white로 지정
//gearType = auto, door = 4로 지정
System.out.println("main 시작 c1생성");
Car c1 = new Car();
System.out.println("main 시작 c2생성");
Car c2 = new Car("blue");
System.out.println("c1의 color = " + c1.color + ", gearType = " + c1.gearType + ", door = " + c1.door);
System.out.println("c1의 color = " + c2.color + ", gearType = " + c2.gearType + ", door = " + c2.door);
}
}** 예제 (this.) **
class Car{
String color;
String gearType;
int door;
Car(){
// this.color = "white";
// this.gearType = "auto";
// this.door = 4;
this("white", "auto", 4); //this 같은 클래스 내에서 다른생성자 호출(매개변수 3개를 호출한다는 의미)
System.out.println("매개변수 없음.");
}
Car(String color){
// this.color = color;
// this.gearType = "auto";
// this.door = 4;
this(color, "auto", 4);
System.out.println("매개변수 1개 color");
}
Car(String color, String gearType){ //생성자에서 생성자 호출 가능
// this.color = color;
// this.gearType = gearType;
// this.door = 2;
this(color, gearType, 2);
System.out.println("매개변수 2개 color, gearType");
}
Car(String color, String gearType, int door){
this.color = color;
this.gearType = gearType;
this.door = door;
System.out.println("매개변수 3개");
}
public class MySample1116_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main 시작 c1생성");
Car c1 = new Car(); // 객체생성하면서 매개변수없는 생성자 호출
System.out.println("main 시작 c2생성");
Car c2 = new Car("blue");
System.out.println("main 시작 c3생성");
Car c3 = new Car("red", "auto");
System.out.println("c1의 color = " + c1.color + ", gearType = " + c1.gearType + ", door = " + c1.door);
System.out.println("c2의 color = " + c2.color + ", gearType = " + c2.gearType + ", door = " + c2.door);
System.out.println("c3의 color = " + c3.color + ", gearType = " + c3.gearType + ", door = " + c3.door);
}
}
결과
main 시작 c2생성
매개변수 3개
매개변수 1개 color
main 시작 c3생성
매개변수 3개
매개변수 2개 color, gearType
c1의 color = white, gearType = auto, door = 4
c2의 color = blue, gearType = auto, door = 4
c3의 color = red, gearType = auto, door = 2
** 예제 1116_4 **
* 생성자를 이용한 인스턴스 복사
class Car1{
String color;
String gearType;
int door;
Car1(){
this("white", "auto", 6); //생성자에서 다른생성자 호출시(this) 항상 첫번째줄에 와야한다.
this.color = "white";
this.gearType = "auto";
this.door = 6;
}
Car1(Car1 c){ //매개변수가 객체(참조형 변수)
this(c.color, c.gearType, c.door);
// this.color = c.color;
// this.gearType = c.gearType;
// this.door = c.door;
}
Car1(String color, String gearType, int door){
this.color = color;
this.gearType = gearType;
this.door = door;
}
}
public class MySample1116_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//생성자 - 생성자를 이용한 인스턴스 복사
Car1 c1 = new Car1();
Car1 c2 = new Car1(c1);
Car1 c3 = new Car1(c1);
System.out.println("c1 color = " + c1.color + ", gearType = " + c1.gearType + ", door = " + c1.door);
System.out.println("c2 color = " + c2.color + ", gearType = " + c2.gearType + ", door = " + c2.door);
System.out.println("c3 color = " + c3.color + ", gearType = " + c3.gearType + ", door = " + c3.door);
c1.door = 50;
c2.color = "pink";
System.out.println("c1 color = " + c1.color + ", gearType = " + c1.gearType + ", door = " + c1.door);
System.out.println("c2 color = " + c2.color + ", gearType = " + c2.gearType + ", door = " + c2.door);
System.out.println("c3 color = " + c3.color + ", gearType = " + c3.gearType + ", door = " + c3.door);
}
}** 예제 1116_5 **
* 클래스 초기화 블럭 / 인스턴스 초기화 블럭
public class MySample1116_5 {
// static int cv = 1;
// int iv = 2;
//
// //클래스 초기화 블럭 (생성자보다 먼저 실행됨) -> 한번만실행
// static {
// System.out.println("static 초기화영역");
// cv = 10;
// }
//
// //인스턴스 초기화 블럭 -> new 생길때 실행
// {
// System.out.println("인스턴스 초기화 영역");
// iv = 20;
// }
//
// MySample1116_5(){
// System.out.println("MySample1116_5() 생성자호출");
// }
// public static void main(String[] args) {
//
// //초기화 블럭
// System.out.println("main 메서드 시작");
// MySample1116_5 m1 = new MySample1116_5();
//
// System.out.println("main메서드 두번째 실행");
// MySample1116_5 m2 = new MySample1116_5();
//
// System.out.println("main 메서드 끝");
//
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product p1 = new Product();
Product p2 = new Product();
Product p3 = new Product();
System.out.println("p1 제품번호 serialNo : " + p1.serialNo);
System.out.println("p2 제품번호 serialNo : " + p2.serialNo);
System.out.println("p3 제품번호 serialNo : " + p3.serialNo);
System.out.println("객체 생성 수 : " + Product.count);
}
}
class Product{
static int count = 0;
int serialNo;
{
System.out.println("인스턴스 초기화 블럭 시작 count : " + count + ", sreialNo : " + serialNo);
++count;
serialNo = count;
System.out.println("인스턴스 초기화 블럭 끝 count : " + count + ", sreialNo : " + serialNo);
}
Product(){
System.out.println("Product() 생성자");
}
}** 예제 1116_6 **
public class MySample1116_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//초기화 블럭
/*
출력예)Static method : 1
Static block : 2
Static method : 3
instance method : 4
instance block : 5
instance method : 6
constructor : 7
instance method : 8
instance block : 9
instance method : 10
constructor : 11
*/
STest.test();
STest a = new STest();
STest b = new STest();
}
}
class STest{ //클래스 영역에 정의된 변수는 초기화(입주청소) 해준다.
static int cnt;
static { //클래스 초기화 영역
test(); //test();만 보고 클래스 메서드인것과 같은 클래스내에 정의되어있다를 알 수 있음.
cnt++;
System.out.println("static block : " + cnt);
}
{ //인스턴스 초기화 영역
instanceMethod();
cnt++;
System.out.println("instance block : " + cnt);
}
STest(){
instanceMethod();
cnt++;
System.out.println("constructor : " + cnt);
}
static void test() {
cnt++; //클래스 변수임을 알 수 있다.
System.out.println("static method : " + cnt);
}
void instanceMethod() {
cnt++;
System.out.println("instance method : " + cnt);
}
}
// 생성자 객체 생성 (입주청소) -> 인스턴스 초기화 블럭 실행 -> 생성자 실행
| 11/21 수업 (16일차) _ 오버라이딩 / 접근 제어자 (3) | 2023.11.21 |
|---|---|
| 11/17 수업 (15회차) _ 상속 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| 11/15 수업(13회차) _ 매개 변수 예제/ 반환 타입 예제 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
| 11/14 수업 (12일차) (1) | 2023.11.14 |
| 11/13 수업 (11일차) (2) | 2023.11.13 |
* 기본형 매개변수
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
//객체지향프로그램 = 기본형 매개변수 시작
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data d = new Data();
d.x = 10;
System.out.println("main() x : " + d.x);
change(d.x);
//클래스or인스턴스명이 앞에 안와도 괜찮은 이유 : 같은 클래스 내에 있는 클래스메소드(static) 호출이기때문
System.out.println("main() after x : " + d.x);
}
//기본형 매개변수
static void change(int x) //void : change 끝났을 때 반환되는 값이 없다.
{
x = 1000;
System.out.println("change() x : " + x);
}* 참조형 매개변수
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
//참조형 매개변수 시작
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Data d = new Data();
d.x = 10;
System.out.println("main() x : " + d.x);
change(d);
System.out.println("main() after x : " + d.x);
}
static void change(Data d)
{
d.x = 1000;
System.out.println("change() x : " + d.x);
}
}* 참조형 반환타임(return) + 참조형 매개변수
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
//참조형 반환타입(리턴타입) 시작
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Data d = new Data();
d.x = 10;
Data d2 = change(d);
System.out.println("d.x = " + d.x);
System.out.println("d2.x = " + d2.x); //d.x와 d2.x의 값은 동일하지만 서로다른 주소값이다.
}
static Data change(Data d)
{
Data tmp = new Data();
tmp.x = d.x ;
return tmp;
}
}* 참조형 반환타입 / 기본형 매개변수
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
//매개변수는 기본현, 반환타입(return타입) 참조형 시작
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 5;
Data d;
System.out.println("main() a : " + a);
d = change(a);
System.out.println("main() after d.x : " + d.x);
}
static Data change(int a)
{
Data tmp = new Data();
tmp.x = a + 10;
return tmp;
}
//매개변수는 기본현, 반환타입(return타입) 참조형 끝
}** 실습_참조형 매개변수/참조형 반환타입 **
/* 1
문제)Data객체에 y변수 추가하고 main에서 2개 정수를 입력받아 Data 객체 각 변수에 대입하고.
main에서 각 값을 출력한 후 copy 메서드를 통해 값에 2를 곱한 결과를 출력하는 프로그램.
입력예)정수 2개를 입력하세요.>10 20
출력예)main 입력값 d.x = 10, d.y : 20
copy 메서드 d.x = 10, d.y : 20
copy 메서드 tmp.x = 20, tmp.y : 40
main 마지막 d.x = 10, d.y : 20
main 마지막 d2.x = 20, d2.y : 40
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
Data d = new Data();
d.x = scn.nextInt();
d.y = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("main 입력값 d.x = " + d.x + ", d.y : " + d.y);
copy(d);
Data d2 = copy(d);
System.out.println("main 마지막 d.x = " + d.x + ", d.y : " + d.y);
System.out.println("main 마지막 d2.x = " + d2.x + ", d2.y : " + d2.y);
}
static Data copy(Data d) //main d와 d자체는 다른 주소지만, 두개의 d가 바라보는 주소값은 같다.
{
System.out.println("copy 메서드 d.x = " + d.x + ", d.y : " + d.y);
Data tmp = new Data();
tmp.x = d.x * 2;
tmp.y = d.y * 2;
System.out.println("copy 메서드 tmp.x = " + tmp.x + ", tmp.y : " + tmp.y);
return tmp;
}
}* 배열을 이용한 참조형 매개변수
public class MySample {
//배열을 이용한 참조형 매개변수
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = {10, 20};
System.out.println("main() a[0] : " + a[0]);
change(a);
System.out.println("main() a[0] : " + a[0]);
}
static void change(int[] x)
{
x[0] = 2000;
System.out.println("change() x : " + x[0]);
}
}** 실습1115 **
/* 2
문제)위와 동일한 형태로 하되 결과는 다르게 구현
출력예)main 입력값 d.x = 10, d.y : 20
copy 메서드 tmp.x = 10, tmp.y : 20
copy 메서드 tmp.x = 20, tmp.y : 40
main 마지막 d.x = 20, d.y : 40
단, copy메서드의 반환타입(리턴타입) 없음.
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Data
{
int x;
int y;
}
public class MySample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
Data d = new Data();
d.x = scn.nextInt();
d.y = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("main 입력값 d.x = " + d.x + ", d.y : " + d.y);
copy(d);
System.out.println("main 마지막 d.x = " + d.x + ", d.y : " + d.y);
}
static void copy(Data tmp)
{
System.out.println("copy 메서드 tmp.x =" + tmp.x + ", tmp.y : " + tmp.y);
tmp.x = tmp.x * 2;
tmp.y = tmp.y * 2;
System.out.println("copy 메서드 tmp.x =" + tmp.x + ", tmp.y : " + tmp.y);
}
}** 실습1115 **
/* 3
문제)배열에 {3, 2, 1, 6, 5, 4}를 초기값으로 선언후에 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램.
단, 각 메서드는 배열출력은 printArr, 배열의 모든 합은 sumArr,
배열 정렬은 sortArr로 선언하여 구현함.
sumArr 메서드만 리턴타입이 존재함.
출력예)[3,2,1,6,5,4]
[1,2,3,4,5,6]
sum = 21
*/
//배열은 시작주소와 길이를 같이 가지고 다닌다.
import java.util.Scanner;
//class Data
//{
// int x;
// int y;
//}
public class MySample1115{
/* 3
문제)배열에 {3, 2, 1, 6, 5, 4}를 초기값으로 선언후에 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램.
단, 각 메서드는 배열출력은 printArr, 배열의 모든 합은 sumArr,
배열 정렬은 sortArr로 선언하여 구현함.
sumArr 메서드만 리턴타입이 존재함.
출력예)[3,2,1,6,5,4]
[1,2,3,4,5,6]
sum = 21
*/
//배열은 시작주소와 길이를 같이 가지고 다닌다.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[] {3, 2, 1, 6, 5, 4}; //int[] arr = {3, 2, 1, 6, 5, 4}; 이렇게해도된다.
printArr(arr);
sortArr(arr);
printArr(arr);
System.out.println("sum = " + sumArr(arr));
}
static void sortArr(int[] x) //클래스 메서드 | int[] x -> 배열로 받겠다는 의미
{
int i, j, tmp;
for(i = 0 ; i < x.length - 1 ; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1 ; j < x.length ; j++)
{
if(x[i] > x[j])
{
tmp = x[i];
x[i] = x[j];
x[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
static void printArr(int[] arr)
{
int i;
System.out.print("[");
for(i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
// //쉼표를 먼저 찍을 경우
// if(i != 0 && i != arr.length)
// System.out.print(", ");
System.out.printf("%d", arr[i]);
if(i != arr.length -1)
System.out.print(", ");
}
System.out.print("] \n");
}
static int sumArr(int[]a)
{
int sum = 0, i;
for(i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++)
{
sum += a[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
** 실습1115_2 **
//객체지향프로그램 - 참조형 매개변수
/* 4
문제)두 정수를 Add클래스 a, b변수에 입력받은 후 더하기, 뺴기, 곱하기, 나누기 메서드를 이용하여
결과를 모두 main에서 출력하는 프로그램.(결과는 c변수 사용)
단, 더하기 add, 빼기 sub, 곱하기 mul, 나누기 div 로 정의하며,
참조형 매개변수를 활용한 메서드 구현, 전부 반환타입이 없음.
입력예)두 정수를 입력하세요.>5 3
출력예)더하기 : 8
뺴기 : 2
곱하기 : 15
나누기 : 1
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Add
{
int a;
int b;
int c;
}
public class MySample1115_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//객체지향프로그램 - 참조형 매개변수
/* 4
문제)두 정수를 Add클래스 a, b변수에 입력받은 후 더하기, 뺴기, 곱하기, 나누기 메서드를 이용하여
결과를 모두 main에서 출력하는 프로그램.(결과는 c변수 사용)
단, 더하기 add, 빼기 sub, 곱하기 mul, 나누기 div 로 정의하며,
참조형 매개변수를 활용한 메서드 구현, 전부 반환타입이 없음.
입력예)두 정수를 입력하세요.>5 3
출력예)더하기 : 8
뺴기 : 2
곱하기 : 15
나누기 : 1
*/
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 정수를 입력하세요.>");
Add ad = new Add(); //Add 클래스의 인스턴스 객체 생성
ad.a = scn.nextInt();
ad.b = scn.nextInt();
add(ad);
System.out.println("더하기 : " + ad.c);
sub(ad);
System.out.println("빼기 : " + ad.c);
mul(ad);
System.out.println("곱하기 : " + ad.c);
div(ad);
System.out.println("나누기 : " + ad.c);
}
static void add(Add a){
a.c = a.a + a.b;
}
static void sub(Add ad){
if (ad.a > ad.b)
ad.c = ad.a - ad.b;
else
ad.c = ad.b - ad.a;
}
static void mul(Add ad){
ad.c = ad.a * ad.b;
}
static void div(Add ad){
ad.c = ad.a / ad.b;
}
}** 실습1115_2 **
//참조형 매개변수를 이용한 메서드를 Add 클래스에 구현한 경우
//참조형 매개변수를 이용한 메서드를 Add 클래스에 구현한 경우
class Add{
int a;
int b;
int c;
static void add(Add a){
a.c = a.a + a.b;
}
static void sub(Add ad){
if (ad.a > ad.b)
ad.c = ad.a - ad.b;
else
ad.c = ad.b - ad.a;
}
static void mul(Add ad){
ad.c = ad.a * ad.b;
}
void div(Add ad){ //인스턴스 메소드
ad.c = ad.a / ad.b;
}
}
//참조형 매개변수를 이용한 메서드를 Add 클래스에 구현한 경우
public class MySample1115_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 정수를 입력하세요.>");
Add ad = new Add(); //Add 클래스의 인스턴스 객체 생성
ad.a = scn.nextInt();
ad.b = scn.nextInt();
Add.add(ad);
System.out.println("더하기 : " + ad.c);
Add.sub(ad);
System.out.println("빼기 : " + ad.c);
Add.mul(ad);
System.out.println("곱하기 : " + ad.c);
ad.div(ad);
System.out.println("나누기 : " + ad.c);
}
}
** 메서드 오버로딩 (overloading) **
한 클래스 내에 같은 이름의 메서드를 여러개 정의
메서드 이름이 같아야 함
매개변수의 개수 또는 타입이 다르게 구현
반환 타입은 오버로딩을 구현하는데 아무런 영향을 주지 못함
예 : System.out.println 메서드
매개변수로 지정하는 값의 타팁에 따라 호출되는 println메서드가 다름
void println()
** 실습1115_3 **
public class MySample1115_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 오버로딩
MySample1115_3 m = new MySample1115_3();
System.out.println("sum()메서드 매개변수 2개 : " + m.sum(5, 8));
System.out.println("sum()메서드 매개변수 3개 : " + m.sum(1, 2, 3));
m.sum(2);
}
int sum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
void sum(int a) {
System.out.println("sum()메서드 1개 a : " + a);
}
int sum(int a, int b, int c){
return a + b + c;
}
}** 실습1115_4 **
// 메소드 오버로딩
class MyMath{
int a;
int b;
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
int add() {
return a + b;
}
int subtract() {
return a - b;
}
int multiply() {
return a * b;
}
int divide() {
return a / b;
}
}
public class MySample1115_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 오버로딩
MyMath m = new MyMath();
m.a = 200;
m.b = 100;
System.out.println(m.add(200, 100));
System.out.println(m.subtract(200, 100));
System.out.println(m.multiply(200, 100));
System.out.println(m.divide(200, 100));
System.out.println(m.add());
System.out.println(m.subtract());
System.out.println(m.multiply());
System.out.println(m.divide());
}
}** 실습1115_5 **
//메서드 오버로딩
/*
출력예)Java
a : 100
a : 89 b : 99
double a : 99.12
total rest 결과 : 198.24 (바로 위 99.12 * 2 한 값)
단, 인스턴스변수 없음
*/
class OverLoad1{
int a, b;
void test() {
System.out.println("Java");
}
void test(int a) {
System.out.println("a : " + a);
}
void test(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("a : " + a + " b : " + b);
}
double test(double a) {
System.out.println("double a : " + a);
return a * 2;
}
}
public class MySample1115_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 오버로딩
/*
출력예)Java
a : 100
a : 89 b : 99
double a : 99.12
total rest 결과 : 198.24 (바로 위 99.12 * 2 한 값)
단, 인스턴스변수 없음
*/
OverLoad1 o = new OverLoad1();
double t;
o.test();
o.test(100);
o.test(89, 90);
t = o.test(99.12); // t = 의 뜻은 o.test(99.12)에 리턴이있다는 의미.
System.out.println("total rest 결과 : " + t);
}
}
| 11/17 수업 (15회차) _ 상속 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
|---|---|
| 11/16 수업 (14회차) _ 메소드 오버로딩 / 생성자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| 11/14 수업 (12일차) (1) | 2023.11.14 |
| 11/13 수업 (11일차) (2) | 2023.11.13 |
| 11/10 수업 (10일차) (0) | 2023.11.10 |
** 실습 1113 **
class Card
{
String kind; //인스턴스 변수
int number;
static int width = 100; //클래스변수 -> 객체생성안해도 된다. Card. 으로 호출함
static int height = 250; //클래스변수
}
public class MySample1114 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//클래스
System.out.println("Card.width = " + Card.width); //문법이 맞게 호출함
System.out.println("Card.height = " + Card.height);
Card c1 = new Card(); //ㅇ
c1.kind = "Heart";
c1.number = 7;
Card c2 = new Card();
c2.kind = "Spade";
c2.number = 4;
System.out.println("c1은 " + c1.kind + ", " + c1.number + "이며, 크기는 (" + c1.width + ", " + c1.height + ")");
System.out.println("c2은 " + c2.kind + ", " + c2.number + "이며, 크기는 (" + c2.width + ", " + c2.height + ")");
c1.number = 12;
c2.number = 8;
c1.width = 50;
c2.width = 80;
System.out.println("변경 후============================");
System.out.println("c1은 " + c1.kind + ", " + c1.number + "이며, 크기는 (" + c1.width + ", " + c1.height + ")");
System.out.println("c2은 " + c2.kind + ", " + c2.number + "이며, 크기는 (" + c2.width + ", " + c2.height + ")");
}
}** 실습 1114_2 **
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math2
{
//인스턴스 메서드
int add(int a, int b)
{
System.out.println("add메서드 시작 : a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
a = a + 10;
b = b + 10;
int result = a + b;
System.out.println("add메서드 끝 : a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
return result;
}
}
public class MySample1114_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
//계산기 클래스
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
int a = scn.nextInt();
int b = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("main 메서드 호출 전 : a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
Math2 m = new Math2();
int c = m.add(a, b);
System.out.println("main 메서드 호출 후 : a = " + a + ",b = " + b + ", c = " + c);
}
}** 실습 1114_2 **
/* 1
문제)두 정수를 입력받아 더하기, 빼기, 곱하기, 나누기 연산결과 출력.
입력예)두 정수를 입력하세요.>5 3
출력예)add(a, b) = 8
subtract(a, b) = 2
multiply(a, b) = 15
divide(a, b) = 1.66666666666667(소수점은 실수로 표련 - double)
단, 클래스는 Math3로 한다.
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math3
{
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int subtract(int a, int b)
{
//항상 큰수에서 작은수를 뺄수있게 처리
if(a > b)
return a - b;
else //return을 하려면 모든경우가 들어가야한다 -> esle 안쓰면 오류난다.
return b - a;
}
int multiply(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
double divide(int a, int b)
{
return (double)a / b;
}
}
public class MySample1114_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 정수를 입력하세요.>");
int a = scn.nextInt();
int b = scn.nextInt();
Math3 m3 = new Math3();
int i = m3.add(a, b);
int j = m3.subtract(a, b);
int k = m3.multiply(a, b);
double l = m3.divide(a, b);
System.out.println("add(a, b) = " + i);
System.out.println("subtract(a, b) = " + j);
System.out.println("multiply(a, b) = " + k);
System.out.println("divide(a, b) = " + l);
//변수 선언 안하고 바로 프린트
System.out.println("add(a, b) = " + m3.add(a, b));
System.out.println("subtract(a, b) = " + m3.subtract(a, b));
System.out.println("multiply(a, b) = " + m3.multiply(a, b));
System.out.println("divide(a, b) = " + m3.divide(a, b));
}
}** 실습 1114_2 **
//위 문제를 인스턴스변수를 이용하여 더하기, 빼기, 곱하기, 나누기 연산결과 출력.
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math3
{
int a, b;
int add()
{
return a + b;
}
int subtract()
{
//항상 큰수에서 작은수를 뺄수있게 처리
if(a > b)
return a - b;
else //return을 하려면 모든경우가 들어가야한다 -> esle 안쓰면 오류난다.
return b - a;
}
int multiply()
{
return a * b;
}
double divide()
{
return (double)a / b;
}
}
public class MySample1114_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
Math3 m3 = new Math3();
System.out.print("두 정수를 입력하세요.>");
int a = scn.nextInt();
int b = scn.nextInt();
m3.a = a;
m3.b = b;
// int a = scn.nextInt(); / m3.a = a; 합쳐서 사용
m3.a = scn.nextInt();
m3.b = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("add(a, b) = " + m3.add());
System.out.println("subtract(a, b) = " + m3.subtract());
System.out.println("multiply(a, b) = " + m3.multiply());
System.out.println("divide(a, b) = " + m3.divide());
}
}** 실습 1114_2 **
//위와 동일한 결과로 클래스 변수를 이용한 계산기
//Math3 클래스에대한 객체인스턴스 m1, m2에 대해서 정의한 후
//m1과 m2에서 각각 같은 변수를 공유한다는 의미로 출력
//클래스 변수병은 기존 소스를 수정하여 a, b 그대로 사용
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math3
{
static int a, b;
int add()
{
return a + b;
}
int subtract()
{
//항상 큰수에서 작은수를 뺄수있게 처리
if(a > b)
return a - b;
else //return을 하려면 모든경우가 들어가야한다 -> esle 안쓰면 오류난다.
return b - a;
}
int multiply()
{
return a * b;
}
double divide()
{
return (double)a / b;
}
}
public class MySample1114_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 정수를 입력하세요.>");
Math3.a = scn.nextInt();
Math3.b = scn.nextInt();
Math3 m1 = new Math3();
Math3 m2 = new Math3();
System.out.println("add(a, b) = " + m1.add());
System.out.println("subtract(a, b) = " + m1.subtract());
System.out.println("multiply(a, b) = " + m1.multiply());
System.out.println("divide(a, b) = " + m1.divide());
System.out.println("add(a, b) = " + m2.add());
System.out.println("subtract(a, b) = " + m2.subtract());
System.out.println("multiply(a, b) = " + m2.multiply());
System.out.println("divide(a, b) = " + m2.divide());
}
}
** 스택 & 큐 **
* 스택
데이터를 일시적으로 저장하기위해 사용하는 자료구조로, 데이터이 입력과 출력순서는 후입선루 (LIFO.Last In First Out)
가장 나중에 넣은 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내는 구조.
** 실습 1114_3 **
public class MySample1114_3 {
static void firstMethod()
{
System.out.println("firstMethod() start..."); //2
secondMathod();
System.out.println("firstMethod() end..."); //7
}
static void secondMathod()
{
System.out.println("secondMethod() start..."); //3
thiredMathod();
System.out.println("secondMethod() end..."); //6
}
static void thiredMathod()
{
System.out.println("thiredMathod start..."); //4
System.out.println("thiredMathod end..."); //5
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메서드 호출 순서 - 스택
System.out.println("main start..."); //1
firstMethod();
System.out.println("main end..."); //8
}
}** 실습1114_3 **
/* 1
문제)정수 2개를 입력받아 메서드 호출전과 후에 대한 결과를 출력하는 프로그램 작성
입력예)정수 2개를 입력하세요.>5 10
출력예)호출 전 a : 5, b : 10 (main메서드에서 출력)
add 메서드 a : 10, b : 20 (add메서드에서 출력)
결과 : 30 (main메서드에서 출력)
호출 후 a : 5, b : 10 (main메서드에서 출력)
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math4
{
int add(int a, int b)
{
a = a * 2;
b = b * 2;
int result = a + b;
System.out.println("add 메서드 a : " + a + ", b : " + b);
return result;
}
}
public class MySample1114_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
int a = scn.nextInt();
int b = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("호출 전 a : " + a + ", b : " + b);
Math4 x = new Math4();
// x.add(a, b);
System.out.println("결과 : " + x.add(a, b));
System.out.println("호출 후 a : " + a + ", b : " + b);
}
}//위와 동일한 결과로 지역변수가 아닌 인스턴스 변수로 이용시.
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math4
{
//인스턴스 변수 적용시
int a, b;
int add(int a, int b)
{
a = a * 2;
b = b * 2;
int result = a + b;
System.out.println("add 메서드 a : " + a + ", b : " + b);
return result;
}
}
public class MySample1114_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
//위와 동일한 결과로 지역변수가 아닌 인스턴스 변수로 이용시.
Math4 m = new Math4(); //인스턴스 변수쓰려고 객체생성
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
m.a = scn.nextInt();
m.b = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("호출 전 a : " +m. a + ", b : " + m.b);
System.out.println("결과 : " + m.add(m.a, m.b));
System.out.println("호출 후 a : " + m.a + ", b : " + m.b);
}
}//위와 동일할 결과로 지역변수나 인스턴스 변수가 아닌 클래스변수로 이용시.
import java.util.Scanner;
class Math4
{
//클래스 변수만 이용하여 출력.
static int a, b;
int add()
{
a = a * 2;
b = b * 2;
int result = a + b;
System.out.println("add 메서드 a : " + a + ", b : " + b);
return result;
}
}
public class MySample1114_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 2개를 입력하세요.>");
Math4.a = scn.nextInt();
Math4.b = scn.nextInt();
Math4 m = new Math4();
System.out.println("호출 전 a : " + Math4. a + ", b : " + Math4.b);
System.out.println("결과 : " + m.add(Math4.a, Math4.b));
//m.add(m.a, m.b) 하면 버그남(m에 노란줄 뜬다.)
//m.add(Math4.a, Math4.b)에는 (Math4.a, Math4.b)가 아닌 값만 전달된다.
System.out.println("호출 후 a : " + Math4.a + ", b : " + Math4.b);
}
}
| 11/16 수업 (14회차) _ 메소드 오버로딩 / 생성자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
|---|---|
| 11/15 수업(13회차) _ 매개 변수 예제/ 반환 타입 예제 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
| 11/13 수업 (11일차) (2) | 2023.11.13 |
| 11/10 수업 (10일차) (0) | 2023.11.10 |
| 11/09 수업 (9일차) (2) | 2023.11.09 |